Entheogens are psychoactive substances, including psychedelic drugs used throughout history in sacred contexts.

Cercis canadensis, the eastern redbud, is a large deciduous shrub or small tree, native to eastern North America from southern Michigan south to central Mexico, west to New Mexico. Species thrive as far west as California and as far north as southern Ontario. It is the state tree of Oklahoma. The prevalence of the so-called "Columbus strain" has seen the residents of Columbus, Wisconsin, embrace the plant in their city's identity. Known as the "Redbud City," the town hosts "Redbud Day" annually the Saturday before Mother's Day, organizing a variety of themed events to recognize the tree.

Erythrina herbacea, commonly known as the coral bean, Cherokee bean, Mamou plant in South Louisiana, red cardinal or cardinal spear, is a flowering shrub or small tree found throughout the southeastern United States and northeastern Mexico; it has also been reported from parts of Central America and, as an introduced species, from Pakistan. Various other systematic names have been used for this plant in the past, including Erythrina arborea, Erythrina hederifolia, Erythrina humilis, Erythrina rubicunda, Corallodendron herbaceum and Xyphanthus hederifolius.

Styphnolobium is a genus of flowering plants in the pea family, Fabaceae. It includes nine species of small trees and shrubs native to China and to the Americas, from the southern United States to Colombia. It belongs to subfamily Faboideae, and was formerly included within a broader interpretation of the genus Sophora. It was recently assigned to the unranked, monophyletic Cladrastis clade. They differ from the genus Calia (mescalbeans) in having deciduous leaves and flowers in axillary, not terminal, racemes. The leaves are pinnate, with 9–21 leaflets, and the flowers in pendulous racemes similar to those of the black locust. Necklacepod is a common name for plants in this genus.

Sophora is a genus of about 45 species of small trees and shrubs in the pea family Fabaceae. The species have a pantropical distribution. The generic name is derived from sophera, an Arabic name for a pea-flowered tree.

Parkinsonia aculeata is a species of perennial flowering tree in the pea family, Fabaceae. Common names include palo verde, Mexican palo verde, Parkinsonia, Jerusalem thorn, jelly bean tree, palo de rayo, and retama.

Mimosa tenuiflora, syn. Mimosa hostilis, also known as jurema preta, calumbi (Brazil), tepezcohuite (México), carbonal, cabrera, jurema, black jurema, and binho de jurema, is a perennial tree or shrub native to the northeastern region of Brazil and found as far north as southern Mexico, and the following countries: El Salvador, Honduras, Panama, Colombia and Venezuela. It is most often found in lower altitudes, but it can be found as high as 1,000 m (3,300 ft).

Robinia neomexicana, the New Mexican, New Mexico, Southwest, desert, pink, or rose locust, is a shrub or small tree in the subfamily Faboideae of the family Fabaceae.

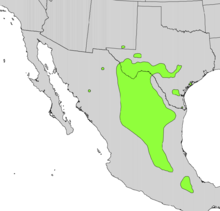
Dermatophyllum/Sophora secundiflora is a genus of three or four species of shrubs and small trees in the family Fabaceae. The genus is native to southwestern North America from western Texas to New Mexico and Arizona in the United States, and south through Chihuahua, Coahuila, and Nuevo León in northern Mexico. Members of the genus are commonly known as mescalbean, mescal bean, or frijolito. One of the common names of Dermatophyllum secundiflorum is Texas mountain laurel, although the name mountain laurel also refers to the very dissimilar and unrelated genus Kalmia and the name laurel refers generally to plants in the unrelated order Laurales. Dermatophyllum secundiflorum is one of the most abundant woody species in the Texas Hill Country or Edwards Plateau.

Castanospermum is a monotypic genus in the legume family Fabaceae. The sole species is Castanospermum australe, commonly known as Moreton Bay chestnut or black bean, which is native to rainforested areas on the east coast of Queensland and northeastern New South Wales, and to the southwest Pacific islands of Vanuatu and New Caledonia

Albizia julibrissin, the Persian silk tree, pink silk tree, or mimosa tree, is a species of tree in the Fabaceae family, native to southwestern and eastern Asia.
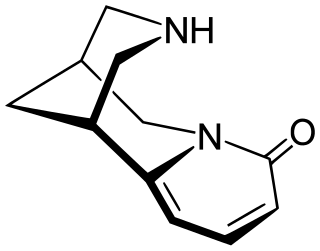
Cytisine, also known as baptitoxine, cytisinicline, or sophorine, is an alkaloid that occurs naturally in several plant genera, such as Laburnum and Cytisus of the family Fabaceae. It has been used medically to help with smoking cessation. It has been found effective in several randomized clinical trials, including in the United States and New Zealand, and is being investigated in additional trials in the United States and a non-inferiority trial in Australia in which it is being compared head-to-head with the smoking cessation aid varenicline. It has also been used entheogenically via mescalbeans by some Native American groups, historically in the Rio Grande Valley predating even peyote.

Sophora chrysophylla, known as māmane in Hawaiian, is a species of flowering plant in the pea and bean family, Fabaceae, that is endemic to Hawaii. It is highly polymorphic, growing as a shrub or tree, and able to reach a height of 15 m (49 ft) in tree form. Yellow flowers are produced in winter and spring.

Styphnolobium japonicum, the Japanese pagoda tree is a species of deciduous tree in the subfamily Faboideae of the pea family Fabaceae.

The peyote is a small, spineless cactus which contains psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. Peyote is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl peyōtl, meaning "caterpillar cocoon", from a root peyōni, "to glisten". Peyote is native to Mexico and southwestern Texas. It is found primarily in the Sierra Madre Occidental, the Chihuahuan Desert and in the states of Nayarit, Coahuila, Nuevo León, Tamaulipas, and San Luis Potosí among scrub. It flowers from March to May, and sometimes as late as September. The flowers are pink, with thigmotactic anthers.

Canavalia rosea is a species of flowering plant of the genus Canavalia in the pea family of Fabaceae, it has a pantropical and subtropical distribution in upper beaches, cliffs, and dunes. Common names include beach bean, bay bean, sea bean, greater sea bean, seaside jack-bean, coastal jack-bean, and MacKenzie bean.

Erythrostemon mexicanus, formerly Caesalpinia mexicana, is a species of plant in the genus Erythrostemon, within the pea family, Fabaceae. Common names include Mexican holdback, Mexican caesalpinia, and tabachín del monte. It is native to the extreme lower Rio Grande Valley of Texas and to parts of Mexico: in the northeast and further south along the Gulf coast as well as the Pacific coast in Nayarit, Jalisco, Colima, and a small portion of Sinaloa.

Ebenopsis ebano is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, that is native to the coastal plain of southern Texas in the United States and eastern Mexico. It is commonly known as Texas ebony or ebano.

Sophora tomentosa, also known as necklacepod, yellow necklacepod, and occasionally as silver bush, is a pantropical shrub or small tree in the family Fabaceae. It commonly ranges in height from 4 to 10 feet and often occurs in coastal conditions and near wetlands. The common name Necklacepod is derived from the characteristic string of seed pods that develop after its yellow flowers germinate into seeds.

Dermatophyllum gypsophilum is a rare species of flowering plant in the legume family known by the common names Guadalupe Mountain necklacepod, Guadalupe mescalbean, and gypsum necklace. It is native to New Mexico and Texas in the United States, and it is known from one location in Chihuahua in Mexico.