
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix. Gaps are inserted between the residues so that identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. Sequence alignments are also used for non-biological sequences such as calculating the distance cost between strings in a natural language, or to display financial data.
The Protein Information Resource (PIR), located at Georgetown University Medical Center, is an integrated public bioinformatics resource to support genomic and proteomic research, and scientific studies. It contains protein sequences databases
Clustal is a computer program used for multiple sequence alignment in bioinformatics. The software and its algorithms have gone through several iterations, with ClustalΩ (Omega) being the latest version as of 2011. It is available as standalone software, via a web interface, and through a server hosted by the European Bioinformatics Institute.
The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) is an intergovernmental organization (IGO) which, as part of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) family, focuses on research and services in bioinformatics. It is located on the Wellcome Genome Campus in Hinxton near Cambridge, and employs over 600 full-time equivalent (FTE) staff.
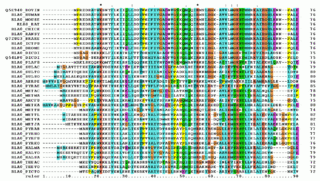
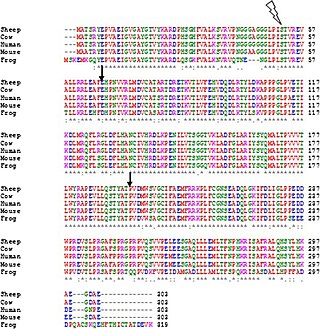
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) is the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. These alignments are used to infer evolutionary relationships via phylogenetic analysis and can highlight homologous features between sequences. Alignments highlight mutation events such as point mutations, insertion mutations and deletion mutations, and alignments are used to assess sequence conservation and infer the presence and activity of protein domains, tertiary structures, secondary structures, and individual amino acids or nucleotides.

John Frederick William Birney is joint director of EMBL's European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI), in Hinxton, Cambridgeshire and deputy director general of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL). He also serves as non-executive director of Genomics England, chair of the Global Alliance for Genomics and Health (GA4GH) and honorary professor of bioinformatics at the University of Cambridge. Birney has made significant contributions to genomics, through his development of innovative bioinformatics and computational biology tools. He previously served as an associate faculty member at the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute.
T-Coffee is a multiple sequence alignment software using a progressive approach. It generates a library of pairwise alignments to guide the multiple sequence alignment. It can also combine multiple sequences alignments obtained previously and in the latest versions can use structural information from Protein Data Bank (PDB) files (3D-Coffee). It has advanced features to evaluate the quality of the alignments and some capacity for identifying occurrence of motifs (Mocca). It produces alignment in the aln format (Clustal) by default, but can also produce PIR, MSF, and FASTA format. The most common input formats are supported.

David J. Lipman is an American biologist who from 1989 to 2017 was the director of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) at the National Institutes of Health. NCBI is the home of GenBank, the U.S. node of the International Sequence Database Consortium, and PubMed, one of the most heavily used sites in the world for the search and retrieval of biomedical information. Lipman is one of the original authors of the BLAST sequence alignment program, and a respected figure in bioinformatics. In 2017, he left NCBI and became Chief Science Officer at Impossible Foods.
MUltiple Sequence Comparison by Log-Expectation (MUSCLE) is a computer software for multiple sequence alignment of protein and nucleotide sequences. It is licensed as public domain. The method was published by Robert C. Edgar in two papers in 2004. The first paper, published in Nucleic Acids Research, introduced the sequence alignment algorithm. The second paper, published in BMC Bioinformatics, presented more technical details.

Webb Colby Miller is an American bioinformatician who is professor in the Department of Biology and the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at The Pennsylvania State University.
Anders Krogh is a bioinformatician at the University of Copenhagen, where he leads the university's bioinformatics center. He is known for his pioneering work on the use of hidden Markov models in bioinformatics, and is co-author of a widely used textbook in bioinformatics. In addition, he also co-authored one of the early textbooks on neural networks. His current research interests include promoter analysis, non-coding RNA, gene prediction and protein structure prediction.

Sean Roberts Eddy is Professor of Molecular & Cellular Biology and of Applied Mathematics at Harvard University. Previously he was based at the Janelia Research Campus from 2006 to 2015 in Virginia. His research interests are in bioinformatics, computational biology and biological sequence analysis. As of 2016 projects include the use of Hidden Markov models in HMMER, Infernal Pfam and Rfam.

Burkhard Rost is a scientist leading the Department for Computational Biology & Bioinformatics at the Faculty of Informatics of the Technical University of Munich (TUM). Rost chairs the Study Section Bioinformatics Munich involving the TUM and the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU) in Munich. From 2007-2014 Rost was President of the International Society for Computational Biology (ISCB).

Gary Stormo is an American geneticist and currently Joseph Erlanger Professor in the Department of Genetics and the Center for Genome Sciences and Systems Biology at Washington University School of Medicine in St Louis. He is considered one of the pioneers of bioinformatics and genomics. His research combines experimental and computational approaches in order to identify and predict regulatory sequences in DNA and RNA, and their contributions to the regulatory networks that control gene expression.
EPD is a biological database and web resource of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoters with experimentally defined transcription start sites. Originally, EPD was a manually curated resource relying on transcript mapping experiments targeted at individual genes and published in academic journals. More recently, automatically generated promoter collections derived from electronically distributed high-throughput data produced with the CAGE or TSS-Seq protocols were added as part of a special subsection named EPDnew. The EPD web server offers additional services, including an entry viewer which enables users to explore the genomic context of a promoter in a UCSC Genome Browser window, and direct links for uploading EPD-derived promoter subsets to associated web-based promoter analysis tools of the Signal Search Analysis (SSA) and ChIP-Seq servers. EPD also features a collection of position weight matrices (PWMs) for common promoter sequence motifs.

Alexander George Bateman is a computational biologist and Head of Protein Sequence Resources at the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI), part of the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Cambridge, UK. He has led the development of the Pfam biological database and introduced the Rfam database of RNA families. He has also been involved in the use of Wikipedia for community-based annotation of biological databases.
Paul Martin Sharp is a British bioinformatician who is a professor of genetics at the University of Edinburgh, where he holds the Alan Robertson chair of genetics in the Institute of Evolutionary Biology.
Peter D. Karp is director of the Bioinformatics Research Group at SRI International in Menlo Park, California. Karp leads the development of the BioCyc database collection. BioCyc databases combine genome, metabolic pathway, and regulatory information for thousands of organisms.
Toby James Gibson is a group leader and biochemist at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Heidelberg known for his work on Clustal. According to Nature, Gibson's co-authored papers describing Clustal are among the top ten most highly cited scientific papers of all time.










