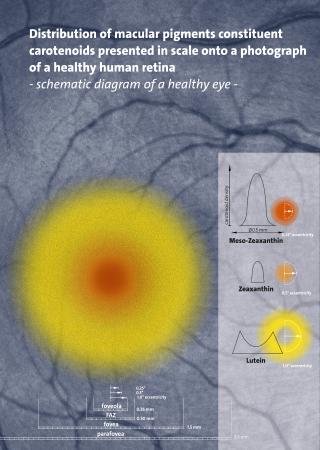
Carotenoids are yellow, orange, and red organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, corn, tomatoes, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Over 1,100 identified carotenoids can be further categorized into two classes – xanthophylls and carotenes.

Teicoplanin is an antibiotic used in the prophylaxis and treatment of serious infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. It is a semisynthetic glycopeptide antibiotic with a spectrum of activity similar to vancomycin. Its mechanism of action is to inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis.
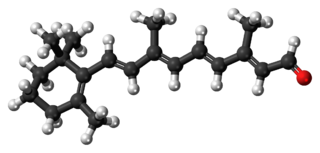
Retinal is a polyene chromophore. Retinal, bound to proteins called opsins, is the chemical basis of visual phototransduction, the light-detection stage of visual perception (vision).

Novobiocin, also known as albamycin or cathomycin, is an aminocoumarin antibiotic that is produced by the actinomycete Streptomyces niveus, which has recently been identified as a subjective synonym for S. spheroides a member of the class Actinomycetia. Other aminocoumarin antibiotics include clorobiocin and coumermycin A1. Novobiocin was first reported in the mid-1950s.

Carotenoid oxygenases are a family of enzymes involved in the cleavage of carotenoids to produce, for example, retinol, commonly known as vitamin A. This family includes an enzyme known as RPE65 which is abundantly expressed in the retinal pigment epithelium where it catalyzed the formation of 11-cis-retinol from all-trans-retinyl esters.
CRT is the gene cluster responsible for the biosynthesis of carotenoids. Those genes are found in eubacteria, in algae and are cryptic in Streptomyces griseus.

In enzymology, beta-carotene 15,15'-dioxygenase, (EC 1.13.11.63) is an enzyme with systematic name beta-carotene:oxygen 15,15'-dioxygenase (bond-cleaving). In human it is encoded by the BCDO2 gene. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
In enzymology, a carotene 7,8-desaturase (EC 1.14.99.30) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-methylcoclaurine 3'-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.13.71) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Beta-apo-4'-carotenal oxygenase (EC 1.2.1.82, beta-apo-4'-carotenal dehydrogenase, YLO-1, carD (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 4'-apo-beta,psi-carotenal:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:

15-cis-phytoene desaturases, are enzymes involved in the carotenoid biosynthesis in plants and cyanobacteria. Phytoene desaturases are membrane-bound enzymes localized in plastids and introduce two double bonds into their colorless substrate phytoene by dehydrogenation and isomerize two additional double bonds. This reaction starts a biochemical pathway involving three further enzymes called the poly-cis pathway and leads to the red colored lycopene. The homologous phytoene desaturase found in bacteria and fungi (CrtI) converts phytoene directly to lycopene by an all-trans pathway.
9,9'-dicis-zeta-carotene desaturase is an enzyme with systematic name 9,9'-dicis-zeta-corotene:quinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4,4'-Diapophytoene desaturase is an enzyme with systematic name 15-cis-4,4'-diapophytoene:FAD oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Chlorophyllide-a oxygenase (EC 1.14.13.122), chlorophyllide a oxygenase, chlorophyll-b synthase, CAO) is an enzyme with systematic name chlorophyllide-a:oxygen 7-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reactions
All-trans-8'-apo-beta-carotenal 15,15'-oxygenase (EC 1.14.99.41, Diox1, ACO, 8'-apo-beta-carotenal 15,15'-oxygenase) is an enzyme with systematic name all-trans-8'-apo-beta-carotenal:oxygen 15,15'-oxidoreductase (bond-cleaving). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Carotene epsilon-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.99.45, CYP97C1, LUT1) is an enzyme with systematic name alpha-carotene:oxygen oxidoreductase (3-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Demethylspheroidene O-methyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name S-adenosyl-L-methionine:demethylspheroidene O-methyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
4,4'-diapophytoene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name farnesyl-diphosphate:farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Prolycopene isomerase is an enzyme with systematic name 7,9,7',9'-tetracis-lycopene cis-trans-isomerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Lycopene β-cyclase is an enzyme with systematic name carotenoid beta-end group lyase (decyclizing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction








