 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Mucolitico Maggioni |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
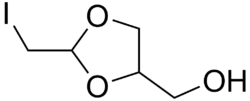
| Formula | C5H9IO3 |
| Molar mass | 244.028 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Domiodol is a mucolytic and expectorant. [1] It has been marketed in Italy by Maggioni under the trade name Mucolitico Maggioni and sold in syrup, sachet, and tablet form, with a dosage of 60mg three to four times daily in adults. Contraindications include severe renal or hepatic insufficiency. [2]