
Pollen is a powdery substance produced by most types of flowers of seed plants for the purpose of sexual reproduction. It consists of pollen grains, which produce male gametes.

Droseraceae is a family of carnivorous flowering plants, also known as the sundew family. It consists of approximately 180 species in three extant genera, the vast majority being in the sundew genus Drosera. The family also contains the well-known Venus flytrap and the more obscure waterwheel plant, both of which are the only living species of their respective genera. Representatives of the Droseraceae are found on all continents except Antarctica.

Palynology is the study of microorganisms and microscopic fragments of mega-organisms that are composed of acid-resistant organic material and occur in sediments, sedimentary rocks, and even some metasedimentary rocks. Palynomorphs are the microscopic, acid-resistant organic remains and debris produced by a wide variety of plants, animals, and Protista that have existed since the late Proterozoic.

Winteraceae is a primitive family of tropical trees and shrubs including 93 species in five genera. It is of particular interest because it is such a primitive angiosperm family, distantly related to Magnoliaceae, though it has a much more southern distribution. Plants in this family grow mostly in the southern hemisphere, and have been found in tropical to temperate climate regions of Malesia, Oceania, eastern Australia, New Zealand, Madagascar and the Neotropics, with most of the genera concentrated in Australasia and Malesia. The five genera, Takhtajania, Tasmannia, Drimys, Pseudowintera, and Zygogynum s.l. all have distinct geographic extant populations. Takhtajania includes a single species, T. perrieri, endemic only to Madagascar, Tasmannia has the largest distribution of genera in Winteraceae with species across the Philippines, Borneo, New Guinea, Eastern Australia, and Tasmannia, Drimys is found in the Neotropical realm, from southern Mexico to the subarctic forests of southern South America, Pseudowintera is found only in New Zealand, and Zygogynum has species in New Guinea and New Caledonia.

Roridula is a genus of evergreen, insect-trapping shrubs, with two species, of about 1⅓–2 m. It is the only genus in the family Roridulaceae. It has thin, woody, shyly branching, upright, initially brown, later grey stems, with lance- to awl-shaped leaves crowded at their tips. The star-symmetrical flowers consist from the outside in of five, green or reddish, free sepals, alternating with five white, pink or purple, free petals. Further to the middle and opposite the sepals are five stamens with the anthers initially kinked down. These suddenly flip up if the nectar-containing swelling at its base is being touched. The center of the flower is occupied by a superior ovary. The leaves and sepals carry many sticky tentacles of different sizes, that trap insects. Roridula does not break down the insect proteins, but bugs of the genus Pameridea prey on the trapped insects. These later deposit their feces on the leaves, which take up nutrients from the droppings. The species can be found in the Western Cape province of South Africa. They are commonly known as dewstick or fly bush in English and vlieëbos or vlieëbossie in Afrikaans.

Coriaria is the sole genus in the family Coriariaceae, which was described by Linnaeus in 1753. It includes 14 species of small trees, shrubs and subshrubs, with a widespread but disjunct distribution across warm temperate regions of the world, occurring as far apart as the Mediterranean region, southern and eastern Asia, New Zealand, the Pacific Ocean islands, and Central and South America.

Drosera regia, commonly known as the king sundew, is a carnivorous plant in the sundew genus Drosera that is endemic to a single valley in South Africa. The genus name Drosera comes from the Greek word droseros, meaning "dew-covered". The specific epithet regia is derived from the Latin for "royal", a reference to the "striking appearance" of the species. Individual leaves can reach 70 cm (28 in) in length. It has many unusual relict characteristics not found in most other Drosera species, including woody rhizomes, operculate pollen, and the lack of circinate vernation in scape growth. All of these factors, combined with molecular data from phylogenetic analysis, contribute to the evidence that D. regia possesses some of the most ancient characteristics within the genus. Some of these are shared with the related Venus flytrap (Dionaea muscipula), which suggests a close evolutionary relationship.

Microcachrys tetragona, known as creeping pine or creeping strawberry pine, is a species of dioecious conifer belonging to the podocarp family (Podocarpaceae). It is the sole species of the genus Microcachrys. The plant is endemic to western Tasmania, where it is a low shrub growing to 1 m tall at high altitudes. Its leaves are scale-like, arranged in opposite decussate pairs, superficially resembling those of the unrelated Diselma archeri (Cupressaceae). It shares the common name Creeping pine with several other plants. Females produce tiny, red, edible berries in summer.

Trochodendron is a genus of flowering plants with one living species, Trochodendron aralioides, and six extinct species known from the fossil record. It was often considered the sole genus in the family Trochodendraceae, though botanists now also include the distinct genus Tetracentron in the family.

Velloziaceae is a family of monocotyledonous flowering plants. The APG II system, of 2003, also recognizes this family, and assigns it to the order Pandanales.

Cymodoceaceae is a family of flowering plants, sometimes known as the "manatee-grass family", which includes only marine species.

Symplocos is a genus of flowering plants in the order Ericales. It contains about 300 species distributed in Asia and the Americas. Many species grow in humid tropical regions. This is sometimes considered to be the only genus in family Symplocaceae. Plants in this family are shrubs and trees with white or yellow flowers. The oldest fossils of the genus date to the lower Eocene of Europe and North America, with the genus being present in Europe as late as the Pliocene. Fossil seeds of †Symplocos granulosa are frequent in sediment rock layers of the Late Oligocene to the Late Miocene of Denmark, Germany, Austria and Poland. The fossil seeds are very similar to the seeds of the extan southern Chinese species Symplocos glandulifera and Symplocos sulcata. Fossil seeds of †Symplocos paucicostata are known from the Middle Pliocene sediment rock layers in Reuver, the Netherlands and from the Late Pliocene sediment rock layers in northern Italy. The fossil seeds are very similar to the seeds of the extant East Asian species Symplocos paniculata
Orbicules are small acellular structures of sporopollenin that might occur on the inner tangential and radial walls of tapetal cells. The ornamentation of the orbicule surface often resembles that of the pollen sexine. Different hypotheses about their function have been proposed, including them just being a by-product of pollen wall sporopollenin synthesis.

Archaeamphora longicervia is a fossil plant species, the only member of the hypothetical genus Archaeamphora. Fossil material assigned to this taxon originates from the Yixian Formation of northeastern China, dated to the Early Cretaceous.
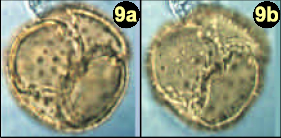
Droseridites is a genus of extinct plants of possible droseracean or nepenthacean affinity. It is a form taxon known only from fossil pollen. Species assigned to this genus originate from numerous regions of the world, including Europe, India, Egypt, the Arabian Peninsula, and the Kerguelen Islands.
Droserapites is a genus of extinct plants of somewhat uncertain droseracean affinity. It is a form taxon known only from fossil pollen.
This article records new taxa of plants that are scheduled to be described during the year 2018, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleobotany that occurred in the year 2018.
This article records new taxa of fossil plants that are scheduled to be described during the year 2020, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleobotany that are scheduled to occur in the year 2020.
This article records new taxa of fossil plants that are scheduled to be described during the year 2021, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleobotany that are scheduled to occur in the year 2021.
This paleobotany list records new fossil plant taxa that were to be described during the year 2023, as well as notes other significant paleobotany discoveries and events which occurred during 2023.













