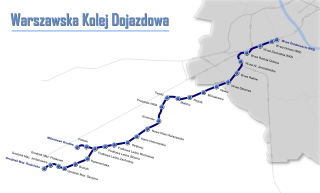
Warsaw Commuter Railway is a light rail commuter line in Poland's capital city of Warsaw. The line, together with its two branches, links Warsaw with the municipalities of Michałowice, Pruszków, Brwinów, Podkowa Leśna, Milanówek and Grodzisk Mazowiecki to the south-west of Warsaw.

ET22 is a Polish six-axle electric freight locomotive built by Pafawag from 1969 to 1989. Factory designation is 201E. With 1183 units, it is one of the most numerous standard gauge electric locomotive built in Europe. Further 23 units were built for Morocco as E-1000 class.

PKP Class Pt47 is a Polish steam locomotive. An improvement of the successful pre-war PKP class Pt31 class, the main difference is the addition of circular tubes in the fire chamber, thereby significantly increased boiler performance. This class also featured a superheater and many have mechanical stokers to feed coal into the firebox. 180 locomotives were built in total between 1948 and 1951. The designation stood for fast passenger (P) 2-8-2 (t) locomotive designed in 1947.

Masovian Railways, in Polish Koleje Mazowieckie, is a regional rail operator in the Masovian Voivodeship of Poland.

Warsaw has seen major infrastructural changes over the past few years amidst increased foreign investment and economic growth. The city has a much improved infrastructure with new roads, flyovers, bridges, etc. Public transport in Warsaw is ubiquitous, serving the city with buses, tramways, urban railway and Metro.

Warszawa Włochy railway station is a railway station in the Włochy district of Warsaw, Poland. It stands on the junction of lines 1 and 3: from here trains can either run on Line 1 towards Łódź or Line 3 towards Poznań. It comprises two platforms connected by an underground pedestrian tunnel and a station building complete with ticket machines and bicycle parking.

Alstom Konstal is a company based in Chorzów, Poland producing rail vehicles, in particular metro cars and trams, as well as components for trains.

The Fablok T3A also known as TKh49 or Ferrum 47 / 724 is a class of Polish steam industrial tank locomotive. It was built by Fablok in 1948-1961 years.

Konstal N was a tram model based on the German Kriegsstraßenbahnwagen concept, manufactured between 1948 and 1956 by the companies Konstal in Chorzów, Gdańsk Shipyard no. 3 and Sanok Railcar Factory "Sanowag". The narrow-gauge version was built from 1950 to 1956. Trailers were marked ND or 2ND. The N was the first tram manufactured in Poland after the Second World War.

Konstal 114Na is an articulated low-floor tram, manufactured in 1997 by Konstal works in Chorzów, in a quantity of 2 units for the Gdańsk Municipal Transport Company. It is the second low-floor tram type produced in Poland after the 112N. A significant part of the solutions was taken from the previously produced single unit of the 112N type.

Pesa Acatus is a standard-gauge electric multiple unit produced in a single copy at the Pesa plant in Bydgoszcz in 2006, specifically for the Marshal's Office of the Łódź Voivodeship. During test runs, it was a four-car unit, and it is nowadays operated in a three-car configuration.

Pafawag 101N was a two-car, low-floor electric multiple unit (EPU) tram produced by Pafawag in Wrocław from 1968 to 1972. A total of 40 101Ns were built for the Warsaw Commuter Railway.

Pesa 401M is a control car used as a trailer for Pesa 214M railbuses of the SA106 series. This wagon was built by Pesa for the Marshal's Office of the Kuyavian–Pomeranian Voivodeship, with a total of 5 units produced.

Newag 19WE is a standard-gauge, four-car electric multiple unit (EMU) produced between 2008 and 2010 at the Newag plant in Nowy Sącz. A total of 4 units were built, which are operated by Szybka Kolej Miejska in Warsaw.

PKP class EW55 were standard-gauge, three-car, high-platform electric multiple units produced between 1958 and 1962 in a quantity of 72 units by the Pafawag factory in Wrocław. Starting in 1959, they were directed to Katowice and Warsaw. In 1964, the vehicles ended service in Upper Silesia, and their operation was finally concluded in 1995.

The Pesa 214M is a family of standard-gauge diesel railcars produced by Pesa Bydgoszcz between 2001 and 2016, intended for regional transport on non-electrified lines. The family includes: 214M (SA106), 214Ma (SA103), and 214Mb (SA135). A total of 56 units were produced, which are operated by Arriva, Koleje Dolnośląskie, Masovian Railways, and Polregio.

Pesa Acatus II is a four-car, partially low-floor, standard-gauge electric multiple unit of Polish production, manufactured by Pesa at the turn of 2010 and 2011. Five units were purchased by the local government of the Lesser Poland Voivodeship. Initially, the vehicles were operated by Przewozy Regionalne, and later by Koleje Małopolskie, which have additionally owned the vehicles since 2018.

Pafawag 3WE and 3WEa are standard gauge three-car high-platform electric multiple units produced by Pafawag in Wrocław between 1974 and 1980, with a total of 28 units built.

Pafawag 6WE and 6WEb are standard-gauge, three-car electric multiple units produced in Poland. They were manufactured in a quantity of 2 units at the Pafawag factory in Wrocław in 1990 for Szybka Kolej Miejska in the Tricity area. Since 2007, these units have been operated by Masovian Railways.

Pesa 620M is a broad-gauge diesel railcar produced since 2004 by Pesa for the Lithuanian Railways and Ukrainian Railways, and since 2011, in cooperation with Belkommunmash, also for the Belarusian Railway. A total of 29 units were produced.




















