Taiping, Tai-p’ing, or Tai Ping most often refers to:

The An Lushan rebellion was a civil war in China that lasted from 755 to 763, at the approximate midpoint of the Tang dynasty (618–907). It began as a commandery rebellion attempting to overthrow and replace the Tang government with the rogue Yan dynasty. The rebels succeeded in capturing the imperial capital Chang'an after the emperor had fled to Sichuan, but eventually succumbed to internal divisions and counterattacks by the Tang and their allies. The rebellion spanned the reigns of three Tang emperors: Xuanzong, Suzong, and Daizong.

Dongting Lake is a large, shallow lake in northeastern Hunan Province, China. It is a flood basin of the Yangtze River, so its volume depends on the season. The provinces of Hubei and Hunan are named after their location relative to the lake: Hubei means "North of the Lake" and Hunan, "South of the Lake".

An Lushan was a Chinese military general and rebel leader during the Tang dynasty and is primarily known for instigating the An Lushan Rebellion which devastated China and killed millions of people.

Huangshan, literally meaning the Yellow Mountain(s), is a mountain range in southern Anhui province in eastern China. It was originally called "Yishan", and it was renamed because of a legend that Emperor Xuanyuan once made alchemy here. Vegetation on the range is thickest below 1,100 meters (3,600 ft), with trees growing up to the treeline at 1,800 meters (5,900 ft).

The Chinese Basketball Association, often abbreviated as the CBA, is the first-tier professional men's basketball league in China.
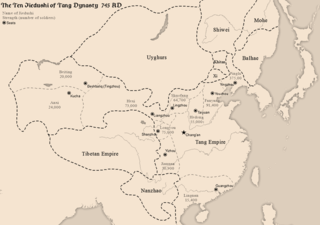
The jiedushi or jiedu, was a regional military governor in China; the title was established in the Tang dynasty and abolished in the Yuan dynasty. The post of jiedushi has been translated as "military commissioner", "legate", or "regional commander". Originally introduced in 711 to counter external threats, the jiedushi were posts authorized with the supervision of a defense command often encompassing several prefectures, the ability to maintain their own armies, collect taxes and promote and appoint subordinates.

Tourism in China is a growing industry that is becoming a significant part of the Chinese economy. The rate of tourism has expanded over the last few decades since the beginning of reform and opening-up. The emergence of a newly rich middle class and an easing of restrictions on movement by the Chinese authorities are both fueling this travel boom. China has become one of world's largest outbound tourist markets. According to Euromonitor International, economic growth and higher incomes in nearby Asian countries will help China to become the world's number one tourist destination by 2030.
Geshu Han, formally Prince Wumin of Xiping (西平武愍王), was a general of Tang China who was of Turgesh extraction. A veteran of many battles, he became a powerful general late in the reign of Emperor Xuanzong of Tang and in 756 became responsible for defending Tong Pass against the rebel forces of An Lushan.

The Eight Views of Xiaoxiang are scenes of the Xiaoxiang region, in what is now modern Hunan Province, China, that were the subject of the poems and depicted in well-known drawings and paintings from the time of the Song Dynasty. The Eight Views of Xiaoxiang can refer either to various sets of paintings which have been done on this theme, the various verse series on the same theme, or to combinations of both. The Xiaoxiang theme is part of a long poetic and artistic legacy.

The Eight Views of Ōmi are traditional scenic views of Ōmi Province which is now Shiga Prefecture in Japan.

The Eight Views of Taiwan have been variously defined throughout Taiwan's history.

Hangzhou–Nanchang high-speed railway or Hangchāng HSR is a dual-track, electrified, high-speed rail line between Hangzhou, Zhejiang, Huangshan, Anhui and Nanchang, Jiangxi. It can be divided into the Hangzhou–Huangshan section and the Huangshan–Nanchang section.

Xiaoxiang, also transliterated XiaoXiang, Hsiao Hsiang, and Chiu Chiang, in some older sources, refers to the "lakes and rivers" region in south-central China south of the middle-reaches of the Yangtze River and corresponding, more or less, with Hunan province. Xiaoxiang is less a precise geographic entity than a concept. Xiaoxiang is used in the genre of Xiaoxiang poetry of Classical Chinese poetry and in literature for symbolic purposes, in part because this was a significant area, which at least through the Song dynastic era China was still considered a wild place full of malaria, barbarians, and wild beasts. Indeed, for much of early Chinese history, this area belonged not to China, but to the independent state of Chu. Beginning at least with Qu Yuan, in the third century BCE, this region came to symbolically represent the unjust exile of a talented minister or government official by an unappreciative king or emperor.
Wang Min is a former politician of the People's Republic of China. He successively served as Communist Party Secretary of Liaoning province, Party Secretary and Governor of Jilin province, and Vice Governor of Jiangsu province. Once considered a promising future leader in the Communist Party, Wang retired from his provincial leadership positions in 2015, before coming under investigation for corruption in 2016. He was sentenced to life in prison upon being convicted on charges of bribery and dereliction of duty.
"Autumn Day in Kui Prefecture" is a poem by 8th-century Chinese poet Du Fu (712–770). The full title of this poem is Autumn Day in Kui Prefecture, A Song Submitted to Supervisor Zheng and Advisor Li, in One Hundred Rhymes. As a poem, "Autumn Day in Kui Prefecture" is an example of Tang poetry, which received considerable attention during the Song dynasty, in Song poetry, and later, even through modern times. During the Song dynasty Du Fu's "Autumn Day in Kui Prefecture" received particular attention, with the poem being subtly alluded to through rhyme-scheme referencing by Su Shi and his circle: in other words, Su Shi and the poets of his circle wrote poems which utilized the same rhyming words from Du Fu's poem, thus subtly referencing the sense and sentiment of Du Fu's line, but without overtly stating what might be censured as inappropriate. This allowed him and others to express opinions about government and society, without suffering the consequences, as Su Shi had previously done, in the Crow Terrace Poetry Trial, when his poetry was used as evidence resulting in his conviction and exile.

Zashiki Hakkei is a series of eight prints from 1766 by the Japanese ukiyo-e artist Suzuki Harunobu. They were the first full-colour nishiki-e prints and are considered representative examples of Harunobu's work. The prints are mitate-e parodies of popular themes of the 11th-century Chinese landscape painting series, Eight Views of Xiaoxiang; Harunobu replaces natural scenery with domestic scenes.

The Mogao Christian painting, also known as Painting of a Christian figure or Fragment of a Christian figure, is a fragmentary silk painting of a haloed man with crosses on his head and chest who has been interpreted as a Christian figure associated with the Church of the East. The painting dates to the end of the 9th century, during the Guiyi rule of Dunhuang under the Zhang family. It was discovered by the Hungarian-born British archaeologist Aurel Stein at the Library Cave of the Mogao Caves in 1908, and is now kept in the British Museum, London.
The Eight Poetic PortrayalsViews of Taiwan’s Famous Landscapes is a unique genre of classical Chinese poetry during the Qing period of Taiwan, primarily associated with the “Eight Landscapes of Taiwan”. Most of these poems are written in the regulated verse, with seven-character eight-line regulated verse being the most common. Also, many authors of these poems did not personally visit the locations described, so these poems are not entirely factual and contain many imaginative elements.













