El Porvenir, New Mexico | |
|---|---|
 NM Highway 65 passing through El Porvenir, New Mexico. Hermit Peak is visible in the distance. | |
| Coordinates: 35°41′48″N105°22′58″W / 35.69667°N 105.38278°W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | New Mexico |
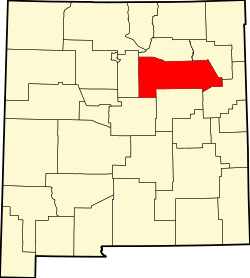
| County | San Miguel |
| Elevation | 7,290 ft (2,220 m) |
| Time zone | UTC-7 (Mountain (MST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-6 (MDT) |
| Area code | 505 |
| GNIS feature ID | 906073 [1] |
El Porvenir is an unincorporated community in San Miguel County, New Mexico, United States. [1] [2]