
Johnson & Johnson (J&J) is an American multinational corporation founded in 1886 that develops medical devices, pharmaceutical, and consumer packaged goods. Its common stock is a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average and the company is ranked No. 37 on the 2018 Fortune 500 list of the largest United States corporations by total revenue. Johnson & Johnson is one of the world's most valuable companies.
Stryker Corporation is an American multinational medical technologies corporation based in Kalamazoo, Michigan. Stryker's products include implants used in joint replacement and trauma surgeries; surgical equipment and surgical navigation systems; endoscopic and communications systems; patient handling and emergency medical equipment; neurosurgical, neurovascular and spinal devices; as well as other medical device products used in a variety of medical specialties.

Boston Scientific Corporation, doing business as Boston Scientific, is a manufacturer of medical devices used in interventional medical specialties, including interventional radiology, interventional cardiology, peripheral interventions, neuromodulation, neurovascular intervention, electrophysiology, cardiac surgery, vascular surgery, endoscopy, oncology, urology and gynecology.
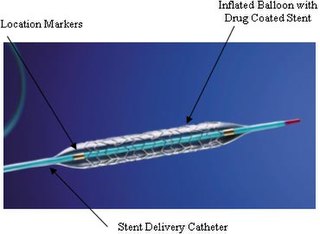
An implant is a medical device manufactured to replace a missing biological structure, support a damaged biological structure, or enhance an existing biological structure. Medical implants are man-made devices, in contrast to a transplant, which is a transplanted biomedical tissue. The surface of implants that contact the body might be made of a biomedical material such as titanium, silicone, or apatite depending on what is the most functional. In some cases implants contain electronics e.g. artificial pacemaker and cochlear implants. Some implants are bioactive, such as subcutaneous drug delivery devices in the form of implantable pills or drug-eluting stents.

A laparoscopic adjustable gastric band, commonly called a lap-band, A band, or LAGB, is an inflatable silicone device placed around the top portion of the stomach to treat obesity, intended to decrease food consumption.
Pelvic organ prolapse (POP) is characterized by descent of pelvic organs from their normal positions. In women, the condition usually occurs when the pelvic floor collapses after gynecological cancer treatment, childbirth or heavy lifting.

An umbilical hernia is a health condition where the abdominal wall behind the navel is damaged. It may cause the navel to bulge outwards—the bulge consisting of abdominal fat from the greater omentum or occasionally parts of the small intestine. The bulge can often be pressed back through the hole in the abdominal wall, and may "pop out" when coughing or otherwise acting to increase intra-abdominal pressure. Treatment is surgical, and surgery may be performed for cosmetic as well as health-related reasons.

Prolene is a synthetic, monofilament, nonabsorbable polypropylene suture. It is indicated for skin closure and general soft tissue approximation and ligation. Its advantages include minimal tissue reactivity and durability. Disadvantages include fragility, high plasticity, high expense, and difficulty of use compared to standard nylon sutures.
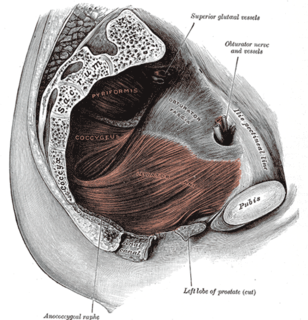
Stress incontinence, also known as stress urinary incontinence (SUI) or effort incontinence is a form of urinary incontinence. It is due to inadequate closure of the bladder outlet by the urethral sphincter.

A breast implant is a prosthesis used to change the size, shape, and contour of a person's breast. In reconstructive plastic surgery, breast implants can be placed to restore a natural looking breast following a mastectomy, to correct congenital defects and deformities of the chest wall or, cosmetically, to enlarge the appearance of the breast through breast augmentation surgery.

Uterine prolapse is when the uterus descends towards or through the opening of the vagina. Symptoms may include vaginal fullness, pain with sex, trouble urinating, urinary incontinence, and constipation. Often it gets worse over time. Low back pain and vaginal bleeding may also occur.
Surgical staples are specialized staples used in surgery in place of sutures to close skin wounds, connect or remove parts of the bowels or lungs. The use of staples over sutures reduces the local inflammatory response, width of the wound, and the time it takes to close.

Surgical suture is a medical device used to hold body tissues together after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. A number of different shapes, sizes, and thread materials have been developed over its millennia of history. Surgeons, physicians, dentists, podiatrists, eye doctors, registered nurses and other trained nursing personnel, medics, clinical pharmacists and veterinarians typically engage in suturing. Surgical knots are used to secure the sutures.
Mentor Worldwide LLC is an American company that supplies surgical aesthetics products to plastic surgeons. The company is based in Santa Barbara, California. It produces one of two silicone gel breast implants. Titled MemoryGel, the product was approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on November 17, 2006. The other FDA-approved products are developed by competitors Allergan and Sientra. Mentor also produces a range of lipoplasty equipment for liposuction procedures as well as a Niacin-based skincare product line called NIA 24.

The vaginal vault is the expanded region of the vaginal canal at the internal end of the vagina.

C. R. Bard, Inc., now branded simply as Bard, headquartered in Murray Hill, New Jersey, USA, was a developer, manufacturer, and marketer of medical technologies in the fields of vascular, urology, oncology, and surgical specialties before its acquisition by BD.
Inguinal hernia surgery is an operation to repair a weakness in the abdominal wall that abnormally allows abdominal contents to slip into a narrow tube called the inguinal canal in the groin region.
George Fowlie Merson FRSE FPS FCS (1866–1959) was a Scottish pharmacist who produced an artificial surgical catgut called Mersuture. In authorship he appears as G. F. Merson.
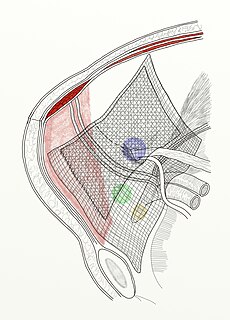
Biomesh is a type of surgical mesh made from an organic biomaterial. Biologic mesh is primarily indicated for several types of hernia repair, including inguinal and ventral hernias, hernia prophylaxis, and contaminated hernia repairs. However, it has also been used in pelvic floor dysfunction, parotidectomy, and reconstructive plastic surgery. The development of biologic mesh largely has derived from the need of a biocompatible material that addresses "the problems associated with a permanent synthetic mesh, including chronic inflammation, foreign body reaction, fibrosis, and mesh infection." As of 2015, however, the efficacy and optimal use of biological mesh products remains in question.

Surgical mesh is a loosely woven sheet which is used as either a permanent or temporary support for organs and other tissues during surgery. Surgical mesh is created from both inorganic and biological materials and is used in a variety of surgeries. Though hernia repair surgery is the most common application, it can also be used for reconstructive work, such as in pelvic organ prolapse.















