Angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitors are a class of medication used primarily for the treatment of high blood pressure and heart failure. They work by causing relaxation of blood vessels as well as a decrease in blood volume, which leads to lower blood pressure and decreased oxygen demand from the heart.

The renin–angiotensin system (RAS), or renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS), is a hormone system that regulates blood pressure, fluid and electrolyte balance, and systemic vascular resistance.

Bradykinin (BK) (Greek brady-, slow; -kinin, kīn(eîn) to move) is a peptide that promotes inflammation. It causes arterioles to dilate (enlarge) via the release of prostacyclin, nitric oxide, and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and makes veins constrict, via prostaglandin F2, thereby leading to leakage into capillary beds, due to the increased pressure in the capillaries. Bradykinin is a physiologically and pharmacologically active peptide of the kinin group of proteins, consisting of nine amino acids.
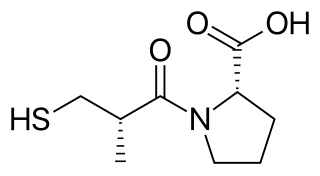
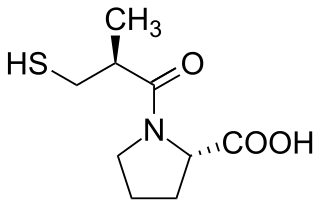
Captopril, sold under the brand name Capoten among others, is an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and some types of congestive heart failure. Captopril was the first oral ACE inhibitor found for the treatment of hypertension. It does not cause fatigue as associated with beta-blockers. Due to the adverse drug event of causing hyperkalemia, as seen with most ACE Inhibitors, the medication is usually paired with a diuretic.

Angiotensin-converting enzyme, or ACE, is a central component of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS), which controls blood pressure by regulating the volume of fluids in the body. It converts the hormone angiotensin I to the active vasoconstrictor angiotensin II. Therefore, ACE indirectly increases blood pressure by causing blood vessels to constrict. ACE inhibitors are widely used as pharmaceutical drugs for treatment of cardiovascular diseases.

Lisinopril is a medication belonging to the drug class of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and is used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and heart attacks. For high blood pressure it is usually a first-line treatment. It is also used to prevent kidney problems in people with diabetes mellitus. Lisinopril is taken by mouth. Full effect may take up to four weeks to occur.

Ramipril, sold under the brand name Altace among others, is an ACE inhibitor type medication used to treat high blood pressure, heart failure, and diabetic kidney disease. It can also be used as a preventative medication in patients over 55 years old to reduce the risk of having a heart attack, stroke or cardiovascular death in patients shown to be at high risk, such as some diabetics and patients with vascular disease. It is a reasonable initial treatment for high blood pressure. It is taken by mouth.
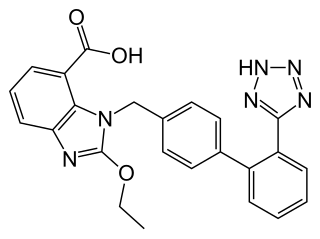
Candesartan is an angiotensin receptor blocker used mainly for the treatment of high blood pressure and congestive heart failure. Candesartan has a very low maintenance dose. The metabolism for the drug is unique as it is a cascading prodrug. Candesartan has good bioavailibility and is more potent among the AT-1 receptor antagonists.

Prolyl endopeptidase (PE) also known as prolyl oligopeptidase or post-proline cleaving enzyme is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PREP gene.
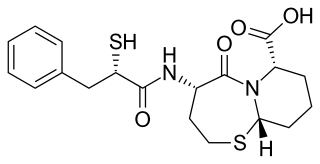
Omapatrilat is an experimental antihypertensive agent that was never marketed. It inhibits both neprilysin and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). NEP inhibition results in elevated natriuretic peptide levels, promoting natriuresis, diuresis, vasodilation, and reductions in preload and ventricular remodeling.

Moexipril an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor used for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. Moexipril can be administered alone or with other antihypertensives or diuretics.
Fasudil (INN) is a potent Rho-kinase inhibitor and vasodilator. Since it was discovered, it has been used for the treatment of cerebral vasospasm, which is often due to subarachnoid hemorrhage, as well as to improve the cognitive decline seen in stroke patients. It has been found to be effective for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension. It has been demonstrated that fasudil could improve memory in normal mice, identifying the drug as a possible treatment for age-related or neurodegenerative memory loss.

An Oligopeptidase is an enzyme that cleaves peptides but not proteins. This property is due to its structure: the active site of this enzyme is located at the end of a narrow cavity which can only be reached by peptides.

Sorbinil (INN) is an aldose reductase inhibitor being investigated for treatment of diabetic complications including neuropathy and retinopathy. Aldose reductase is an enzyme present in lens and brain that removes excess glucose by converting it to sorbitol. Sorbitol accumulation can lead to the development of cataracts in the lens and neuropathy in peripheral nerves. Sorbinil has been shown to inhibit aldose reductase in human brain and placenta and calf and rat lens. Sorbinil reduced sorbitol accumulation in rat lens and sciatic nerve of diabetic rats orally administered 0.25 mg/kg sorbinil.

Kelatorphan is a drug which acts as a powerful and complete inhibitor of nearly all of the enzymes responsible for catabolism of the endogenous enkephalins, including neutral endopeptidase (NEP), dipeptidyl peptidase III (DPP3), aminopeptidase N (APN), and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). In mice, with the intracerebroventricular co-administration of a 50 µg dose of kelatorphan (this route is necessary because kelatorphan is incapable of crossing the blood-brain-barrier) hence alongside exogenous [Met]enkephalin (ED50 approximately 10 ng), it potentiated the analgesic effects of the latter by 50,000 times. Kelatorphan also displays potent antinociceptive effects alone, and does not depress respiration, although at high doses it actually increases it.

Tynorphin is a synthetic opioid peptide which is a potent and competitive inhibitor of the enkephalinase class of enzymes which break down the endogenous enkephalin peptides. It specifically inactivates dipeptidyl aminopeptidase III (DPP3) with very high efficacy, but also inhibits neutral endopeptidase (NEP), aminopeptidase N (APN), and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to a lesser extent. It has a pentapeptide structure with the amino acid sequence Val-Val-Tyr-Pro-Trp (VVYPW).
Sacubitril/valsartan, sold under the brand name Entresto, is a fixed-dose combination medication for use in heart failure. It consists of the neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril and the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan. The combination is sometimes described as an "angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor" (ARNi). It is recommended for use as a replacement for an ACE inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor blocker in people with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.

Sacubitril is an antihypertensive drug used in combination with valsartan. The combination drug sacubitril/valsartan, known during trials as LCZ696 and marketed under the brand name Entresto, is a treatment for heart failure. It was approved under the FDA's priority review process for use in heart failure on July 7, 2015.

Ceronapril in a phosphonate ACE inhibitor that was never marketed.

Angiotensin (1-7) is an active heptapeptide of the renin–angiotensin system (RAS).



















