Enzyme kinetics is the study of the rates of enzyme-catalysed chemical reactions. In enzyme kinetics, the reaction rate is measured and the effects of varying the conditions of the reaction are investigated. Studying an enzyme's kinetics in this way can reveal the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme, its role in metabolism, how its activity is controlled, and how a drug or a modifier might affect the rate.

An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction.

Formestane, formerly sold under the brand name Lentaron among others, is a steroidal, selective aromatase inhibitor which is used in the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer in postmenopausal women. The drug is not active orally, and was available only as an intramuscular depot injection. Formestane was not approved by the United States FDA and the injectable form that was used in Europe in the past has been withdrawn from the market. Formestane is an analogue of androstenedione.

Mexazolam is a drug which is a benzodiazepine derivative. Mexazolam has been trialed for anxiety and was found to be effective in alleviating anxiety at one week follow-up. Mexazolam is metabolised via the CYP3A4 pathway. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors including simvastatin, simvastatin acid, lovastatin, fluvastatin, atorvastatin and cerivastatin inhibit the metabolism of mexazolam, but not the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor pravastatin. Its principal active metabolites are chlorodesmethyldiazepam and chloroxazepam.
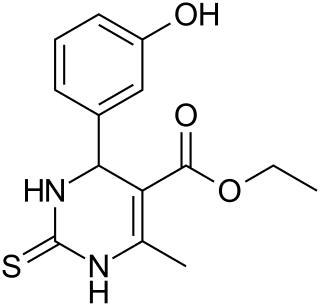
Monastrol is a cell-permeable small molecule inhibitor discovered by Thomas U. Mayer in the lab of Tim Mitchison. Monastrol was shown to inhibit the kinesin-5, a motor protein important for spindle bipolarity.
Brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitors are G-protein coupled receptors belonging to the class B secretin subfamily. Members include:

Cinanserin (INN) is a 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptor antagonist which was discovered in the 1960s.

BTS 74,398 is a centrally acting stimulant drug which was developed for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. It inhibits the synaptic reuptake of dopamine, serotonin and noradrenaline, making it a triple reuptake inhibitor. It was effective in animal models of Parkinson's disease, but was unsuccessful in human trials.
Thymidylate synthase inhibitors are chemical agents which inhibit the enzyme thymidylate synthase and have potential as an anticancer chemotherapy. This inhibition prevents the methylation of C5 of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) thereby inhibiting the synthesis of deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). The downstream effect is promotion of cell death because cells would not be able to properly undergo DNA synthesis if they are lacking dTMP, a necessary precursor to dTTP. Five agents were in clinical trials in 2002: raltitrexed, pemetrexed, nolatrexed, Plevitrexed( ZD9331/BGC9331), and GS7904L.
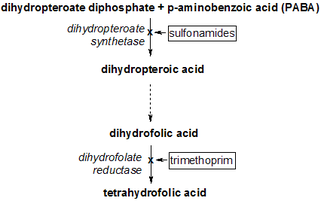
A dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor is a molecule that inhibits the function of dihydrofolate reductase, and is a type of antifolate.

Lubazodone is an experimental antidepressant which was under development by Yamanouchi for the treatment for major depressive disorder in the late 1990s and early 2000s but was never marketed. It acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and 5-HT2A receptor antagonist, and hence has the profile of a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). The drug has good selectivity against a range of other monoamine receptors, with its next highest affinities being for the α1-adrenergic receptor and the 5-HT2C receptor. Lubazodone is structurally related to trazodone and nefazodone, but is a stronger serotonin reuptake inhibitor and weaker as a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist in comparison to them and is more balanced in its actions as a SARI. It reached phase II clinical trials for depression, but development was discontinued in 2001 reportedly due to the "erosion of the SSRITooltip selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor market in the United States".

JZ-IV-10 is a piperidine derivative related to cocaine which acts as a highly potent serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor. The eugeroic modafinil was used as a lead to fuel this compound's discovery.
Canertinib (CI-1033) is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of cancer. It is an irreversible tyrosine-kinase inhibitor with activity against EGFR (IC50 0.8 nM), HER-2 (IC50 19 nM) and ErbB-4 (IC50 7 nM). By 2015, Pfizer had discontinued development of the drug.

HU-336 is a strongly antiangiogenic compound, significantly inhibiting angiogenesis at concentrations as low as 300 nM. It inhibits angiogenesis by directly inducing apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells without changing the expression of pro- and antiangiogenic cytokines and their receptors. HU-336 is highly effective against tumor xenografts in nude mice. Although it is technically the oxidized quinone of delta-8 THC, it is entirely non psychoactive.

Arachidonoyl serotonin is an endogenous lipid signaling molecule. It was first described in 1998 as being an inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). In 2007, it was shown to have analgesic properties and to act as an antagonist of the TRPV1 receptor. In 2011, it was shown to be present in the ileum and jejunum of the gastrointestinal tract and modulate glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) secretion. In addition to this, in 2016, AA-5-HT was also found to affect the signaling mechanisms responsible for anxiety, by inhibiting dopamine release from the Basolateral amygdala following fear behavior. In 2017, AA-5-HT was tested in its effects on the sleep wake cycle, where it was found to affect the sleep homeostasis when used in conjunction with molecules and chemicals that affect wake-related neurotransmitters.
An enkephalinase inhibitor is a type of enzyme inhibitor which inhibits one or more members of the enkephalinase class of enzymes that break down the endogenous enkephalin opioid peptides. Examples include racecadotril, ubenimex (bestatin), RB-101, and D-phenylalanine, as well as the endogenous opioid peptides opiorphin and spinorphin. It also includes RB-3007, Semax and Selank. Analgesic, anticraving, antidepressant, anxiolytic, and antidiarrheal effects are common properties of enkephalinase inhibitors.
An endocannabinoid enhancer (eCBE) is a type of cannabinoidergic drug that enhances the activity of the endocannabinoid system by increasing extracellular concentrations of endocannabinoids. Examples of different types of eCBEs include fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) inhibitors, monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) inhibitors, and endocannabinoid transporter (eCBT) inhibitors. An example of an actual eCBE is AM404, the active metabolite of the analgesic paracetamol and a dual FAAH inhibitor and eCBRI.
Competitive inhibition is interruption of a chemical pathway owing to one chemical substance inhibiting the effect of another by competing with it for binding or bonding. Any metabolic or chemical messenger system can potentially be affected by this principle, but several classes of competitive inhibition are especially important in biochemistry and medicine, including the competitive form of enzyme inhibition, the competitive form of receptor antagonism, the competitive form of antimetabolite activity, and the competitive form of poisoning.
BW284C51 is a selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It is also a nicotinic antagonist.

Nirmatrelvir is an antiviral medication developed by Pfizer which acts as an orally active 3C-like protease inhibitor. It is part of a nirmatrelvir/ritonavir combination used to treat COVID-19 and sold under the brand name Paxlovid.