| Glyceollin synthase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.14.13.85 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
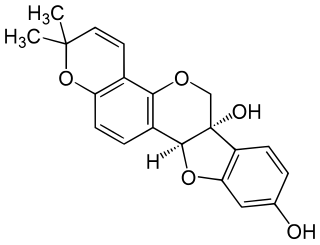
In enzymology, glyceollin synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the last committed step in glyceollin biosynthesis. This enzyme has been classified as a cytochrome dependent monooxygenase. It uses cyclization of prenyl residue to convert glyceollidins (I and II) into glyceollins (I - III).
This enzyme catalyzes the following chemical reaction:
- 2-(or 4-)dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan + NADPH + H+ + O2 glyceollin + NADP+ + 2 H2O
The five substrates of this enzyme are 2-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan, 4-dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan, NADPH, H+, and O2, whereas its three products are glyceollin, NADP+, and H2O.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on paired donors, with O2 as oxidant and incorporation or reduction of oxygen. The oxygen incorporated need not be derived from O2 with NADH or NADPH as one donor, and incorporation of one atom o oxygen into the other donor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 2-(or 4-)dimethylallyl-(6aS,11aS)-3,6a,9-trihydroxypterocarpan,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (cyclizing). This enzyme participates in isoflavonoid biosynthesis.