
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology of the teeth of an animal.

Eomaia is a genus of extinct fossil mammals containing the single species Eomaia scansoria, discovered in rocks that were found in the Yixian Formation, Liaoning Province, China, and dated to the Barremian Age of the Lower Cretaceous about 125 million years ago. The single fossil specimen of this species is 10 centimetres (3.9 in) in length and virtually complete. An estimate of the body weight is 20–25 grams (0.71–0.88 oz). It is exceptionally well-preserved for a 125-million-year-old specimen. Although the fossil's skull is squashed flat, its teeth, tiny foot bones, cartilages and even its fur are visible.

Afrotheria is a superorder of placental mammals, the living members of which belong to groups that are either currently living in Africa or of African origin: golden moles, elephant shrews, otter shrews, tenrecs, aardvarks, hyraxes, elephants, sea cows, and several extinct clades. Most groups of afrotheres share little or no superficial resemblance, and their similarities have only become known in recent times because of genetics and molecular studies. Many afrothere groups are found mostly or exclusively in Africa, reflecting the fact that Africa was an island continent from the Cretaceous until the early Miocene around 20 million years ago, when Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia.

Andrewsarchus, meaning "Andrews' ruler", is an extinct genus of artiodactyl that lived during the Middle Eocene in what is now China. The genus was first described by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1924 with the type species A. mongoliensis based on a largely complete cranium. A second species, A. crassum, was described in 1977 based on teeth. A mandible, formerly described as Paratriisodon, does probably belong to Andrewsarchus as well. The genus has been historically placed in the families Mesonychidae or Arctocyonidae, or was considered to be a close relative of whales. It is now regarded as the sole member of its own family, Andrewsarchidae, and may have been related to entelodonts. Fossils of Andrewsarchus have been recovered from the Middle Eocene Irdin Manha, Lushi, and Dongjun Formations of Inner Mongolia, each dated to the Irdinmanhan Asian land mammal age.

Phosphatherium escuillei Gheerbrant, Sudre et Cappetta 1996 is a basal proboscidean that lived in Africa during the early Eocene, by 56-55 Ma. It is one of the earliest known proboscidean, together with Eritherium azzouzorum from the Selandian. It was found in phosphorites beds from the base of the Ypresian stage of the Ouled Abdoun Basin, which is best known for its exceptionally rich marine vertebrate fauna.

Eritherium is an extinct genus of early Proboscidea found in the Ouled Abdoun basin, Morocco. It lived about 60 million years ago. It was first named by Emmanuel Gheerbrant in 2009 and the type species is Eritherium azzouzorum. Eritherium is the oldest, smallest and most primitive known elephant relative.

Hipposideros besaoka is an extinct bat from Madagascar in the genus Hipposideros. It is known from numerous jaws and teeth, which were collected in a cave at Anjohibe in 1996 and described as a new species in 2007. The site where H. besaoka was found is at most 10,000 years old; other parts of the cave have yielded H. commersoni, a living species of Hipposideros from Madagascar, and some material that is distinct from both species. H. besaoka was larger than H. commersoni, making it the largest insectivorous bat of Madagascar, and had broader molars and a more robust lower jaw. As usual in Hipposideros, the second upper premolar is small and displaced from the toothrow, and the second lower premolar is large.

Triisodon is a genus of extinct mesonychian mammal that existed during the Early Paleocene of New Mexico, North America, from about 63.5-62.0 Ma. The genus was named by Edward Drinker Cope in 1881 as a member of the Acreodi, a now invalid taxon that encompassed creodonts, mesonychians and certain arctocyonians. Cope described the type specimen of T. quivirensis as "about the size of a wolf." A smaller species, T. crassicuspis, has also been identified from the same region. Since material from this genus is incomplete, the exact size of adults and whether they showed sexual dimorphism or regional variations in size is unknown.
Deccanolestes is a scansorial, basal Euarchontan from the Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) and Paleocene Intertrappean Beds of Andhra Pradesh, India. It may be closely related to Sahnitherium. Deccanolestes has been referred to Palaeoryctidae in the past, but recent evidence has shown that it is either the most basal Euarchontan, as the earliest known Adapisoriculid, or as a stem-afrotherian.
Plesiopithecus is an extinct genus of early strepsirrhine primate from the late Eocene.
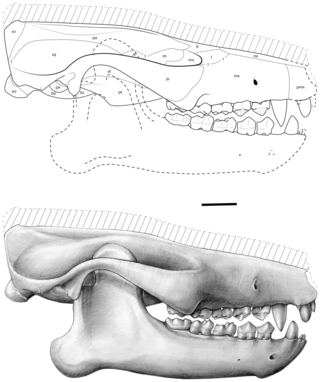
Ocepeia is an extinct genus of afrotherian mammal that lived in present-day Morocco during the middle Paleocene epoch, approximately 60 million years ago. First named and described in 2001, the type species is O. daouiensis from the Selandian stage of Morocco's Ouled Abdoun Basin. A second, larger species, O. grandis, is known from the Thanetian, a slightly younger stage in the same area. In life, the two species are estimated to have weighed about 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) and 10 kg (22 lb), respectively, and are believed to have been specialized leaf-eaters. The fossil skulls of Ocepeia are the oldest known afrotherian skulls, and the best-known of any Paleocene mammal in Africa.

The Oulad Abdoun Basin is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years.

Abdounodus is an extinct genus of mammal known from the middle Paleocene of Northern Africa. The sole species, A. hamdii, is known from teeth and jaw bones discovered in the Ouled Abdoun Basin of present-day Morocco in 2001.
Azygonyx was a small tillodont mammal, likely the size of a cat to raccoon, that lived in North America during the Paleocene and Eocene in the early part of the Cenozoic Era. The only fossils that have been recovered are from the Willwood and Fort Union Formations in the Bighorn Basin of Wyoming, United States, and date to the Clarkforkian to Wasatchian, about 56 to 50 million years ago. Fifty-six collections that have been recovered thus far include the remains of Azygonyx. Azygonyx survived the Paleocene Eocene Thermal Maximum along with other mammals like Phenacodus and Ectocion, both of which were ground-dwelling mammals. Azygonyx probably was a generalist terrestrial mammal that may have roamed around the ground, but was also capable of climbing trees.
Navajovius is an extinct genus of plesiadapiforms that lived during the Paleocene epoch. Plesiadapiforms were small, arboreal mammals that are theorized to be either closely related to primates or dermopterans. Navajovius has only been documented from localities within North America. This genus was officially named in 1921 by Walter Granger and William Matthew and the type specimen is housed at the American Museum of Natural History.
Saxonella is a genus of extinct primate from the Paleocene Epoch, 66–56 Ma. The genus is present in the fossil record from around ~62–57 Ma. Saxonella has been found in fissure fillings in Walbeck, Germany as well as in the Paskapoo Formation in Alberta, Canada. Saxonella is one of five families within the superfamily Plesiadapoidae, which appears in the fossil record from the mid Paleocene to the early Eocene. Analyses of molars by paleontologists suggest that Saxonella most likely had a folivorous diet.

Periptychus is an extinct genus of mammal belonging to the family Periptychidae. It lived from the Early to Late Paleocene and its fossil remains have been found in North America.
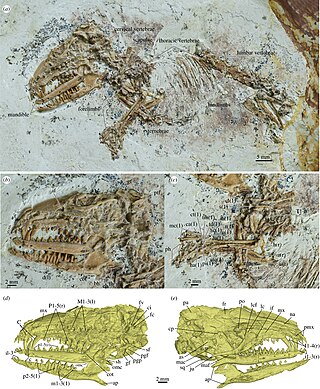
Cokotherium is an extinct genus of eutherian mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. It includes a single species, Cokotherium jiufotangensis, known from a single partial skeleton, missing a portion of the hindlimbs and tail. It was recovered from the Jiufotang Formation, the upper part of the fossiliferous Jehol biota. The generic name of Cokotherium honors the nickname of the late paleontologist Chuan-Kui Li, a specialist on the Jiufotang Formation. The specific name refers to the formation in question. Cokotherium is one of the youngest and most well-preserved Early Cretaceous eutherians, illustrating an array of transitional conditions between Early Cretaceous and Late Cretaceous members of Eutheria.
Chaoyangodens is an extinct genus of eutriconodont mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. It includes a single species, Chaoyangodens lii, known from a single complete skeleton recovered from the Dawangzhangzi bed of the Yixian Formation, part of the fossiliferous Jehol biota. Chaoyangodens was a moderate-sized Mesozoic mammal. The generic name refers to Chaoyang Prefecture while the specific name honors the collector of the fossil, Hai-Jun Li. Chaoyangodens is intermediate in age between Liaoconodon and a diverse fauna of eutriconodonts from older beds of the Yixian Formation. Like Liaoconodon, it is not easily equated with other eutriconodonts, since it bears distinctive dental traits relative to recognized eutriconodont subgroups.

Paenungulatomorpha is a clade of afrotherian mammals that can be characterized according to Gheerbrant et al. (2016):
by a mandibular retromolar fossa, the absence of hypocone, an ectoloph selenodont and linked to strong styles such as mesostyle in basal taxa, and a more or less developed pseudohypocone.
















