
Perissodactyla is an order of ungulates. The order includes about 17 living species divided into three families: Equidae, Rhinocerotidae (rhinoceroses), and Tapiridae (tapirs). They typically have reduced the weight-bearing toes to three or one of the five original toes, though tapirs retain four toes on their front feet. The nonweight-bearing toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or positioned posteriorly. By contrast, artiodactyls bear most of their weight equally on four or two of the five toes: their third and fourth toes. Another difference between the two is that perissodactyls digest plant cellulose in their intestines, rather than in one or more stomach chambers as artiodactyls, with the exception of Suina, do.

Tapirs are large, herbivorous mammals belonging to the family Tapiridae. They are similar in shape to a pig, with a short, prehensile nose trunk. Tapirs inhabit jungle and forest regions of South and Central America and Southeast Asia. They are one of three extant branches of Perissodactyla, alongside equines and rhinoceroses. Only a single genus, Tapirus, is currently extant. Tapirs migrated into South America during the Pleistocene epoch from North America after the formation of the Isthmus of Panama as part of the Great American Interchange. Tapirs were formerly present across North America, but became extinct in the region at the end of the Late Pleistocene, around 12,000 years ago.

The South American tapir, also commonly called the Brazilian tapir, the Amazonian tapir, the maned tapir, the lowland tapir, anta, and la sachavaca, is one of the four recognized species in the tapir family. It is the largest surviving native terrestrial mammal in the Amazon.

Tapirus is a genus of tapir which contains the living tapir species. The Malayan tapir is usually included in Tapirus as well, although some authorities have moved it into its own genus, Acrocodia.

The Malayan tapir, also called Asian tapir, Asiatic tapir, oriental tapir, Indian tapir, piebald tapir, or black-and-white tapir, is the only living tapir species outside of the Americas. It is native to Southeast Asia from the Malay Peninsula to Sumatra. It has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List since 2008, as the population is estimated to comprise fewer than 2,500 mature individuals.

The mountain tapir, also known as the Andean tapir or woolly tapir, is the smallest of the four widely recognized species of tapir. It is found only in certain portions of the Andean Mountain Range in northwestern South America. As such, it is the only tapir species to live outside of tropical rainforests in the wild. It is most easily distinguished from other tapirs by its thick woolly coat and white lips.

The Baird's tapir, also known as the Central American tapir, is a species of tapir native to Mexico, Central America, and northwestern South America. It is the largest of the three species of tapir native to the Americas, as well as the largest native land mammal in both Central and South America.
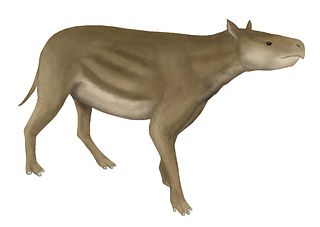
Heptodon is an extinct genus of tapir-type herbivore of the family Helaletidae endemic to North America during the Early Eocene. It lived from 50.3—48.6 mya, existing for approximately 1.7 million years.

The giant tapir is an extinct species of tapir that lived in southern China, Vietnam and Laos, with reports suggesting it also lived in Taiwan, Java, and potentially Borneo. The species has been recorded from Middle and Late Pleistocene. There is only weak evidence for a Holocene survival. Tapirus augustus was larger than any living tapir, with an estimated weight of about 623 kilograms (1,373 lb). The species was also placed in its own genus of Megatapirus, however, it is now conventionally placed within Tapirus.

Protapirus is an extinct genus of tapir known from the Oligocene and Miocene of North America and Eurasia.

Tapiroidea is a superfamily of perissodactyls which includes the modern tapirs and their extinct relatives. Taxonomically, they are placed in suborder Ceratomorpha along with the rhino superfamily, Rhinocerotoidea.The first members of Tapiroidea appeared during the Early Eocene, 55 million years ago, and were present in North America and Asia during the Eocene. Tapiridae first appeared during the early Oligocene in Europe, and are thought to have originated from the tapiroid family Helaletidae.

Tapirus polkensis, the pygmy tapir, is a small prehistoric tapir that lived in North America during the late Miocene and early Pliocene. T. polkensis had an estimated mass of around 125 kg (276 lb), making it smaller than any extant tapir.

Tapirus californicus, the California tapir, is an extinct species of tapir that inhabited North America during the Pleistocene. It became extinct about 13,000 years ago.

Tapirus merriami, commonly called Merriam's tapir, is an extinct species of tapir which inhabited North America during the Pleistocene.

Tapirus haysii is an extinct species of tapir that inhabited North America during the early to middle Pleistocene Epoch (~2.5–1 Ma). The fossil remains of two juvenile T. haysii were collected in Hillsborough County, Florida on August 31, 1963. It was the second largest North American tapir; the first being T. merriami.

Tapirus veroensis is an extinct tapir species that lived in the area of the modern eastern and southern United States during the Pleistocene epoch (Irvingtonian-Rancholabrean). Tapirus veronensis is thought to have gone extinct around 11,000 years ago.
Tapirus mesopotamicus is an extinct species of tapir that lived in South America during the Pleistocene. It is considered a possible ancestor of all extant South American tapirs.
Tapirus rondoniensis is an extinct species of large sized tapir that lived in northwestern parts of Brazil during the Pleistocene. Fossils of the species were found in the Río Madeira Formation of Rondônia, after which the species is named.
Paracolodon is an extinct genus of tapiroid perissodactyl belonging to the family Helaletidae. Fossils have been found in Mongolia and the Inner Mongolia region of China.

Deperetellidae is an extinct family of herbivorous odd-toed ungulates containing the genera Bahinolophus, Deperetella, Irenolophus, and Teleolophus. Their closest living relatives are tapirs. Deperetellids are known from the Middle Eocene deposits of China, Mongolia, Kyrgyzstan and Myanmar.


























