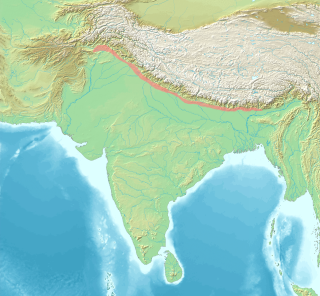
The Sivalik Hills, also known as Churia Hills, are a mountain range of the outer Himalayas. The literal translation of "Sivalik" is 'tresses of Shiva'. The hills are known for their numerous fossils, and is also home to the Soanian Middle Paleolithic archaeological culture.

Diatomys is an extinct rodent genus known from Miocene deposits in China, Japan, Pakistan, and Thailand. The fossil range is from the late Early Miocene to the Middle Miocene.

The South Asian Stone Age spans the prehistoric age from the earliest use of stone tools in the Paleolithic period to the rise of agriculture, domestication, and pottery in the Neolithic period across present-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Sri Lanka. Like in all parts of the world, in South Asia, the divisions of the stone age into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Neolithic periods do not carry precise chronological boundaries; instead, they describe broad phases of technological and cultural development based on the tools and artifacts found at various archaeological sites.

Rhamphosuchus is an extinct genus of gavialid crocodylians. It lived during the Pliocene and its fossils have been found in two regions; the Siwalik Hills of Pakistan and India as well as the Sindh region of Pakistan. Its type species is Rhamphosuchus crassidens, which is only known from incomplete sets of fossils, mostly teeth and skulls. Four species traditionally placed in the genus Gavialis may be included as well.

The geology of Nepal is dominated by the Himalaya, the highest, youngest and a very highly active mountain range. Himalaya is a type locality for the study of on-going continent-continent collision tectonics. The Himalayan arc extends about 2,400 km (1,500 mi) from Nanga Parbat by the Indus River in northern Pakistan eastward to Namche Barwa by the gorge of the Tsangpo-Brahmaputra in eastern Tibet. About 800 km (500 mi) of this extent is in Nepal; the remainder includes Bhutan and parts of Pakistan, India, and China.

Indopithecus giganteus is an extinct species of large ape that lived in the late Miocene of the Siwalik Hills in northern India. Although frequently assigned to the more well-known genus Gigantopithecus, recent authors consider it to be a distinct genus in its own right.

Giraffokeryx is an extinct genus of medium-sized giraffids known from the Miocene of the Indian subcontinent and Eurasia. It is distinguished from other giraffids by the four ossicones on its head; one pair in front of the eyes on the anterior aspect of the frontal bone and the other behind the eyes in the frontoparietal region overhanging the temporal fossae. It has a brachydont dentition like in other giraffids and its legs and feet are of medium length. Giraffokeryx is considered monotypic by most authors, in the form of G. punjabiensis, but other species have been assigned to the genus:
The Soanian culture is a prehistoric technological culture from the Siwalik Hills, Pakistan. It is named after the Soan Valley in Pakistan.
Hydaspitherium is an extinct genus of giraffid artiodactyls that lived during the Cenozoic era during the Miocene epoch to the Pliocene epoch in Pakistan. Giraffids are represented in the late Miocene epoch of the Siwaliks by large Sivatheriinae such as Sivatherium, Bramatherium, Helladotherium, and Hydaspitherium. Hydaspitherium has been proposed to be synonymous with Bramatherium. H. megacephalum is restricted to the Dhok Pathan Formation in northern Pakistan.

Aceratherium is an extinct genus of rhinocerotid of the subfamily Aceratheriinae that lived in Eurasia during the Miocene.
Crocodylus palaeindicus is an extinct species of crocodile from southern Asia. C. palaeindicus lived from the Miocene to the Pliocene. It may be an ancestor of the living Mugger crocodile.
Indraloris is a fossil primate from the Miocene of India and Pakistan in the family Sivaladapidae. Two species are now recognized: I. himalayensis from Haritalyangar, India and I. kamlialensis from the Pothohar Plateau, Pakistan. Other material from the Potwar Plateau may represent an additional, unnamed species. Body mass estimates range from about 2 kg (4.4 lb) for the smaller I. kamlialensis to over 4 kg (8.8 lb) for the larger I. himalayensis.
Hadromys loujacobsi is an extinct species of rat, known only from three molars of early Pleistocene origin. They were found in the Upper Siwalik Group in the Punjab region of Pakistan.

The Himalayan foreland basin is an active collisional foreland basin system in South Asia. Uplift and loading of the Eurasian Plate on to the Indian Plate resulted in the flexure (bending) of the Indian Plate, and the creation of a depression adjacent to the Himalayan mountain belt. This depression was filled with sediment eroded from the Himalaya, that lithified and produced a sedimentary basin ~3 to >7 km deep. The foreland basin spans approximately 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) in length and 450 kilometres (280 mi) in width. From west to east the foreland basin stretches across five countries: Pakistan, India, Nepal, Bangladesh, and Bhutan.
Sivaladapis is a genus of adapiform primate that lived in Asia during the middle Miocene.

Enhydriodon is an extinct genus of mustelids known from Africa, Pakistan, and India that lived from the late Miocene to the early Pleistocene. It contains nine confirmed species, two debated species, and at least a few other undescribed species from Africa. The genus belongs to the tribe Enhydriodontini in the otter subfamily Lutrinae. Enhydriodon means "otter tooth" in Ancient Greek and is a reference to its dentition rather than to the Enhydra genus, which includes the modern sea otter and its two prehistoric relatives.
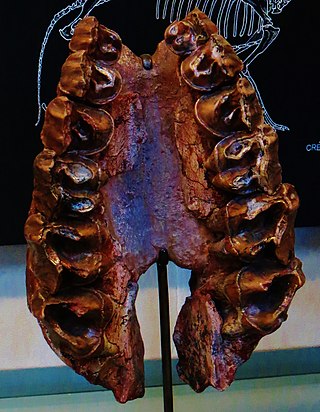
Ronzotherium is an extinct genus of perissodactyl mammal from the family Rhinocerotidae. The name derives from the hill of 'Ronzon', the French locality near Le Puy-en-Velay at which it was first discovered, and the Greek suffix 'therium' meaning 'beast'. At present 5 species have been identified from several localities in Europe and Asia, spanning the Late Eocene to Upper Oligocene.
Sivapardus is an extinct, little-known genus of feline with only one species assigned to it, Sivapardus punjabiensis. It was described in 1969 by the paleontologist Abu Bakr based on a partial mandible from the Upper Siwaliks in Pakistan; the locality it was found at is estimated to be from the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene. S. punjabiensis was a large cat with a short and broad snout that may have lived on open grasslands.

Protanancus is an extinct genus of amebelodontid proboscidean from Kenya, Pakistan and Thailand. The genus consists solely of type species P. macinnesi. The generic name is derived from the unrelated Anancus, and the Greek prōtos "first".
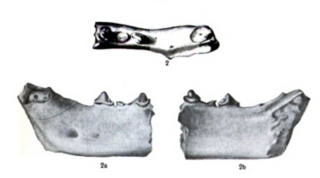
Sivasmilus is a fossil genus of barbourofelid containing only a single species, Sivasmilus copei. It is known from only a single specimen, a partial mandible collected from the Chinji Formation in the Lower Siwaliks in Pakistan, estimated to be from the Miocene. The fossil was originally described in 1915 when it was assigned to the fossil feline Sivaelurus chinjiensis, but was used as the basis of a new genus and species in 1929 by Hungarian paleontologist Miklós Kretzoi. Sivasmilus copei was a relatively small, cat-like animal.























