| Hesperocyonines Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Skull of Mesocyon coryphaeus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Carnivora |
| Family: | Canidae |
| Subfamily: | † Hesperocyoninae |
| Genera | |
| |
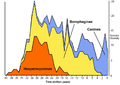
The extinct Hesperocyoninae are one of three subfamilies found within the canid family. The other two canid subfamilies are the extinct Borophaginae and extant Caninae. [1]