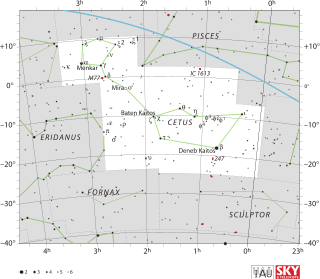
Cetus is a constellation, sometimes called 'the whale' in English. The Cetus was a sea monster in Greek mythology which both Perseus and Heracles needed to slay. Cetus is in the region of the sky that contains other water-related constellations: Aquarius, Pisces and Eridanus.

Fornax is a constellation in the southern celestial hemisphere, partly ringed by the celestial river Eridanus. Its name is Latin for furnace. It was named by French astronomer Nicolas Louis de Lacaille in 1756. Fornax is one of the 88 modern constellations.
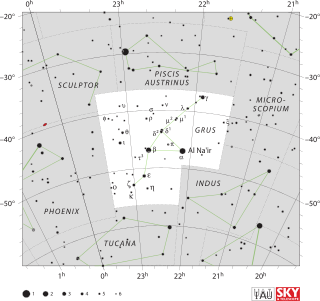
Grus is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the crane, a type of bird. It is one of twelve constellations conceived by Petrus Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. Grus first appeared on a 35-centimetre-diameter (14-inch) celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas Uranometria of 1603. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave Bayer designations to its stars in 1756, some of which had been previously considered part of the neighbouring constellation Piscis Austrinus. The constellations Grus, Pavo, Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds".

An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the four main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae, along with spiral and lenticular galaxies. Elliptical (E) galaxies are, together with lenticular galaxies (S0) with their large-scale disks, and ES galaxies with their intermediate scale disks, a subset of the "early-type" galaxy population.

Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work The Realm of the Nebulae and, as such, form part of the Hubble sequence. Most spiral galaxies consist of a flat, rotating disk containing stars, gas and dust, and a central concentration of stars known as the bulge. These are often surrounded by a much fainter halo of stars, many of which reside in globular clusters.

An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure.

Pavo is a constellation in the southern sky whose name is Latin for 'peacock'. Pavo first appeared on a 35-cm (14 in) diameter celestial globe published in 1598 in Amsterdam by Petrus Plancius and Jodocus Hondius and was depicted in Johann Bayer's star atlas Uranometria of 1603, and was likely conceived by Plancius from the observations of Pieter Dirkszoon Keyser and Frederick de Houtman. French explorer and astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille gave its stars Bayer designations in 1756. The constellations Pavo, Grus, Phoenix and Tucana are collectively known as the "Southern Birds".

A lenticular galaxy is a type of galaxy intermediate between an elliptical and a spiral galaxy in galaxy morphological classification schemes. It contains a large-scale disc but does not have large-scale spiral arms. Lenticular galaxies are disc galaxies that have used up or lost most of their interstellar matter and therefore have very little ongoing star formation. They may, however, retain significant dust in their disks. As a result, they consist mainly of aging stars. Despite the morphological differences, lenticular and elliptical galaxies share common properties like spectral features and scaling relations. Both can be considered early-type galaxies that are passively evolving, at least in the local part of the Universe. Connecting the E galaxies with the S0 galaxies are the ES galaxies with intermediate-scale discs.

IC 10 is an irregular galaxy in the constellation Cassiopeia. It was discovered by Lewis Swift in 1887 and in 1935 Nicholas Mayall became the first to suggest that the object is extragalactic. Edwin Hubble suspected it might belong to the Local Group of galaxies, but its status remained uncertain for decades. The radial velocity of IC 10 was measured in 1962, and it was found to be approaching the Milky Way at approximately 350 km/s, strengthening the evidence for its membership in the Local Group. Its membership in the group was finally confirmed in 1996 by direct measurements of its distance based on observations of Cepheids; most estimates place the galaxy 2–3 million light years from Earth, with some estimates ranging from 1.5–4.5 million light years. Despite its closeness, the galaxy is rather difficult to study because it lies near the plane of the Milky Way and is therefore heavily obscured by interstellar matter.

A dwarf galaxy is a small galaxy composed of about 1000 up to several billion stars, as compared to the Milky Way's 200–400 billion stars. The Large Magellanic Cloud, which closely orbits the Milky Way and contains over 30 billion stars, is sometimes classified as a dwarf galaxy; others consider it a full-fledged galaxy. Dwarf galaxies' formation and activity are thought to be heavily influenced by interactions with larger galaxies. Astronomers identify numerous types of dwarf galaxies, based on their shape and composition.

NGC 1569 is a dwarf irregular galaxy in Camelopardalis. The galaxy is relatively nearby and consequently, the Hubble Space Telescope can easily resolve the stars within the galaxy. The distance to the galaxy was previously believed to be only 2.4 Mpc. However, in 2008 scientists studying images from Hubble calculated the galaxy's distance at nearly 11 million light-years away, about 4 million light-years farther than previously thought, meaning it is a member of the IC 342 group of galaxies.

Interacting galaxies are galaxies whose gravitational fields result in a disturbance of one another. An example of a minor interaction is a satellite galaxy disturbing the primary galaxy's spiral arms. An example of a major interaction is a galactic collision, which may lead to a galaxy merger.

NGC 1097 is a barred spiral galaxy about 45 million light years away in the constellation Fornax. It was discovered by William Herschel on 9 October 1790. It is a severely interacting galaxy with obvious tidal debris and distortions caused by interaction with the companion galaxy NGC 1097A.

NGC 6872, also known as the Condor Galaxy, is a large barred spiral galaxy of type SB(s)b pec in the constellation Pavo. It is 212 million light-years (65 Mpc) from Earth. NGC 6872 is interacting with the lenticular galaxy IC 4970, which is less than one twelfth as large. The galaxy has two elongated arms with a diameter based on ultraviolet light of over 522,000 light-years (160,000 pc), and a D25.5 isophotal diameter of over 717,000 light-years (220,000 pc), making it the largest known spiral galaxy. It was discovered on 27 June 1835 by English astronomer John Herschel.

IC 4970 is an unbarred lenticular galaxy of type SA0^- pec: in the constellation Pavo. It is 212 million light-years (65 Mpc) from Earth and is interacting with the barred spiral galaxy NGC 6872. It was discovered on 21 September 1900 by American astronomer DeLisle Stewart.

Arp 147 is an interacting pair of ring galaxies. It lies 430 million to 440 million light years away in the constellation Cetus and does not appear to be part of any significant galaxy group. The system was originally discovered in 1893 by Stephane Javelle and is listed in the Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies.

IC 5052 is a barred spiral galaxy located in the constellation Pavo. It is located at a distance of circa 25 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that IC 5052 is about 40,000 light years across. It was discovered by DeLisle Stewart on August 23, 1900.

Bedin I is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy located in the constellation Pavo. It is situated around 28.38 million light-years from Earth, behind the globular cluster NGC 6752. Bedin I is possibly one of the oldest galaxies known, having formed around 10–13 billion years ago, and is one of the most isolated dwarf galaxies known, situated around 2.12 million light-years away from NGC 6744, its nearest neighbor with which it may be physically associated. As such, it has been deemed by astronomers as a "fossil" from the early universe. It was accidentally discovered by Italian astronomer Luigi Bedin, whose team was studying white dwarfs in NGC 6752 using the Hubble Space Telescope in September 2018; the discovery was announced in a paper published in January 2019.

IC 4662, also known as ESO 102-14 is an irregular galaxy located in the constellation Pavo 7.96 million light years away. It was discovered by Robert T. A. Innes in 1901. It has a diameter of 7000 light years and an angular size of 3.2' x 1.9'.



















