| Ictidopappus Temporal range: early Paleocene | |
|---|---|
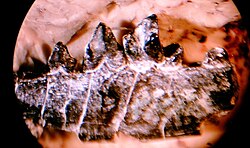 | |
| lower jaw of Ictidopappus mustelinus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Family: | † Viverravidae |
| Subfamily: | † Ictidopappinae Van Valen, 1969 [1] |
| Genus: | † Ictidopappus Simpson, 1935 |
| Type species | |
| †Ictidopappus mustelinus Simpson, 1935 [2] | |
| Synonyms | |
synonyms of subfamily:
| |
Ictidopappus ("grandfather of weasels") is an extinct genus of mammals from extinct subfamily Ictidopappinae within extinct family Viverravidae, that lived in North America during the early Paleocene. [3] [4]