
The Treatment Action Campaign (TAC) is a South African HIV/AIDS activist organisation which was co-founded by the HIV-positive activist Zackie Achmat in 1998. TAC is rooted in the experiences, direct action tactics and anti-apartheid background of its founder. TAC has been credited with forcing the reluctant government of former South African President Thabo Mbeki to begin making antiretroviral drugs available to South Africans.

Lamivudine, commonly called 3TC, is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS. It is also used to treat chronic hepatitis B when other options are not possible. It is effective against both HIV-1 and HIV-2. It is typically used in combination with other antiretrovirals such as zidovudine, dolutegravir, and abacavir. Lamivudine may be included as part of post-exposure prevention in those who have been potentially exposed to HIV. Lamivudine is taken by mouth as a liquid or tablet.

The XV International AIDS Conference was held in Bangkok, the capital city of Thailand, from July 11 to July 16, 2004. The main venue for the conference was the IMPACT Muang Thong Thani convention centre at Nonthaburi, north-east of downtown Bangkok. It was the first international AIDS conference to be held in Southeast Asia. International AIDS conferences have been held regularly since the first one in Atlanta in 1985.

The United States President's Emergency Plan For AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) is a United States governmental initiative to address the global HIV/AIDS epidemic and help save the lives of those suffering from the disease. Launched by U.S. President George W. Bush in 2003, as of May 2020, PEPFAR has provided about $90 billion in cumulative funding for HIV/AIDS treatment, prevention, and research since its inception, making it the largest global health program focused on a single disease in history until the COVID-19 pandemic. PEPFAR is implemented by a combination of U.S. government agencies in over 50 countries and overseen by the Global AIDS Coordinator at the United States Department of State. As of 2023, PEPFAR has saved over 25 million lives, primarily in sub-Saharan Africa.
HIV/AIDS has been a public health concern for Latin America due to a remaining prevalence of the disease. In 2018 an estimated 2.2 million people had HIV in Latin America and the Caribbean, making the HIV prevalence rate approximately 0.4% in Latin America.
Mark Arnold Wainberg, was a Canadian HIV/AIDS researcher and HIV/AIDS activist. He was the Director of the McGill University AIDS Centre at the Montreal Jewish General Hospital and Professor of Medicine and of Microbiology at McGill University. His laboratory primarily studies HIV reverse transcriptase, the molecular basis for drug resistance, and gene therapy. He received a B.Sc. from McGill University in 1966, a Ph.D. from Columbia University in 1972, and did his post-doctoral research at Hadassah Medical School of the Hebrew University.

Joseph Marie Albert "Joep" Lange was a Dutch clinical researcher specialising in HIV therapy. He served as the president of the International AIDS Society from 2002 to 2004. He was a passenger on Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, which was shot down on 17 July 2014 over Ukraine.

Simon Tseko Nkoli was an anti-apartheid, gay rights and AIDS activist in South Africa. Active in the Congress of South African Students (COSAS), the United Democratic Front, and the Gay Association of South Africa (GASA), he was arrested as part of the Delmas Treason Trial in 1984. After his release in 1988, he founded the Gay and Lesbian Organisation of the Witwatersrand (GLOW) and organized South Africa's first pride parade. His activism influenced the African National Congress (ANC) to enshrine gay rights in the South African constitution. One of the first South Africans to disclose that he was living with HIV/AIDS, Nkoli founded the Township AIDS Project. After his death from AIDS-related complications, his colleagues established the Treatment Action Campaign.

HIV/AIDS was first detected in Canada in 1982. In 2018, there were approximately 62,050 people living with HIV/AIDS in Canada. It was estimated that 8,300 people were living with undiagnosed HIV in 2018. Mortality has decreased due to medical advances against HIV/AIDS, especially highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART).

The Canadian AIDS Society (CAS) is a national charitable organization dedicated to advocating for AIDS Service Organizations across Canada. Established in 1987 amidst the growing HIV/AIDS crisis and an inadequate governmental response, CAS initially began as a grassroots movement and later formalized into a coalition, incorporating in 1988. The decision to relocate to Ottawa was strategic, aiming to enhance engagement with governmental bodies.
AIDS Vancouver, founded in early 1983, is recognized as one of the first community-based non-profit AIDS organizations in Canada, responding to the HIV/AIDS crisis in the Vancouver area. Led by co-founders Gordon Price, Noah Stewart, Dr. Mike Maynard, Daryl Nelson, and Ron Alexander Slater, the organization has aimed to provide support, education, and advocacy for individuals affected by HIV/AIDS. With a focus on grassroots efforts and community mobilization, AIDS Vancouver has been involved in efforts to address the spread of HIV and support individuals living with the virus.

Dolutegravir (DTG), sold under the brand name Tivicay, is an antiretroviral medication used, together with other medication, to treat HIV/AIDS. It may also be used, as part of post exposure prophylaxis, to prevent HIV infection following potential exposure. It is taken by mouth.
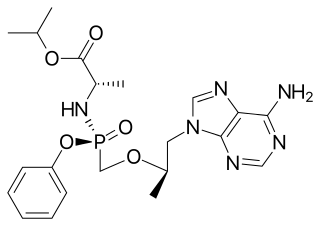
Tenofovir alafenamide, sold under the brand name Vemlidy, is an antiviral medication used against hepatitis B and HIV. It is used for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection in adults with compensated liver disease and is given in combination with other medications for the prevention and treatment of HIV. It is taken by mouth.

The Canadian Association for HIV Research (CAHR) is an organization that represents HIV/AIDS research in Canada or by Canadians. CAHR includes all researchers and all disciplines of the scientific approaches to HIV and AIDS, for the purpose of its better prevention and treatment and ultimately for its eradication and cure. Disciplines represented by CAHR include basic science, clinical science, epidemiology/public health and social science.
Julio S. G. Montaner, is an Argentine-born Canadian physician, professor and researcher. He is the director of the British Columbia Centre for Excellence in HIV/AIDS, the chair in AIDS Research and head of the Division of AIDS in the Faculty of Medicine at the University of British Columbia and the past-president of the International AIDS Society. He is also the director of the John Ruedy Immunodeficiency Clinic, and the Physician Program Director for HIV/AIDS PHC. He is known for his work on HAART, a role in the discovery of triple therapy as an effective treatment for HIV in the late 1990s, and a role in advocating the "Treatment as Prevention" Strategy in the mid-2000s, led by Myron Cohen of the HPTN 052 trial.

Abacavir/dolutegravir/lamivudine, sold under the brand name Triumeq among others, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It is a combination of three medications with different and complementary mechanisms of action: abacavir, dolutegravir and lamivudine.
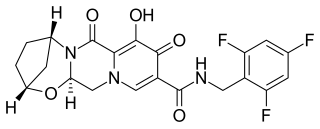
Bictegravir is a second-generation integrase inhibitor (INSTI) class that was structurally derived from an earlier compound dolutegravir by scientists at Gilead Sciences. In vitro and clinical results were presented by Gilead in the summer of 2016. In 2016, bictegravir was in a Phase 3 trial as part of a single tablet regimen in combination with tenofovir alafenamide (TAF) and emtricitabine (FTC) for the treatment of HIV-1 infection.

Socio-political activism to raise awareness about HIV/AIDS as well as to advance the effective treatment and care of people with AIDS (PWAs) has taken place in multiple locations since the 1980s. The evolution of the disease's progress into what's known as the HIV/AIDS pandemic has resulted in various social movements fighting to change both government policies and the broader popular culture inside of different areas. These groups have interacted in a complex fashion with others engaged in related forms of social justice campaigning, with this continuing on to this day.
Dolutegravir/rilpivirine, sold under the brand name Juluca, is a fixed-dose combination antiretroviral medication for the treatment of HIV/AIDS. It contains the medicines dolutegravir and rilpivirine. It is taken by mouth.

Lenacapavir, sold under the brand name Sunlenca, is an antiretroviral medication used to treat HIV/AIDS. It is taken by mouth or by subcutaneous injection.
















