Related Research Articles

Anesthesia or anaesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia, paralysis, amnesia, and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized.

Sevoflurane, sold under the brand name Sevorane, among others, is a sweet-smelling, nonflammable, highly fluorinated methyl isopropyl ether used as an inhalational anaesthetic for induction and maintenance of general anesthesia. After desflurane, it is the volatile anesthetic with the fastest onset. While its offset may be faster than agents other than desflurane in a few circumstances, its offset is more often similar to that of the much older agent isoflurane. While sevoflurane is only half as soluble as isoflurane in blood, the tissue blood partition coefficients of isoflurane and sevoflurane are quite similar. For example, in the muscle group: isoflurane 2.62 vs. sevoflurane 2.57. In the fat group: isoflurane 52 vs. sevoflurane 50. As a result, the longer the case, the more similar will be the emergence times for sevoflurane and isoflurane.

The Apgar score is a quick way for health professionals to evaluate the health of all newborns at 1 and 5 minutes after birth and in response to resuscitation. It was originally developed in 1952 by an anesthesiologist at Columbia University, Virginia Apgar, to address the need for a standardized way to evaluate infants shortly after birth.

Anesthesiology, anaesthesiology, or anaesthesia is the medical specialty concerned with the total perioperative care of patients before, during and after surgery. It encompasses anesthesia, intensive care medicine, critical emergency medicine, and pain medicine. A physician specialized in anesthesiology is called an anesthesiologist, anaesthesiologist, or anaesthetist, depending on the country. In some countries the terms are synonymous, while in other countries they refer to different positions and anesthetist is only used for non-physicians, such as nurse anesthetists.
Awareness under anesthesia, also referred to as intraoperative awareness or accidental awareness during general anesthesia (AAGA), is a rare complication of general anesthesia where patients regain varying levels of consciousness during their surgical procedures. While anesthesia awareness is possible without resulting in any long-term memory of the experience, it is also possible for victims to have awareness with explicit recall, where they can remember the events related to their surgery.

Desflurane (1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether) is a highly fluorinated methyl ethyl ether used for maintenance of general anesthesia. Like halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane, it is a racemic mixture of (R) and (S) optical isomers (enantiomers). Together with sevoflurane, it is gradually replacing isoflurane for human use, except in economically undeveloped areas, where its high cost precludes its use. It has the most rapid onset and offset of the volatile anesthetic drugs used for general anesthesia due to its low solubility in blood.
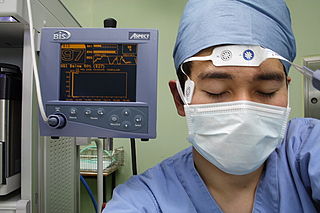
Bispectral index (BIS) is one of several technologies used to monitor depth of anesthesia. BIS monitors are used to supplement Guedel's classification system for determining depth of anesthesia. Titrating anesthetic agents to a specific bispectral index during general anesthesia in adults allows the anesthetist to adjust the amount of anesthetic agent to the needs of the patient, possibly resulting in a more rapid emergence from anesthesia. Use of the BIS monitor could reduce the incidence of intraoperative awareness during anaesthesia. The exact details of the algorithm used to create the BIS index have not been disclosed by the company that developed it.
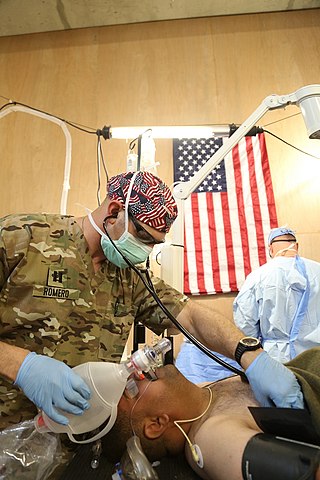
A nurse anesthetist is an advanced practice nurse who administers anesthesia for surgery or other medical procedures. They are involved in the administration of anesthesia in a majority of countries, with varying levels of autonomy.
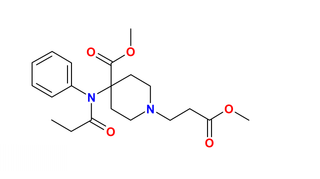
Remifentanil, marketed under the brand name Ultiva is a potent, short-acting synthetic opioid analgesic drug. It is given to patients during surgery to relieve pain and as an adjunct to an anaesthetic. Remifentanil is used for sedation as well as combined with other medications for use in general anesthesia. The use of remifentanil has made possible the use of high-dose opioid and low-dose hypnotic anesthesia, due to synergism between remifentanil and various hypnotic drugs and volatile anesthetics.
Neurosurgical anesthesiology, neuroanesthesiology, or neurological anesthesiology is a subspecialty of anesthesiology devoted to the total perioperative care of patients before, during, and after neurological surgeries, including surgeries of the central (CNS) and peripheral nervous systems (PNS). The field has undergone extensive development since the 1960s correlating with the ability to measure intracranial pressure (ICP), cerebral blood flow (CBF), and cerebral metabolic rate (CMR).
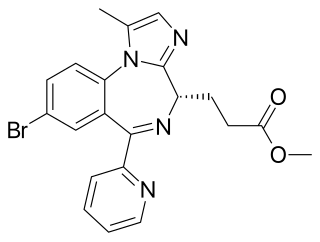
Remimazolam, sold under the brand name Byfavo, is a medication for the induction and maintenance of procedural sedation in adults for invasive diagnostic or surgical procedures lasting 30 minutes or less. It is a benzodiazepine drug, developed by PAION AG in collaboration with several regional licensees as an alternative to the short-acting imidazobenzodiazepine midazolam, for use in the induction of anesthesia and conscious sedation for minor invasive procedures. Remimazolam was found to have both a more rapid onset and a shorter duration than midazolam, and human clinical trials showed a faster recovery time and predictable, consistent pharmacokinetics, suggesting some advantages over existing drugs for these applications.

The history of neuraxial anaesthesia dates back to the late 1800s and is closely intertwined with the development of anaesthesia in general. Neuraxial anaesthesia, in particular, is a form of regional analgesia placed in or around the Central Nervous System, used for pain management and anaesthesia for certain surgeries and procedures.

Kathryn Ann Kelly "Kelly" McQueen is an American anesthesiologist and global health expert. She currently practices anesthesiology at the UW Health University Hospital in Madison, Wisconsin and serves as the chair for the Department of Anesthesiology at the University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public health.
Mervyn Maze, MD, MB ChB has been a Professor in the Departments of Anesthesia and Pain Medicine, Intensive Care at the University of California, San Francisco since 1988. He has also served as Professor and Chair at Imperial College London.

No Pain Labor & Delivery – Global Health Initiative is a non-for-profit organization. Founded in 2006, the program focuses on correcting the unnecessarily high caesarean delivery rate and the poor utilization of neuraxial labor analgesia in China.
Obstetric anesthesia or obstetric anesthesiology, also known as ob-gyn anesthesia or ob-gyn anesthesiology, is a sub-specialty of anesthesiology that provides peripartum pain relief (analgesia) for labor and anesthesia for cesarean deliveries ('C-sections').
The World Federation of Societies of Anaesthesiologists (WFSA) is an international federation of independent national professional associations of anaesthesiologists. The WFSA's Secretariat is based in London, UK.
James Edward Cottrell is the Chair Emeritus, Department of Anesthesiology at SUNY Downstate Medical Center in New York City. He serves as a member of the New York State Board of Regents and is an avid collector of contemporary fine-art.
Beverley Anne Orser is a Canadian anesthesiologist. As a professor at the University of Toronto, Orser was elected a member of the National Academy of Medicine for "her discovery of the unique pharmacological properties of extrasynaptic GABA-A receptors and their mechanistic role in anesthetic- and inflammation-induced impairment of memory, and for her leadership in academic anesthesiology.
Alex Macario is an American anesthesiologist, academic and author. He is a vice-chair for education, a professor in the Department of Anesthesiology, Perioperative and Pain Medicine, and program director for the anesthesiology residency at Stanford University School of Medicine.
References
- ↑ Bacon, Douglas R. (May 1997). "The World Federation of Societies of Anesthesiologists:... : Anesthesia & Analgesia". Anesthesia & Analgesia. 84 (5): 1130–1135. Retrieved 20 February 2021.
- ↑ Walker, Isabeau A.; Shafer, Steven L. (April 2015). "The World Federation of Societies of Anaesthesiologists, International Anesthesia Research Society, and Anesthesia & Analgesia: A Shared Global Vision". Anesthesia & Analgesia. 120 (4): 721–724. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000000639 . PMID 25790206.
- ↑ Bause, George S. (December 2012). "Recovering the Long-Lost Trophy Awarded in 1937 to the Founders McMechan by the International Anesthesia Research Society". Anesthesia & Analgesia. 115 (6): 1433–1436. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31826e7a17 . PMID 23144434.
- ↑ "IARS About Us" . Retrieved June 17, 2014.
- ↑ "SmartTots: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)". Archived from the original on 2011-07-26. Retrieved 2011-01-21.
- ↑ "New Web Site Fosters Wikisthesiology" . Retrieved January 13, 2014.[ dead link ]
- ↑ "OpenAnesthesia.org: 3 Years Old and Growing Like a Weed!" . Retrieved January 13, 2014.