
The Pool Malebo, formerly Stanley Pool, also known as Mpumbu, Lake Nkunda or Lake Nkuna by local indigenous people in pre-colonial times, is a lake-like widening in the lower reaches of the Congo River. The river serves as the border between the Republic of the Congo on the north and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the south.
Protognathosaurus is a genus of herbivorous dinosaur from the Middle Jurassic. It was a sauropod found at Dashanpu in Sichuan in what is present-day China.
Lusitanosaurus is a genus of large basal thyreophoran dinosaur from the Sinemurian stage of Early Jurassic of Portugal. It is the second example of the group from the Lower Jurassic of Europe and it is the oldest known dinosaur from the Iberian Peninsula. It is based on a large left maxilla with teeth that was lost in the fire at Museu Nacional de História Natural e da Ciência, Lisbon, in 1978.

Pelagosaurus is an extinct genus of thalattosuchian crocodyliform that lived during the Toarcian stage of the Lower Jurassic, around 183 Ma to 176 Ma, in shallow epicontinental seas that covered much of what is now Western Europe. The systematic taxonomy of Pelagosaurus has been fiercely disputed over the years, and was assigned to Thalattosuchia after its systematics within Teleosauridae were disputed. Pelagosaurus measured 2–3 m (6.6–9.8 ft) long and weighed 60 kg (130 lb).

Pachythrissops is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish. It contains two species, P. laevis from the Purbeckian of England and P. propterus from the Tithonian of Germany. A third species, P. vectensis, has been reassigned to the elopiform genus Arratiaelops. Pachythrissops is often regarded as one of the most primitive members of the order Ichthyodectiformes; however, a phylogenetic analysis by Cavin et al. (2013) placed it and the related genus Ascalabothrissops outside the group.
Asiatoceratodus is an extinct genus of lungfish which lived during the Middle-Late Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous periods in what is now Asia (Kyrgyzstan), Africa and South America.
Jacques Pellegrin was a French zoologist.
Neopholidophoropsis is an extinct genus of stem-teleost ray-finned fish that lived in what is now Germany during the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous epoch. It contains one species, Neopholidophoropsis serrata.
Bobbichthys is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived in what is now Chile during the Oxfordian stage of the Late Jurassic epoch.
Luisiella is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived during the Kimmeridgian stage of the Late Jurassic epoch. Fossils of the genus have been found in either the Cañadón Calcáreo Formation or Cañadón Asfalto Formation in Chubut Province, Argentina.
Oreochima ellioti is an archaeomaenid ray-finned fish from Lower Jurassic-aged freshwater strata of Antarctica. Fossils come from the Lower Jurassic Carapace Formation (Pliensbachian-Toarcian) of Storm Peak, Antarctica, where a freshwater lake system once existed. O. ellioti is also notable for being one of three archaeomaenid genera found outside of Australia.
Parapleuropholis is an extinct genus of ray-finned fish that lived in what is now the Democratic Republic of the Congo during the early Toarcian stage of the Early Jurassic epoch.
Lualabaea is an extinct genus of prehistoric coelacanth, belonging to the family Mawsoniidae, containing the single species L. lerichei. It has been found in Late Jurassic or Berriasian aged deposits in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
Indocoelacanthus robustus is a fossil sarcopterygian. The holotype specimen was found in Lower Jurassic-aged riverine sediment of the Kota formation, in the Pranhita-Godavari valley at Boraigudem limestone ridge, about 30 kilometers southeast of Sironcha, India. The holotype is preserved in the museum of the Indian Statistical Institute.
Ankylophorus is an extinct genus of stem-teleost ray-finned fish that lived in what is now France during the Late Jurassic. Its type and only species, Ankylophorus similis, was originally named in 1895 as a species of Pholidophorus, but was moved to a separate genus in 1978.
Pholidophoristion is an extinct genus of stem-teleost ray-finned fish that lived in what is now Europe from the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous.
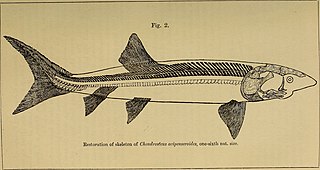
Chondrosteidae is a family of extinct marine actinopterygian fishes in the order Acipenseriformes. Three genera are known from the Early Jurassic of Europe, Chondrosteus, Gyrosteus, and Strongylosteus. Included species were of large size, with body lengths ranging from 2 metres (6.6 ft) up to 7 metres (23 ft). Their skeleton was largely made up of bones, but ossification was reduced compared to other ray-fins.
Henri Émile Sauvage was a French paleontologist, ichthyologist, and herpetologist. He was a leading expert on Mesozoic fish and reptiles.
The Baptist Community of Congo is a Baptist Christian denomination in Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is affiliated with the Church of Christ in the Congo, and the Baptist World Alliance. The headquarters is in Kinshasa.

Ginglymodi is a clade of ray-finned fish containing modern-day gars (Lepisosteidae) and their extinct relatives, including the family Lepidotidae and the orders Semionotiformes and Kyphosichthyiformes, and various other extinct taxa. Ginglymodi is one of the two major subgroups of the infraclass Holostei, the other one being Halecomorphi, which contains the bowfin and its fossil relatives.











