Related Research Articles

The history of the Americas begins with people migrating to these areas from Asia during the height of an ice age. These groups are generally believed to have been isolated from the people of the "Old World" until the coming of Europeans in the 10th century from Iceland led by Leif Erikson, and in 1492 with the voyages of Christopher Columbus.
The 3rd millennium BC spanned the years 3000 to 2001 BC. This period of time corresponds to the Early to Middle Bronze Age, characterized by the early empires in the Ancient Near East. In Ancient Egypt, the Early Dynastic Period is followed by the Old Kingdom. In Mesopotamia, the Early Dynastic Period is followed by the Akkadian Empire. In what is now Northwest India and Pakistan, the Indus Valley civilization developed a state society.

The history of South America is the study of the past, particularly the written record, oral histories, and traditions, passed down from generation to generation on the continent of South America. The continent continues to be home to indigenous peoples, some of whom built high civilizations prior to the arrival of Europeans in the late 1400s and early 1500s. South America has a history that has a wide range of human cultures and forms of civilization. The Caral Supe civilization, also known as the Norte Chico civilization in Peru is the oldest civilization in the Americas and one of the first six independent civilizations in the world; it was contemporaneous with the Egyptian pyramids. It predated the Mesoamerican Olmec by nearly two millennia.

The archaeology of the Americas is the study of the archaeology of the Western Hemisphere, including North America (Mesoamerica), Central America, South America and the Caribbean. This includes the study of pre-historic/Pre-Columbian and historic indigenous American peoples, as well as historical archaeology of more recent eras, including the Trans-Atlantic slave trade and European colonization.

A cradle of civilization is a location and a culture where civilization was developed independent of other civilizations in other locations. The formation of urban settlements (cities) is the primary characteristic of a society that can be characterized as "civilized". Other characteristics of civilization include a sedentary non-nomadic population, monumental architecture, the existence of social classes and inequality, and the creation of a writing system for communication. The transition from simpler societies to the complex society of a civilization is gradual.

The Sacred City of Caral-Supe, or simply Caral, is an archaeological site in Peru where the remains of the main city of the Caral civilization are found. It is located in the Supe valley of Peru, near the current town of Caral, 182 kilometers north of Lima, 23 km from the coast and 350 metres above sea level. It is attributed an antiquity of 5,000 years and it is considered the oldest city in the Americas and one of the oldest in the world. No other site has been found with such a diversity of monumental buildings or different ceremonial and administrative functions in the Americas as early as Caral. It has been declared a Humanity Cultural Heritage site by UNESCO.

For the hydroelectric power plant and HVDC-back-to-back facility in Paraguay, see Acaray Power Plant

Ruth Martha Shady Solís is a Peruvian anthropologist and archaeologist. She is the founder and director of the archaeological project at Caral.

Casma is a city in the coastal desert of Peru, located 330 kilometers (210 mi) northwest of Lima. It is the capital of Casma Province and the third most populous city in the Ancash Region with an estimated population of 29,343 (2015). It is located in the lower Casma Valley, covering an area of 1,205 km2.
Huaricanga is the earliest city of the Norte Chico civilization, called Caral or Caral-Supe in Peru and Spanish language sources. Established around 3500 BC, Huaricanga was the oldest city in the Americas. This Late Archaic site is located in the arid Fortaleza Valley on Peru’s north central coast. It is 14 mi (23 km) inland from the Pacific Ocean. The site covers a total area of 100 hectares, and is the largest Late Archaic construction in the Norte Chico region.
A river valley civilization is an agricultural nation or civilization situated beside and drawing sustenance from a river. A river gives the inhabitants a reliable source of water for drinking and agriculture. Additional benefits include fishing, fertile soil due to annual flooding, and ease of transportation.

Caral–Supe was a complex Pre-Columbian era society that included as many as thirty major population centers in what is now the Caral region of north-central coastal Peru. The civilization flourished between the fourth and second millennia BC, with the formation of the first city generally dated to around 3500 BC, at Huaricanga, in the Fortaleza area. It is from 3100 BC onward that large-scale human settlement and communal construction become clearly apparent, which lasted until a period of decline around 1800 BC. Since the early 21st century, it has been recognized as the oldest-known civilization in the Americas, and as one of the six sites where civilisation separately originated in the ancient world.
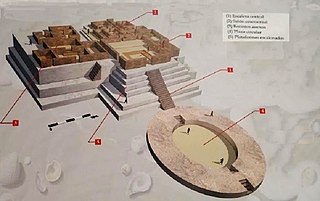
Aspero is a well-studied Late Preceramic site archaeological complex located near the mouth of the Supe River, south of Supe Puerto, on the central coast of Peru. It forms part of the ancient Caral-Supe civilization and was occupied during the Late Archaic period, from before 3000 BCE to around 1800 BCE. It is connected culturally to the ancient city of Caral, located 25 km up-valley, for which it presumably served as a major fishery. The site covers an area of approximately 14 hectares and features numerous temples or huacas, of which the most prominent are the Huaca Alta, the Huaca de los ídolos and the Huaca de los Sacrificios. Remains of human sacrifice have been found in the latter, dated to about 4500 years ago.

The Palpa Province is the smallest of five provinces of the Ica Region of Peru and the only landlocked province of the region. The capital of the province is the city of Palpa.

The Andean civilizations were South American complex societies of many indigenous people. They stretched down the spine of the Andes for 4,000 km (2,500 mi) from southern Colombia, to Ecuador and Peru, including the deserts of coastal Peru, to north Chile and northwest Argentina. Archaeologists believe that Andean civilizations first developed on the narrow coastal plain of the Pacific Ocean. The Caral or Norte Chico civilization of coastal Peru is the oldest known civilization in the Americas, dating back to 3500 BCE. Andean civilization is one of the six "pristine" civilizations of the world, created independently and without influence by other civilizations.

Huaca Prieta is the site of a prehistoric settlement beside the Pacific Ocean in the Chicama Valley, just north of Trujillo, La Libertad Province, Peru. It is a part of the El Brujo Archaeological Complex, which also includes Moche (culture) sites.

Sechin Bajo is a large archaeological site with ruins dating from 3500 BCE to 1300 BCE, making it not only one of the oldest centers of civilization in the Western Hemisphere, but also one of the oldest civilization centers on earth. Sechin Bajo is located in the valley of the Sechin River, about 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) from the Pacific Ocean and about 330 kilometres (210 mi) northwest of Lima, Peru. Sechin Bajo is one ruin among many located in close proximity to each other in the valleys of the Casma and Sechin Rivers.

The Andean preceramic refers to the early period of human occupation in the Andean area of South America that preceded the introduction of ceramics. This period is also called pre-ceramic or aceramic.

The Casma–Sechin culture of Peru refers to the large concentration of pre-historic ruins in the valleys of the Casma River and its tributary the Sechin River and along the nearby coast of the Pacific Ocean. The ruins include major archaeological sites such as Sechin Bajo, Sechin Alto, Cerro Sechin, Mojeque, Chankillo, and Taukachi-Konkan, as well as other smaller sites. Most of these inland sites are found in the river valleys about 20 kilometres (12 mi) distant from the ocean. The seaside sites of Huaynuná and Las Haldas are found about 20 kilometres (12 mi) north and south of the mouth of the Casma River on the coast.

Bandurria is a large archaeological site on the Huaura River in Peru that has been dated to 4,000 BC. It is located about 3 km south of the city of Huacho, in Huacho District, Huaura Province, Lima Region. It corresponds chronologically to the period known as the 'Late Archaic' or 'Late preceramic' covering the years from about 4000 to 2000 BC.
References
- 1 2 Creamer, Winifred; Haas, Jonathan; Jakaitis, Edward; Holguin, Jesus (May 2011). "Far From the Shore: Comparison of Marine Invertebrates in Midden Deposits From Two Sites in the Norte Chico, Peru". The Journal of Island and Coastal Archaeology. 6 (2): 176–195. doi:10.1080/15564894.2011.582071.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Haas, Jonathan; Creamer, Winifred; Ruiz, Alvaro (January 2005). "Dating the Late Archaic occupation of the Norte Chico region in Peru". Nature. 432 (7020): 1020–3. doi:10.1038/nature03146. PMID 15616561.
- ↑ Creamer, Winifred; Ruiz, Alvaro; Haas, Jonathan (September 2007). "Archaeological Investigation of Late Archaic Sites (3000–1800 B.C.) in the Pativilca Valley, Peru". Fieldiana Anthropology. 2007 (40): 1–78. doi:10.3158/0071-4739(2007)189[1:AIOLAS]2.0.CO;2.