Related Research Articles

The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs).

Zelenograd is a city and administrative okrug of Moscow, Russia. The city of Zelenograd and the territory under its jurisdiction form the Zelenogradsky Administrative Okrug (ZelAO), an exclave located within Moscow Oblast, 37 kilometers (23 mi) north-west of central Moscow, along the M10 highway. Zelenograd is the smallest administrative okrug of Moscow by area, the second-lowest by population, and the largest Moscow exclave by area and by population within Moscow Oblast. Zelenograd, if it were a separate settlement, would be the fifth-largest city in Moscow Oblast and one of the 100 largest cities of Russia. Before the expansion of the territory of Moscow in 2012, Zelenograd occupied second place among the administrative okrugs of Moscow, second only to the Eastern Administrative Okrug, in terms of the share of greenery in its total area.

TMS320 is a blanket name for a series of digital signal processors (DSPs) from Texas Instruments. It was introduced on April 8, 1983 through the TMS32010 processor, which was then the fastest DSP on the market.
This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Transnistria, an unrecognized breakaway territory of Moldova and the de facto independent Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic.
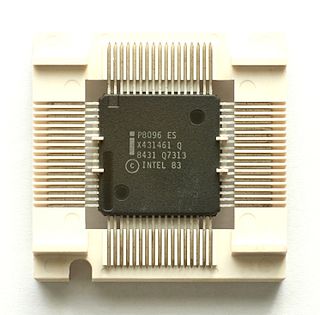
The Intel MCS-96 is a family of microcontrollers (MCU) commonly used in embedded systems. The family is often referred to as the 8xC196 family, or 80196, the most popular MCU in the family. These MCUs are commonly used in hard disk drives, modems, printers, pattern recognition and motor control. In 2007, Intel announced the discontinuance of the entire MCS-96 family of microcontrollers. Intel noted that "There are no direct replacements for these components and a redesign will most likely be necessary."

The KR580VM80A is a Soviet microprocessor, a clone of the Intel 8080 CPU. Different versions of this CPU were manufactured beginning in the late 1970s, the earliest known use being in the SM1800 computer in 1979. Initially called the K580IK80 (К580ИК80), it was produced in a 48-pin planar metal-ceramic package. Later, a version in a PDIP-40 package was produced and was named the KR580IK80A (КР580ИК80А). The pin layout of the latter completely matched that of Intel's 8080A CPU. In 1986 this CPU received a new part number to conform with the 1980 Soviet integrated circuit designation and became known as the KR580VM80A (КР580ВМ80А), the number it is most widely known by today. Normal clock frequency for the K580IK80A is 2 MHz, with speeds up to 2.5 MHz for the KR580VM80A. The KR580IK80A was manufactured in a 6 µm process. In the later KR580VM80A the feature size was reduced to 5 µm and the die became 20% smaller.
The C166 family is a 16-bit microcontroller architecture from Infineon in cooperation with STMicroelectronics. It was first released in 1990 and is a controller for measurement and control tasks. It uses the well-established RISC architecture, but features some microcontroller-specific extensions such as bit-addressable memory and an interrupt system optimized for low-latency. When this architecture was introduced the main focus was to replace 8051 controllers.

The 1801 series CPUs were a family of 16-bit Soviet microprocessors based on the indigenous Elektronika NC microarchitecture cores, but binary compatible with DEC's PDP-11 machines. First released in 1980, various models and variants of the series were among the most popular Soviet microprocessors and dominated embedded systems and military applications of the 1980s. They were also used in widely different areas such as graphing calculators and industrial CNCs, but arguably their most well-known use was in several Soviet general-purpose mini- and microcomputer designs like the SM EVM, DVK, UKNC, and BK families. Due to being the CPU of the popular Elektronika BK home computer, used in its late years as a demo machine, as well as the DVK micros that often offered a first glimpse into the UNIX world, this processor achieved something of a cult status among Soviet and then Russian programmers, and to a lesser extent, international programmers.

The K1810VM86 is a Soviet 16-bit microprocessor, a clone of the Intel 8086 CPU with which it is binary and pin compatible. It was developed between 1982 and 1985. The original K1810VM86 supported a clock frequency of up to 5 MHz while up to 8 MHz were allowed for the later K1810VM86M. The K1810VM86 was manufactured plastic 40-pin dual in-line package or in a 40-pin ceramic dual in-line package. A clone of the related Intel 8088 with its 8-bit bus was manufactured as the K1810VM88, also in plastic and ceramic packages.
The KOMDIV-64 is a family of 64-bit microprocessors developed by the Scientific Research Institute of System Development (NIISI) of the Russian Academy of Sciences and manufactured by TSMC, UMC, GlobalFoundries, and X-Fab. The KOMDIV-64 processors are primarily intended for industrial and high-performance computing applications.
The KOMDIV-32 is a family of 32-bit microprocessors developed and manufactured by the Scientific Research Institute of System Development (NIISI) of the Russian Academy of Sciences. The manufacturing plant of NIISI is located in Dubna on the grounds of the Kurchatov Institute. The KOMDIV-32 processors are intended primarily for spacecraft applications and many of them are radiation hardened (rad-hard).
Multicore is a series of 32-bit microprocessors with embedded DSP cores developed by ELVEES, Russia. The microprocessor is a MIPS32 core or an ARM Cortex-A9 core. Some of the processors in the series are radiation hardened (rad-hard) for space applications.
Angstrem JSC is a Moscow-based company involved in the design and fabrication of electronic products and semiconductors. It produced a range of Soviet-era integrated circuits. After the fall of the Soviet Union, in 90s it has produced a line of calculators and bank cards.

The People's Commissariat for Communications of the USSR was the central state agency of the Soviet Union for communications in the period 1932 to 1946. The Commissariat administered the postal, telegraph and telephone services.

People's Commissariat for Posts and Telegraphs of the USSR was the central organ of the Soviet Union government that was in charge of the organisation and administration of the different forms of communication including posts. It existed between 1923 and 1932.

The soviet integrated circuit designation is an industrial specification for encoding the names of integrated circuits manufactured in the Soviet Union and the Post-Soviet states. 25 years after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, a number of manufacturers in Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, Latvia, and Uzbekistan still use this designation.

The Radio-86RK is a build-it-yourself home computer designed in the Soviet Union. It was featured in the popular Radio magazine for radio hams and electronics hobbyists in 1986. The letters RK in the title stands for the words Radio ham's Computer. Design of the computer was published in a series of articles describing its logical structure, electrical circuitry, drawings of printed circuit boards and firmware. The computer could be built entirely out of standard off-the-shelf parts. Later it was also available in a kit form as well as fully assembled form.
The Ministry of the Electronics Industry was a government ministry in the Soviet Union.

The Micro-80 was the first do-it-yourself home computer in the Soviet Union.
К1839 is a microprocessor chipset developed between 1984 and 1989 at the Angstrem Research Institute by the same team that developed the 1801BMx series of CPUs. It was the first Soviet, and later the first Russian 32-bit microprocessor system. From a programmer's point of view, it was a complete replica of the VAX 11/750 Comet and included floating-point arithmetic, unlike the MicroVAX microprocessors produced by DEC. The chipset included a processor, a coprocessor for integer and floating-point arithmetic, a memory controller and a bus adapter. It was fabricated in a 3 µm process. The Electronika-32 computer and a VAX-PC board were built based on this chipset, as well as the aerospace on-board digital computer SB3541. The 1839 chipset is still in production, and is used in the control systems of the GLONASS-M satellites.
References
- 1 2 "145 серия - Музей электронных раритетов".
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Варламов, И.В. (1989). Микропроцессоры в бытовой технике (in Russian). Радио и связь. ISBN 5256004794.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 Козак, Виктор Романович (24 May 2014). "Номенклатура и аналоги отечественных микросхем". www.inp.nsk.su (in Russian). Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Шахнова, В. А. (1988). Микропроцессоры и микропроцессорные комплекты интегральных микросхем: Справочник. В 2-х т. Том 1 [Microprocessors and microprocessor chip sets: A reference. In 2 volumes. Vol. 1] (in Russian). Moscow: Радио и связь. ISBN 5-256-00371-2 . Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 "Активные элементы". www.155la3.ru (in Russian). Музей электронных раритетов. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 Нестеров, П. В. (1986). Микропроцессоры. В 3-х книгах. Книга 1. Архитектура и проектирование микро-ЭВМ. Организация вычислительных процессов[Microprocessors. In 3 volumes. Volume 1. Architecture and design of microcomputers. Organization of computing processes.] (in Russian). Moscow: ВЫСШАЯ ШКОЛА.
- ↑ Нефедов, А.В. (2001). Интегральные микросхемы и их зарубежные аналоги. Том 04. Серии К507-К543 [Integrated circuits and their foreign equivalents. Volume 04. Series K507-K543.] (in Russian). Moscow: ИП РадиоСофт. ISBN 5-93037-020-6 . Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- 1 2 М. П. Гальперин, В. Я. Кузнецов, Ю. А. Маслеников, В. Е. Панкин, В. П. Цветов, А. И. Боровской. (1980). Микро-ЭВМ "Электроника С5" и их применение [The microcomputer "Elektronika S5" and its application]. Массовая библиотека инженера «Электроника» (in Russian). Moscow: Советское радио.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Ниссельсон, Л.И. (1989). Цифровые и аналоговые интегральные микросхемы (in Russian). Радио и связь. ISBN 5256002597.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 "Soviet microprocessors, microcontrollers, FPU chips and their western analogs". www.cpu-world.com. Retrieved 24 March 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Нефедов, А.В. (2002). Интегральные микросхемы и их зарубежные аналоги. Том 06. Серии К565-К599 [Integrated circuits and their foreign equivalents. Volume 06. Series K565-K599.] (in Russian). Moscow: ИП РадиоСофт. ISBN 5-93037-039-7 . Retrieved 4 October 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Титов М.А., Веревкин А.Ю., Валерьянов В.И. (1994). Изделия электронной техники. Микропроцессоры и однокристальные микроЭВМ [Electronic products. Microprocessors and single-chip microcomputers] (in Russian). Moscow: Радио и связь. ISBN 5-256-01144-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 "Микросхемы вычислительных средств, включая микропроцессоры, микроЭВМ, цифровые процессоры обработки сигналов и контроллеры" [Integrated circuits for computing devices, including microprocessors, microcomputers, digital signal processors, and controllers]. promvpk.ru (in Russian). Promelektronika VPK. Archived from the original on 28 March 2017. Retrieved 25 October 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Микросхемы ПАО Микрон 2020" [Integrated Circuits PAO Mikron 2020](PDF) (in Russian). Mikron. Retrieved 16 February 2021.
- ↑ "К586ВЕ1" [K586VE1](PDF). silirium.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 20 December 2018.
- 1 2 3 "Микроконтроллеры и супервизоры питания Серии 1880; 1881; 1842; 588; 1345; 5518АП1ТБМ" [Microcontrollers and Power Supervisors Series 1880; 1881; 1842; 588; 1345; 5518AP1TBM]. integral.by (in Russian). Minsk: OAO "Integral". Retrieved 6 January 2017.
- 1 2 3 "Руководства" [Manuals]. transistor.by (in Russian). Minsk: "Transistor" branch of OAO "Integral". Archived from the original on 27 March 2015. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ↑ "Музей электронных раритетов - Актив - 4.К602ВМ1".
- 1 2 Нефедов, А.В. (2000). Интегральные микросхемы и их зарубежные аналоги. Том 07. Серии К700-К1043 [Integrated circuits and their foreign equivalents. Volume 07. Series K700-K1043.] (in Russian). Moscow: ИП РадиоСофт. ISBN 5-93037-003-6 . Retrieved 21 October 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 Нефедов, А.В. (2001). Интегральные микросхемы и их зарубежные аналоги. Том 11. Серии К1564-К1814 [Integrated circuits and their foreign equivalents. Volume 11. Series K1564-K1814.] (in Russian). Moscow: ИП РадиоСофт. ISBN 5-93037-049-4 . Retrieved 21 October 2016.
- ↑ "К1801ВЕ1 Однокристальная микро-ЭВМ" [Single-chip microcontroller K1801VE1](PDF). ic-info.ru (in Russian). Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Шахнова, В. А. (1988). Микропроцессоры и микропроцессорные комплекты интегральных микросхем: Справочник. В 2-х т. Том 2 [Microprocessors and microprocessor chip sets: A reference. In 2 volumes. Vol. 2] (in Russian). Moscow: Радио и связь. ISBN 5-256-00373-9 . Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- ↑ "Каталог изделий 2021" [Product catalog 2021](PDF) (in Russian). Voronezh: OAO "VZPP-S". Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 "Изделия отечественного производства" [Domestic products]. spels.ru (in Russian). Moscow: AO "ENPO SPELS". Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- ↑ "The Electronika MK1 red3 PDP-11 Chipset and Tetris". cpushack.com. 6 September 2015. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 Нефедов, А.В. (2001). Интегральные микросхемы и их зарубежные аналоги. Том 12. Серии К1815-К6501 [Integrated circuits and their foreign equivalents. Volume 12. Series K1815-K6501.] (in Russian). Moscow: ИП РадиоСофт. ISBN 5-93037-053-2 . Retrieved 21 October 2016.
- ↑ "Микропроцессорный комплект М1821" [Microprocessor system M1821]. nzpp.ru (in Russian). Novosibirsk: AO NZPP. Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ↑ "The Soviet CMOS 8085 CPU: 1821VM85A". cpushack.com. 24 August 2022. Retrieved 8 December 2022.
- ↑ "Продукция" [Products]. sapfir.ru (in Russian). Moscow: PAO NPP "Sapfir". Retrieved 31 May 2016.
- ↑ "Спецстойкие КМОП КНС СБИС Каталог 2016" [Hardened silicon-on-sapphire CMOS VLSI catalog 2016](PDF) (in Russian). Zelenograd: Angstrem. Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 October 2018. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 "Микропроцессоры и микроконтроллеры" [Microprocessors and microcontrollers]. mvc-nn.ru (in Russian). Nizhny Novgorod: MVC. 2014. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Интегральные микросхемы" [Integrated circuits]. niiet.ru (in Russian). Voronezh: OAO "NIIET". Retrieved 30 March 2021.
- ↑ "КФ1835ВЕ3 – универсальный 16-разрядный микроконтроллер". Радиолюбитель (in Russian). July 1998. pp. 41–43. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- ↑ "МикроЭВМ КА/КР1835ВЕ39(49)". Радиолюбитель (in Russian). May 1993. p. 47. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- ↑ "Микропроцессор КР1835ВМ86". Радиолюбитель (in Russian). May 1993. p. 46. Retrieved 19 April 2016.
- ↑ "32-разрядный VAX-11/750-совместимый микропроцессорный комплект" [32-bit VAX-11/750-compatible microprocessor series] (in Russian). Zelenograd: Angstrem. Archived from the original on 11 April 2021. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
- ↑ "Микроконтроллеры" [Microcontrollers]. nzpp.ru (in Russian). Novosibirsk: AO NZPP. Retrieved 2021-03-19.
- ↑ "КР1858ВМ3" [KR1858VM3]. transistor.by (in Russian). Minsk: "Transistor" branch of OAO "Integral". Archived from the original on 27 March 2015. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ↑ "Микросхема КФ1869ВЕ1" [The integrated circuit KF1869VE1]. Радиолюбитель (in Russian). November 1994. pp. 46–48. Retrieved 7 November 2016.
- ↑ "Универсальная 4-разрядная микро-ЭВМ КФ1869ВЕ2 для бытовой аппаратуры". Радиолюбитель (in Russian). July 1994. pp. 46–47. Retrieved 27 March 2016.
- ↑ "КН1871ВЕ1" [KN1871VE1](PDF). chipfind.ru (in Russian). Zelenograd: Angstrem . Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ↑ "Каталог продукции" [Product catalog]. svetpol.ru (in Russian). Saint Petersburg: ZAO Svetlana Semiconductors . Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ↑ "Л1876" [L1876](PDF). chipfind.ru (in Russian). Zelenograd: Angstrem . Retrieved 28 March 2016.
- ↑ "32-разрядный RISC микропроцессорный комплект" [32-bit microprocessor family]. angstrem.ru (in Russian). Zelenograd: Angstrem. Archived from the original on 7 July 2011. Retrieved 22 November 2016.
- ↑ "Разработка микропроцессоров" [Microprocessor development]. niisi.ru (in Russian). Moscow: NIISI. Archived from the original on 21 February 2001. Retrieved 12 September 2016.
- ↑ "8-разрядный микроконтроллер с архитектурой Тесей" [8-bit microcontroller architecture Theseus] (in Russian). Zelenograd: Angstrem. Archived from the original on 11 April 2021. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 "Микроэлектроника" [Microelectronics] (in Russian). NTC Module. Retrieved 20 April 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Каталог продукции группы компаний "Миландр" 2017" [Product catalog of the Milandr Group 2017](PDF). milandr.ru (in Russian). Moscow: PKK Milandr. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 October 2017. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- ↑ "Milandr K1886VE: The PIC That Went to Russia". cpushack.com. 10 March 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 "Разработка СБИС - Развитие микропроцессоров с архитектурой КОМДИВ" [VLSI development - Development of microprocessors using the KOMDIV architecture]. niisi.ru (in Russian). Moscow: NIISI . Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- 1 2 "Микропроцессоры и СБИС" [Microprocessors and VLSI] (in Russian). Moscow: MCST . Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- 1 2 "Микросхемы" [Integrated circuits] (in Russian). Zelenograd: Elvees Multicore. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ↑ "Микроконтроллеры" [Microcontrollers]. zntc.ru (in Russian). Zelenograd: ZNTC. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- ↑ "16-bit Microcontrollers". www.idm-plus.ru. Zelenograd: IDM-PLUS. Archived from the original on 16 November 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- 1 2 "Российская технологическая платформа МЕМС, разработка и производство СБИС для интеллектуальных датчиков" [A Russian MEMS technology platform; development and production of VLSI IC for intelligent sensors](PDF). mes-conference.ru (in Russian). Zelenograd: ZNTC. 2016. Retrieved 20 October 2017.
- ↑ "Двухъядерный микроконтроллер компании "Миландр" для высоконадёжных применений" [Dual-core microcontroller from Company "Milandr" for high-reliability applications](PDF). milandr.ru (in Russian). Moscow: PKK Milandr. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- ↑ "1903ВЕ91Т НИИЭТ 16-разрядные микроконтроллер" [16-bit microcontroller 1903VE91T from NIIET] (in Russian). Catalog Tomsk. Archived from the original on 10 May 2017. Retrieved 27 September 2022.
- ↑ "Новые разработки ИМС" [Newly developed ICs]. niiet.ru (in Russian). Voronesh: NIIET. Archived from the original on 18 March 2009. Retrieved 28 November 2016.
- 1 2 3 "Радиационно стойкие процессоры" [Radiation-resistant processors] (in Russian). Nizhny Novgorod: NIIIS. Retrieved 28 April 2020.
- ↑ "GLONASS module Geos-3 : Weekend die-shot". zeptobars.com. Zeptobars. 24 March 2013. Retrieved 12 May 2017.
- ↑ "IDM+". www.idm-plus.ru. Zelenograd: IDM-PLUS. Archived from the original on 14 April 2018. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ↑ "СБИС К1917ВА014" [VLSI K1917VA014]. mri-progress.ru (in Russian). Moscow: Progress. Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- ↑ "КАТАЛОГ ИНТЕГРАЛЬНЫЕ МИКРОСХЕМЫ" [Catalog of integrated circuits](PDF) (in Russian). Voronezh: OAO "NIIET". 2022. Retrieved 26 September 2022.
- ↑ "Микросхема процессора цифровой обработки сигналов с ОЗУ 12 Мбит и тактовой частотой 300 МГц 1967ВЦ3Т" [Digital signal processor with 12 MBit RAM and 300 MHz clock 1967VTs3T](PDF). milandr.ru (in Russian). Moscow: PKK Milandr. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 April 2016. Retrieved 16 January 2017.
- ↑ "Микросхема 32-разрядного однокристального микро-ЭВМ с памятью Flash-типа 1986ВЕ9ху" [32-bit single-chip microcomputer with Flash memory 1986VE9xy](PDF). terraelectronica.ru (in Russian). Moscow: PKK Milandr. Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- ↑ "Milandr K1986VE91T – The ARM of Russia". cpushack.com. 19 February 2017. Retrieved 12 April 2017.
- ↑ "МИКРОСХЕМА ИНТЕГРАЛЬНАЯ КА5001ВК1А - Руководство пользователя" [Integrated circuit KA5001VK1A - User's manual](PDF) (in Russian). Voronezh: OAO "NIIET". Retrieved 31 March 2021.
- ↑ "КБ5004ВЕ1 Микроконтроллер интеллектуальной карты" [Microcontroller for intelligent cards KB5004VE1] (in Russian). Zelenograd: Angstrem. Archived from the original on 3 February 2020. Retrieved 23 September 2022.
- 1 2 "Каталог продукции" [Product catalog](PDF) (in Russian). Zelenograd: Angstrem. 2022. Retrieved 22 September 2022.
- ↑ "Микроконтроллеры" [Microcontrollers] (in Russian). Zelenograd: AO Design Centre Soyuz. Retrieved 24 April 2020.
- 1 2 "Каталог продукции 2021" [Product catalog 2021](PDF) (in Russian). Zelenograd: AO Design Centre Soyuz. Retrieved 2021-03-15.
- ↑ "KVARC 32bit MPU with Android KitKat and Linux". km211.com. Zelenograd: KM211. Archived from the original on 24 July 2017. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- 1 2 Yu. Zavalin (2015). "ПОЛУЗАКАЗНЫЕ СнК – ОСНОВА МЕЛКОСЕРИЙНОГО ПРОИЗВОДСТВА СБИС СПЕЦИАЛЬНОГО НАЗНАЧЕНИЯ" [Semi-custom SoC for the production of small-volume VLSI for special applications](PDF). ElectronicsЭЛЕКТРОНИКА (in Russian). No. 9. Technosphera. ISSN 1992-4178 . Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ↑ "ОСВАИВАЕМЫЕ МИКРОСХЕМЫ" [Integrated circuits to be developed]. sktbes.com (in Russian). Voronesh: SKTB ES. Retrieved 29 March 2018.
- ↑ "5539ТР026 и 5539ТР016" [5539TR026 and 5539TR016] (in Russian). Progress. Retrieved 23 April 2020.
- ↑ "Однокристальные микро-эвм" [Single-chip microcomputers]. krystall.net.ua (in Russian). Kiev: Kristall. Archived from the original on 30 May 2012. Retrieved 5 January 2017.