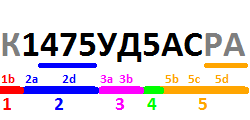
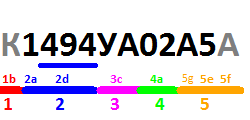
| Group | Description | Example [6] [24] [25] |
|---|
| Russian | English | 1968 | 1973 | 1980 | 2000 | Original | Equivalent |
|---|
| А | A | | Pulse shapers and drivers |
|---|
| АА | AA | — | Address line drivers (esp. for magnetic-core memory) | К170АА7 | SN75327 |
| АГ | AG | — | Square wave pulse shapers (including monostable multivibrators) | К555АГ4 | 74LS221 |
| АИ | AI | — | — | — | Time interval shaper (timer) | 1512АИ1У | |
| АН | AN | — | — | — | Voltage pulse shaper | | |
| АП | AP | — | Other pulse shapers (e.g. digital buffers including tri-state buffers, bubble memory drivers, CCD drivers) | ЭКР1533АП5 | 74ALS244 |
| АР | AR | — | Bit-line drivers (esp. for magnetic-core memory) | 146АР1 | |
| АТ | AT | — | — | — | Current pulse shaper | | |
| АФ | AF | — | Pulse shapers for special waveforms | К174АФ5 | |
| Б | B | | Delay devices [a] | Array of cells |
|---|
| БА | BA | — | — | — | Array of analogue cells [b] | Н1451БА1У-А502 | |
| БК | BK | — | — | — | Array of mixed-signal cells [c] | 1451БК2У | |
| БМ | BM | — | Passive delay device | — | | |
| БП | BP | — | Other delay device | Other array of cells (e.g. gate array plus processor) | К5512БП1Ф | |
| БР | BR | — | Active delay device (e.g. bucket-brigade device) | — | КА528БР2 | |
| БЦ | BTs, BC | — | — | — | Array of digital cells (gate array) [d] | 5585БЦ1У | |
| В | V | | | Computing devices [e] |
|---|
| ВА | VA | — | — | Bus interface | КР580ВА86 | Intel 8286 |
| ВБ | VB | — | — | Synchronization device (e.g. arbiter) | КР1810ВБ89 | Intel 8289 |
| ВВ | VV | — | — | Input / output interface (e.g. serial or parallel interface) | КР580ВВ55А | Intel 8255 |
| ВГ | VG | — | — | Controller (e.g. memory controller, video display controller) | КР1810ВГ88 | Intel 8288 |
| ВД | VD | — | — | — | Controller with digital inputs and outputs | 1875ВД1Т | Intel 80C186 |
| ВЕ | VE | — | — | Single-chip microcontroller | КМ1816ВЕ48 | Intel 8748 |
| ВЖ | VZh | — | — | Specialized device (e.g. error correction circuit) | К1800ВЖ5 | Motorola MC10905 |
| ВИ | VI | — | — | Timer device, real-time clock | | КР580ВИ53 | Intel 8253 |
| ВК | VK | — | — | Combined device (e.g. bus controller, GPIB controller) | КР580ВК28 | Intel 8228 |
| ВМ | VM | — | — | Microprocessor [f] | КР580ВМ80A | Intel 8080 |
| ВН | VN | — | — | Programmable interrupt controller | КР580ВН59 | Intel 8259 |
| ВП | VP | — | — | Other computing devices (e.g. gate array) | К1801ВП1 | |
| ВР | VR | — | — | Extender for e.g. word size, number of ports, number of interrupt lines, available arithmetic operations (esp. a multiplier) | КМ1804ВР1 | AMD Am2902 |
| ВС | VS | — | — | Microprocessor section, esp. bit-slice | КР1804ВС1 | AMD Am2901 |
| ВТ | VT | — | — | Memory controller | КР1810ВТ37 | Intel 8237 |
| ВУ | VU | — | — | Microcode control device | М1804ВУ4 | AMD Am2909 |
| ВФ | VF | — | — | Data transformation functions (calculation of e.g. CRC, Fourier transform) | | 1815ВФ3 | |
| ВХ | VKh, VX, VH | — | — | Devices for calculators | К145ВХ1 | |
| ВЦ | VTs, VC | — | — | — | Digital signal processor [f] | 1867ВЦ10Т | TMS320F240x |
| ВЮ | VYu | — | — | — | Controller with analogue inputs and outputs | К1055ВЮ1Т | |
| ВЯ | VYa | — | — | — | Digital signal processor with analogue inputs and outputs | 1879ВЯ1Я | |
| Г | G | Signal generators and oscillators |
|---|
| ГГ | GG | — | Square wave generators (including astable multivibrators and blocking oscillators) | КР531ГГ1 | 74S124 |
| ГЛ | GL | — | Sawtooth wave generators (e.g. for CRT deflection circuits) | К174ГЛ1 | TDA1170 |
| ГМ | GM | — | Noise generators | К1316ГМ1У | |
| ГН | GN | — | — | — | Programmable signal generators | 1316ГН2Н4 | |
| ГП | GP | — | Other signal generators | КМ1012ГП1 | MM5555 |
| ГС | GS | Sine wave generators (including harmonic oscillators) | К277ГС1 | |
| ГФ | GF | Signal generators for special waveforms (including generators for multiple waveforms) | К174ГФ2 | XR2206 |
| Д | D | Detectors and demodulators |
|---|
| ДА | DA | Amplitude modulation detectors | 235ДА1 | |
| ДИ | DI | Pulse modulation detectors | | |
| ДК | DK | — | — | — | Frequency-phase modulation detectors | | |
| ДН | DN | — | — | — | Voltage detector (monitor) | К1230ДН1БР | MC34161 |
| ДП | DP | Other detectors | К1230ДП46П | MC34064 |
| ДС | DS | Frequency modulation detectors | К2ДС241 | |
| ДФ | DF | Phase modulation detectors | К1102ДФ1 | MC4044 |
| Е | E | Power supply devices |
|---|
| ЕА | EA | — | — | — | Positive fixed-voltage linear regulator | | |
| ЕВ | EV | — | Rectifiers | К299ЕВ1 | |
| ЕГ | EG | — | — | — | Negative adjustable-voltage linear regulator | 1349ЕГ1У | LM137 |
| ЕД | ED | — | — | — | Dual-polarity symmetric fixed-voltage linear regulator | | |
| ЕЕ | EE | — | — | — | Voltage supervisor, reset circuit | 1363ЕЕ1Т | MAX709L |
| ЕИ | EI | — | — | — | Negative fixed-voltage linear regulator | 1343ЕИ5У | 7905 |
| ЕК | EK | — | — | Switched-mode power supply devices | К1156ЕК1АП | LM2596 |
| ЕЛ | EL | — | — | — | Dual-polarity asymmetric fixed-voltage linear regulator | | |
| ЕМ | EM | — | Electric power conversion devices (e.g. thyristor controller) | | КР1182ЕМ2 | |
| ЕН | EN | Linear voltage regulators | КР142ЕН8А | 7808 |
| ЕП | EP | Other power supply devices (e.g. charge pump devices) | КР1168ЕП1 | ICL7660 |
| ЕР | ER | — | — | — | Positive adjustable-voltage linear regulator | 1325ЕР1У | AMS1117 |
| ЕС | ES | — | — | Power supply systems | | |
| ЕТ | ET | Constant-current sources | УР1101ЕТ51 | TSM1051 |
| ЕУ | EU | — | — | Controller for switched-mode power supplies | КР1033ЕУ2 | TDA4605 |
| ЕФ | EF | — | — | — | Adjustable-voltage switched-mode power supply devices | К1290ЕФ1АП | LM2576-ADJ |
| Ж | Zh | Multi-functional devices [g] |
|---|
| ЖА | ZhA | Analog multi-functional devices [h] | — | — | — | К2ЖА375 | |
| ЖВ | ZhV | Analog and logical multi-functional devices [i] | — | — | — | | |
| ЖЕ | ZhE | Analog and pulse multi-functional devices [i] | — | — | — | | |
| ЖГ | ZhG | Logical and pulse multi-functional devices [j] | — | — | — | К1ЖГ453 | |
| ЖИ | ZhI | Pulse multi-functional devices [j] | — | — | — | | |
| ЖК | ZhK | Analog, logical, and pulse multi-functional devices [i] | — | — | — | | |
| ЖЛ | ZhL | Logical multi-functional devices [j] | — | — | — | K5ЖЛ012 | |
| И | I | Digital circuits |
|---|
| ИА | IA | — | — | Arithmetic logic unit [k] | 1815ИА1 | |
| ИВ | IV | — | Encoder [l] | 1564ИВ3 | 54HC147 |
| ИД | ID | Decoder | КР1533ИД4 | 74ALS155 |
| ИЕ | IE | Counter | 533ИЕ7 | 54LS193 |
| ИК | IK | Combination of digital circuits [e] [k] | К145ИК1901 | |
| ИЛ | IL | Half adder | K5ИЛ011 | |
| ИМ | IM | — | Full adder [m] | КМ155ИМ3 | 6483 |
| ИН | IN | — | — | — | Interface receiver, transmitter, or transceiver | 5559ИН1Т | MAX232 |
| ИП | IP | Other digital circuits (e.g. parity bit checker, multiplier) [k] | К155ИП3 | 74181 |
| ИР | IR | Register, shift register | К561ИР2 | 4015 |
| ИС | IS | Full adder [m] | — | — | — | 1ИС061А | |
| ИФ | IF | — | — | — | Function expander (e.g. multiplier) | 1825ИФ1У | |
| ИШ | ISh | Encoder [l] | — | — | — | К5ИШ011 | |
| К | K | Switches and Multiplexers |
|---|
| КД | KD | Diode-based switch | — | — | — | | |
| КЗ | KZ | Opto-electronic switch | — | — | — | | |
| КН | KN | — | Analogue switches and Multiplexers for voltages [n] | КР590КН1 | |
| КП | KP | Other switches and multiplexers (especially digital; also optocouplers) | К561КП1 | 4052 |
| КТ | KT | Transistor-based switch | Analogue switches and Multiplexers for currents [n] | К561КТ3А | 4066 |
| Л | L | Logic gates |
|---|
| ЛА | LA | — | NAND gates [o] | К155ЛА3 | 7400 |
| ЛБ | LB | NAND gates and NOR gates [o] | К134ЛБ1 | |
| ЛД | LD | — | Expander [p] | К155ЛД1 | 7460 |
| ЛЕ | LE | — | NOR gates [o] | КР1533ЛЕ1 | 74ALS02 |
| ЛИ | LI | AND gates | КР531ЛИ3 | 74S11 |
| ЛК | LK | AND-OR-NOT/AND-OR gates [q] | 199ЛК3 | |
| ЛЛ | LL | OR gates | К555ЛЛ1 | 74LS32 |
| ЛМ | LM | — | OR-NOT/OR gates | 1500ЛМ101 | Fairchild F100101 |
| ЛН | LN | NOT gates | 136ЛН1 | 54L04 |
| ЛП | LP | Expander [p] | Other gates (e.g. XOR gates, majority function gates) [r] | К555ЛП5 | 74LS86 |
| ЛР | LR | AND-OR-NOT gates | КР531ЛР11 | 74S51 |
| ЛС | LS | AND-OR gates [q] | К561ЛС2 | 4019 |
| ЛЭ | LE | Other gates [r] | — | — | — | К1ЛЭ941 | |
| М | M | Modulators |
|---|
| МА | MA | Amplitude modulators (e.g. ring modulator) | КР140МА1 | |
| МИ | MI | Pulse modulators | К854МИ1 | |
| МП | MP | Other modulators (e.g. quadrature amplitude modulator) | 1324МП1У | AD8346 |
| МС | MS | Frequency modulators | 219МС2 | |
| МФ | MF | Phase modulators | К1327МФ1У | |
| Н | N | Arrays of electronic components |
|---|
| НД | ND | Diode array | 542НД1 | |
| НЕ | NE | Capacitor array | 820НЕ1Б | |
| НК | NK | Array with a combination of components | 2НК041 | |
| НП | NP | — | Array of other components | | |
| НР | NR | — | Resistor array [s] | К301НР1А | |
| НС | NS | Resistor array [s] | — | — | — | 3НС011А | |
| НТ | NT | Transistor array | КР198НТ5Б | |
| НФ | NF | — | — | Array with a specific function (e.g. resistor ladder) | 317НФ1 | |
| П | P | Signal converters |
|---|
| ПА | PA | — | Digital-to-analogue converter [t] | КР572ПА7Б | AD7541 |
| ПВ | PV | — | Analogue-to-digital converter [u] | 1108ПВ1 | TDC1013J |
| ПД | PD | Decoding converter (incl. Digital-to-analogue converter [t] ) | Pulse duration converter | К1102ПД1 | |
| ПЕ | PE | — | — | Analogue frequency multiplier | | | |
| ПК | PK | Coding converter (incl. Analogue-to-digital converter [u] ) | — | — | — | К1ПК201 |
| — | — | Analogue frequency divider [v] | К1055ПК1Т1 | |
| ПЛ | PL | — | — | Frequency synthesizer | КР1508ПЛ1 | NJ88C30 |
| ПМ | PM | Signal shape converter | Power converter (including attenuators) | | КР1446ПМ1 | |
| ПН | PN | Voltage converter | Voltage or current converter [w] | К252ПН1 | |
| ПП | PP | Other converter (including photovoltaic optocouplers) | КР572ПП2 | ICL7104 |
| ПР | PR | — | Code converter | К155ПР7 | 74185 |
| ПС | PS | Frequency converter (including frequency mixers, analog multipliers) [x] | К174ПС1 | |
| ПТ | PT | — | — | — | Digital potentiometer | 1315ПТ11Т | AD8400 |
| ПУ | PU | Signal level converter (including impedance matching, logic voltage level shifters) | К561ПУ4 | 4050 |
| ПФ | PF | Phase converter [y] | Functional signal converter (e.g. digital autocorrelator) | 5862ПФ1Н4 | |
| ПЦ | PTs, PC | — | — | Digital frequency divider | К555ПЦ1 | 74LS292 |
| Р | R | | Memory devices [z] |
|---|
| РА | RA | — | Analogue memory | Associative memory | К589РА04 | Intel 3104 |
| РВ | RV | — | Matrix of ROM elements (e.g. diode matrix) [aa] | К539РВ1А | |
| РГ | RG | — | — | — | FIFO [ab] | 1642РГ1РБМ | IDT7205L |
| РД | RD | — | — | — | DRAM [ac] | 1654РД2 | MT48LC4M16A2P |
| РЕ | RE | — | ROM (including PROM) [ad] | Mask ROM [ad] | К155РЕ21 | 74187 |
| РК | RK | — | — | — | Multi-ported RAM (e.g. dual-ported RAM) [ab] | 1642РК1УБМ | IDT7005 |
| РМ | RM | — | Matrix of RAM elements [aa] | К188РМ1 | |
| РН | RN | — | — | — | NVRAM | | |
| РП | RP | — | Other memory devices (e.g. dual-ported RAM) [ab] | Other memory devices | К1800РП6 | Motorola MC10806 |
| РР | RR | — | — | EEPROM [ad] | EEPROM or flash memory with a parallel interface [ae] | КМ1609РР1 | 2816 |
| РС | RS | — | — | — | EEPROM or flash memory with a serial interface [ae] | 1644PC1ATБM | 24FC65 |
| РТ | RT | — | — | PROM [ad] | 530РТ1 | 54S287 |
| РУ | RU | — | RAM (DRAM or SRAM) | SRAM [ac] | КР537РУ16А | 6264 |
| РФ | RF | — | — | EPROM [ad] | КМ573РФ8А | 27256 |
| РЦ | RTs, RC | — | — | Bubble memory | К1602РЦ2Б | |
| С | S | Comparators |
|---|
| СА | SA | Amplitude (signal level) comparator [af] | Voltage comparator | К1401СА1 | LM339 |
| СВ | SV | Timing comparator | К2СВ381 | |
| СК | SK | — | — | Amplitude (signal level) comparator (including sample-and-hold circuits) [af] | КР1100СК3 | LF398 |
| СП | SP | — | Other comparator (especially digital comparator) | Other comparator | К555СП1 | 74LS85 |
| СС | SS | Frequency comparator | К284СС2Б | |
| СФ | SF | Phase comparator [ag] | — | | |
| СЦ | STs | — | — | — | Digital comparator | | |
| Т | T | Triggers / Flip-Flops |
|---|
| ТВ | TV | — | JK flip-flops | К555ТВ6 | 74LS107 |
| ТД | TD | Dynamic flip-flops | | |
| ТК | TK | Combination of triggers / flip-flops | K5TK011 | |
| ТЛ | TL | — | Schmitt triggers [ah] | К555ТЛ2 | 74LS14 |
| ТМ | TM | — | D flip-flops | КР1533ТМ2 | 74ALS74 |
| ТП | TP | — | Other triggers / flip-flops | 290ТП1 | |
| ТР | TR | RS flip-flops | КР1533ТР2 | 74ALS279 |
| ТС | TS | T flip-flops [ai] | — | — | — | 2ТС051 | |
| ТТ | TT | — | T flip-flops [ai] | 6500ТТ1 | |
| ТШ | TSh | Schmitt triggers [ah] | — | — | — | К1ТШ181Г | |
| У | U | Amplifiers |
|---|
| УБ | UB | Video amplifier | — | — | — | К1УБ181Б | |
| — | — | — | Instrumentation amplifier | К1463УБ1Р | |
| УВ | UV | — | Radio frequency (high frequency) amplifier | 171УВ2 | μA733 |
| УГ | UG | — | — | — | Low-noise amplifier | | |
| УД | UD | — | Operational amplifier or Differential amplifier [aj] | Operational amplifier | КР140УД7 | μA741 |
| УЕ | UE | — | Unity gain buffer (e.g. emitter follower) [ak] | КР1436УЕ1 | |
| УИ | UI | Pulse amplifier | КР1054УИ1 | TBA2800 |
| УК | UK | — | — | Wideband amplifier (e.g. video amplifier) | К174УК1 | TCA660 |
| УЛ | UL | — | Read amplifier (e.g. for magnetic core memory, magnetic tape, magnetic disks) | КР1075УЛ1 | TA7784P |
| УМ | UM | — | Indicator amplifier | 564УМ1 | 4054 |
| УН | UN | — | Audio frequency (low frequency) amplifier | КР1438УН2 | LM386 |
| УП | UP | Other amplifier (e.g. log amplifier, limiter, gyrator) | 174УП2 | TL441CN |
| УР | UR | — | Intermediate-frequency amplifier | К174УР1 | TBA120 |
| УС | US | Sine wave amplifier | — | Differential amplifier [aj] | К157УС1 | |
| УТ | UT | DC amplifier [aj] | КР119УТ1 | |
| УУ | UU | — | — | — | Programmable-gain amplifier | К1463УУ1 | AD620 |
| УФ | UF | — | — | — | Functional amplifier (e.g. Log amplifier) | 1313УФ1АУ | |
| УЭ | UE | Unity gain buffer (e.g. emitter follower) [ak] | — | — | — | К2УЭ182 | |
| Ф | F | Filters |
|---|
| ФА | FA | — | — | — | Adaptive filter | | |
| ФБ | FB | — | — | — | Band-pass filter [al] | | |
| ФВ | FV | High-pass filter | 528ФВ1 | |
| ФГ | FG | Band-stop filter [am] | — | — | — | | |
| ФЕ | FE | — | Band-pass filter [al] | — | 811ФЕ1 | |
| ФМ | FM | — | — | — | Programmable filter | | |
| ФН | FN | Low-pass filter | И1146ФН1 | |
| ФП | FP | Band-pass filter [al] | Other filter | КР1146ФП1 | MK5912 |
| ФР | FR | — | Band-stop filter [am] | | |
| ФС | FS | Smoothing filter | — | — | — | | |
| ФУ | FU | — | — | — | Universal filter | 1478ФУ1Т | MAX274 |
| Х | Kh, X, H | | Multi-functional devices [g] |
|---|
| ХА | KhA, XA, HA | — | Analog multi-functional devices [h] | КР1568ХА3 | TDA4555 |
| ХБ | KhB, XB, HB | — | — | — | Multifunctional device for radio, television, tape recorders, displays | К1879ХБ1Я | |
| ХВ | KhV, XV, HV | — | — | — | Multi-functional device for automotive electronics | К1323ХВ1Р | L497B |
| ХД | KhD, XD, HD | — | — | — | Multi-functional device for telecommunications | 1892ХД1Я | |
| ХИ | KhI, XI, HI | — | — | Array of analogue cells [an] | Multi-functional device for photo- and video cameras | | |
| ХК | KhK, XK, HK | — | Combination of multifunctional devices (including mixed-signal multi-functional devices) [i] | КР1051ХК1 | TDA8432 |
| ХЛ | KhL, XL, HL | — | Digital multi-functional devices [j] | КР1568ХЛ2 | TDA3048 |
| ХМ | KhM, XM, HM | — | — | Array of digital cells (gate array) [d] | — | 1515ХМ1 | |
| ХН | KhN, XN, HN | — | — | Array of analogue cells [b] | — | Н1451ХН3-А502 | |
| ХП | KhP, XP, HP | — | Other multi-functional devices (e.g. programmable logic devices) | Other multi-functional devices [ao] | КР1556ХП4 | PAL16R4 |
| ХР | KhR, XR, HR | — | — | — | Multi-functional circuit for household devices | К1331ХР1П | |
| ХС | KhS, XS, HS | — | — | — | Programmable logic devices [ap] | 5577ХС2Т | Actel RH1020 |
| ХТ | KhT, XT, HT | — | — | Array of mixed-signal cells [c] | — | 5515ХТ1У | |
| ХХ | KhKh, XX, HH | — | — | — | Multi-functional devices for power electronics | 1474ХХ3Т | HCPL316J |
| Ц | Ts, C | | | Charge-coupled device image sensors |
|---|
| ЦЛ | TsL, CL | — | — | One-dimensional (linear) image sensor | 1200ЦЛ3 | CCD131 |
| ЦМ | TsM, CM | — | — | Two-dimensional image sensor | К1200ЦМ1 | CCD211 |
| ЦП | TsP, CP | — | — | Other image sensor | | |
| Ч | Ch | | | | Transducers / Sensors |
|---|
| ЧВ | ChV | — | — | — | Humidity sensor | | |
| ЧГ | ChG | — | — | — | Gas sensor | | |
| ЧД | ChD | — | — | — | Pressure sensor | К1245ЧД1Н3 | |
| ЧИ | ChI | — | — | — | Ionizing radiation sensor | | |
| ЧМ | ChM | — | — | — | Mechanical displacement sensor [aq] | 1243ЧМ3Н4 | |
| ЧП | ChP | — | — | — | Other sensor | К5331ЧП01Т | |
| ЧТ | ChT | — | — | — | Temperature sensor [ar] | 1019ЧТ4У | LM135 |
| ЧЭ | ChE | — | — | — | Electromagnetic field sensor | | |
| Ш | Sh | Delay devices [a] | | | |
|---|
| ШП | ShP | Other delay device | — | — | — | | |
| ШС | ShS | Active or passive delay device | — | — | — | | |
| Э | E | | | | Delay devices [a] |
|---|
| ЭМ | EM | — | — | — | Passive delay device | | |
| ЭП | EP | — | — | — | Other delay device | | |
| ЭР | ER | — | — | — | Active delay device (e.g. bucket-brigade device) | | |
| Я | Ya | Memory devices [z] |
|---|
| ЯЛ | YaL | Magnetic memory device | — | — | — | | |
| ЯП | YaP | Other memory device (e.g. RAM or ROM memory element) | — | — | — | K5ЯП011 | |
| ЯМ | YaM | Matrix of memory elements (RAM or ROM) [aa] | — | — | — | К1ЯМ881 | |
|