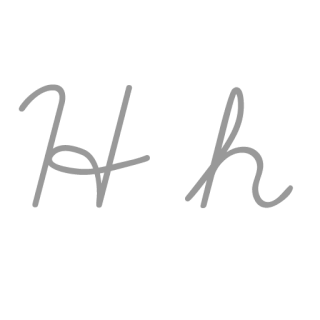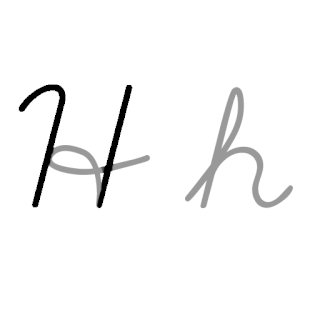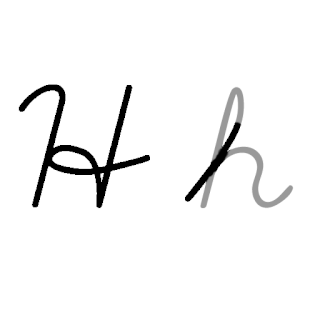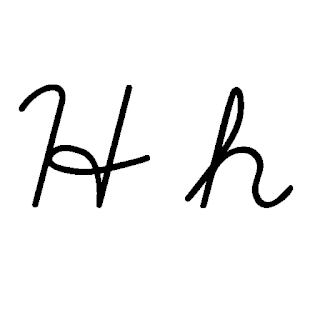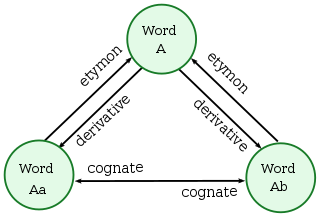
In linguistics, cognates, also called lexical cognates, are words that have a common etymological origin. Cognates are often inherited from a shared parent language, but they may also involve borrowings from some other language. For example, the English words dish, disk and desk, the German word Tisch ("table"), and the Latin word discus ("disk") are cognates because they all come from Ancient Greek δίσκος, which relates to their flat surfaces. Cognates may have evolved similar, different or even opposite meanings, and although there are usually some similar sounds or letters in the words, they may appear to be dissimilar. Some words sound similar, but do not come from the same root; these are called false cognates, while some are truly cognate but differ in meaning; these are called false friends.

In linguistics, the comparative method is a technique for studying the development of languages by performing a feature-by-feature comparison of two or more languages with common descent from a shared ancestor and then extrapolating backwards to infer the properties of that ancestor. The comparative method may be contrasted with the method of internal reconstruction in which the internal development of a single language is inferred by the analysis of features within that language. Ordinarily, both methods are used together to reconstruct prehistoric phases of languages; to fill in gaps in the historical record of a language; to discover the development of phonological, morphological and other linguistic systems and to confirm or to refute hypothesised relationships between languages.

Etruscan was the language of the Etruscan civilization, in Italy, in the ancient region of Etruria. Etruscan influenced Latin but eventually was completely superseded by it. The Etruscans left around 13,000 inscriptions that have been found so far, only a small minority of which are of significant length; some bilingual inscriptions with texts also in Latin, Greek, or Phoenician; and a few dozen loanwords. Attested from 700 BCE to 50 CE, the relation of Etruscan to other languages has been a source of long-running speculation and study, with its being referred to at times as an isolate, one of the Tyrsenian languages, and a number of other less well-known theories.
H, or h, is the eighth letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is aitch, or regionally haitch.

The Italic languages form a branch of the Indo-European language family, whose earliest known members were spoken in the Italian Peninsula in the first millennium BC. The most important of the ancient languages was Latin, the official language of ancient Rome, which conquered the other Italic peoples before the common era. The other Italic languages became extinct in the first centuries AD as their speakers were assimilated into the Roman Empire and shifted to some form of Latin. Between the third and eighth centuries AD, Vulgar Latin diversified into the Romance languages, which are the only Italic languages natively spoken today.

Lydia was an Iron Age kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the modern western Turkish provinces of Uşak, Manisa and inland İzmir. The language of its population, known as Lydian, was a member of the Anatolian branch of Indo-European language family. Its capital was Sardis.

X, or x, is the twenty-fourth and third-to-last letter in the modern English alphabet and the ISO basic Latin alphabet. Its name in English is "ex", plural exes.

The Etruscan civilization of ancient Italy covered a territory, at its greatest extent, of roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria, and northern Lazio, as well as parts of what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto, and Campania.
This is a list of etymological lists.
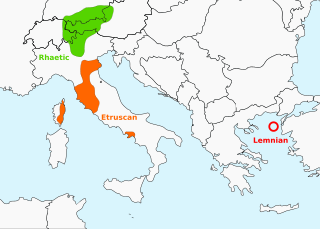
Rhaetic or Raetic, also known as Rhaetian, was a language spoken in the ancient region of Rhaetia in the Eastern Alps in pre-Roman and Roman times. It is documented by around 280 texts dated from the 5th up until the 1st century BC, which were found through Northern Italy, Southern Germany, Eastern Switzerland, Slovenia and Western Austria, in two variants of the Old Italic scripts.

The Faliscan language is the extinct Italic language of the ancient Falisci who lived in Southern Etruria. Together with Latin, it formed the Latino-Faliscan languages group of the Italic languages. It seems probable that the language persisted, being gradually permeated with Latin, until at least 150 BC.
Etruscan numerals are the words and phrases for numbers of the Etruscan language, and the symbols used to write them.
In etymology, two or more words in the same language are called doublets or etymological twins or twinlings when they have different phonological forms but the same etymological root. Often, but not always, the words entered the language through different routes. Given that the kinship between words that have the same root and the same meaning is fairly obvious, the term is mostly used to characterize pairs of words that have diverged at least somewhat in meaning. For example, English pyre and fire are doublets with merely associated meanings despite both descending ultimately from the same Proto-Indo-European (PIE) word *péh₂ur.

Robert Stephen Paul Beekes was a Dutch linguist who was emeritus professor of Comparative Indo-European Linguistics at Leiden University and an author of many monographs on the Proto-Indo-European language.

Tyrsenian, named after the Tyrrhenians, is a proposed extinct family of closely related ancient languages put forward by linguist Helmut Rix (1998), which consists of the Etruscan language of northern, central and south-western Italy, and eastern Corsica (France); the Rhaetic language of the Alps, named after the Rhaetian people; and the Lemnian language of the Aegean Sea. Camunic in northern Lombardy, in between Etruscan and Rhaetic, may belong here too, but the material is very scant. The Tyrsenian languages are generally considered Pre-Indo-European (Paleo-European).
The Pre-Greek substrate consists of the unknown language(s) spoken in prehistoric Greece before the coming of the Proto-Greek language in the area during the Bronze Age. It is possible that Greek acquired some thousand words and proper names from such a language(s), because some of its vocabulary cannot be satisfactorily explained as deriving from Proto-Greek and a Proto-Indo-European reconstruction is almost impossible for such terms.
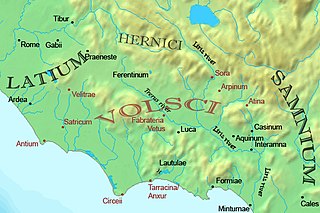
The Latins, sometimes known as the Latians, were an Italic tribe which included the early inhabitants of the city of Rome. From about 1000 BC, the Latins inhabited the small region known to the Romans as Old Latium, that is, the area between the river Tiber and the promontory of Mount Circeo 100 km (62 mi) southeast of Rome. Following the Roman expansion, the Latins spread into the Latium adiectum, inhabited by Osco-Umbrian peoples.

Paleo-Sardinian, also known as Proto-Sardinian or Nuragic, is an extinct language, or perhaps set of languages, spoken on the Mediterranean island of Sardinia by the ancient Sardinian population during the Nuragic era. Starting from the Roman conquest with the establishment of a specific province, a process of language shift took place wherein Latin came slowly to be the only language spoken by the islanders. Paleo-Sardinian is thought to have left traces in the island's onomastics as well as toponyms, which appear to preserve grammatical suffixes, and a number of words in the modern Sardinian language.