A hobby is considered to be a regular activity that is done for enjoyment, typically during one's leisure time. Hobbies include collecting themed items and objects, engaging in creative and artistic pursuits, playing sports, or pursuing other amusements. Participation in hobbies encourages acquiring substantial skills and knowledge in that area. A list of hobbies changes with renewed interests and developing fashions, making it diverse and lengthy. Hobbies tend to follow trends in society. For example, stamp collecting was popular during the nineteenth and twentieth centuries as postal systems were the main means of communication; as of 2023, video games became more popular following technological advances. The advancing production and technology of the nineteenth century provided workers with more leisure time to engage in hobbies. Because of this, the efforts of people investing in hobbies has increased with time.

Leisure has often been defined as a quality of experience or as free time. Free time is time spent away from business, work, job hunting, domestic chores, and education, as well as necessary activities such as eating and sleeping. Leisure as an experience usually emphasizes dimensions of perceived freedom and choice. It is done for "its own sake", for the quality of experience and involvement. Other classic definitions include Thorstein Veblen's (1899) of "nonproductive consumption of time." Free time is not easy to define due to the multiplicity of approaches used to determine its essence. Different disciplines have definitions reflecting their common issues: for example, sociology on social forces and contexts and psychology as mental and emotional states and conditions. From a research perspective, these approaches have an advantage of being quantifiable and comparable over time and place.
Retirement is the withdrawal from one's position or occupation or from one's active working life. A person may also semi-retire by reducing work hours or workload.
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards and concerns".
A health system, health care system or healthcare system is an organization of people, institutions, and resources that delivers health care services to meet the health needs of target populations.
An economic indicator is a statistic about an economic activity. Economic indicators allow analysis of economic performance and predictions of future performance. One application of economic indicators is the study of business cycles. Economic indicators include various indices, earnings reports, and economic summaries: for example, the unemployment rate, quits rate, housing starts, consumer price index, Inverted yield curve, consumer leverage ratio, industrial production, bankruptcies, gross domestic product, broadband internet penetration, retail sales, price index, and changes in credit conditions.
Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. Health can be promoted by encouraging healthful activities, such as regular physical exercise and adequate sleep, and by reducing or avoiding unhealthful activities or situations, such as smoking or excessive stress. Some factors affecting health are due to individual choices, such as whether to engage in a high-risk behavior, while others are due to structural causes, such as whether the society is arranged in a way that makes it easier or harder for people to get necessary healthcare services. Still, other factors are beyond both individual and group choices, such as genetic disorders.

Personal life is the course or state of an individual's life, especially when viewed as the sum of personal choices contributing to one's personal identity.

Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. The term includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health.

Personal finance is the financial management that an individual or a family unit performs to budget, save, and spend monetary resources over time, taking into account various financial risks and future life events.

The healthcare industry is an aggregation and integration of sectors within the economic system that provides goods and services to treat patients with curative, preventive, rehabilitative, and palliative care. It encompasses the creation and commercialization of products and services conducive to the preservation and restoration of well-being. The contemporary healthcare sector comprises three fundamental facets, namely services, products, and finance. It can be further subdivided into numerous sectors and categories and relies on interdisciplinary teams of highly skilled professionals and paraprofessionals to address the healthcare requirements of both individuals and communities.
Youth is the time of life when one is young. The word, youth, can also mean the time between childhood and adulthood (maturity), but it can also refer to one's peak, in terms of health or the period of life known as being a young adult. Youth is also defined as "the appearance, freshness, vigor, spirit, etc., characteristic of one, who is young". Its definitions of a specific age range varies, as youth is not defined chronologically as a stage that can be tied to specific age ranges; nor can its end point be linked to specific activities, such as taking unpaid work, or having sexual relations.

Working (laboring) time is the period of time that a person spends at paid labor. Unpaid labor such as personal housework or caring for children or pets is not considered part of the working week.

Human behavior is the potential and expressed capacity of human individuals or groups to respond to internal and external stimuli throughout their life. Behavior is driven by genetic and environmental factors that affect an individual. Behavior is also driven, in part, by thoughts and feelings, which provide insight into individual psyche, revealing such things as attitudes and values. Human behavior is shaped by psychological traits, as personality types vary from person to person, producing different actions and behavior.

Financial literacy is the possession of skills, knowledge, and behaviors that allow an individual to make informed decisions regarding money. Financial literacy, financial education and financial knowledge are used interchangeably. Financially unsophisticated individuals cannot plan financially because of their poor financial knowledge. Financially sophisticated individuals are good at financial calculations; for example they understand compound interest, which helps them to engage in low-credit borrowing. Most of the time, unsophisticated individuals pay high costs for their debt borrowing.
The economics of happiness or happiness economics is the theoretical, qualitative and quantitative study of happiness and quality of life, including positive and negative affects, well-being, life satisfaction and related concepts – typically tying economics more closely than usual with other social sciences, like sociology and psychology, as well as physical health. It typically treats subjective happiness-related measures, as well as more objective quality of life indices, rather than wealth, income or profit, as something to be maximized.

Play is a range of intrinsically motivated activities done for recreational pleasure and enjoyment. Play is commonly associated with children and juvenile-level activities, but may be engaged in at any life stage, and among other higher-functioning animals as well, most notably mammals and birds.

Official statistics are statistics published by government agencies or other public bodies such as international organizations as a public good. They provide quantitative or qualitative information on all major areas of citizens' lives, such as economic and social development, living conditions, health, education, and the environment.
Multiple sex partners is the measure and incidence of engaging in sexual activities with two or more people within a specific time period. Sexual activity with MSP can happen simultaneously or serially. MSP includes sexual activity between people of a different gender or the same gender. A person can be said to have multiple sex partners, when the person have sex with more than one person at the same time. Another term, polyamorous, is a behavior and not a measure describing multiple romantically sexually or romantically committed relationships at the same time.
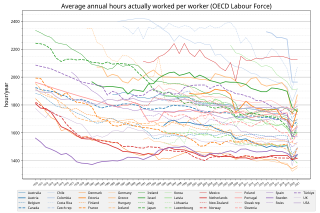
South Korea has been a society that could not guarantee work–life balance historically and legally. But work–life balance in South Korea advanced when Warabel emerged as a neologism, changing the perception of people's work and their basic rights. There are two major movements: improving law and improving people's perceptions.