Example

The geography and climate of Bolivia has led to the formation a wide variety of lakes, from salt saturated lakes in the Altiplano to oxbow lakes in the eastern lowlands. Many of Bolivias lakes are formed only seasonally during the austral summer and remains for the rest of the year as salt flats in the altiplano or swamps in the eastern lowlands.
All major lakes in the Altiplano belong to the same endorheic basin that when supplied with enough water ends at Salar de Uyuni. Many of the lakes in the altiplano show large fluctuations in area like Poopó Lake that has dried up several times through history. The salt flats of Coipasa and Uyuni have only very small surfaces where water can be observed through all year but are covered each year in summer by up to one meter of water.
| Name | Area (km²) | Surface elevation | Max depth | Salinity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titicaca | 3,790 [i 1] | 3,810 m.a.s.l. | 281 m | Brackish |
| Poopó Lake | 1,000 | 3,686 m.a.s.l. | Brackish | |
| Salar de Coipasa | 2,218 | 3,657 m.a.s.l. | - | Saturated in salt |
| Salar de Uyuni | 10,582 | 3,663 m.a.s.l. | - | Saturated in salt |
| Uru Uru | 214 | 3,686 m.a.s.l. | 1.5 m | Brackish to salt |
| Name | Area | Surface elevation | Max depth | Salinity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huaytunas | 329.5 km² | 146 m.a.s.l. | - | Fresh |
| Rogaguado | 315 km² | 143 m.a.s.l. | - | Fresh |
| Rogagua | 155.6 km² | 164 m.a.s.l. | - | Fresh |
| Guachuna | 102.8 km² | 150 m.a.s.l. | - | Fresh |
| El Océano | 100 km² | - | - | Fresh |
| Name | Elevation | Area | Department |
|---|---|---|---|
| Achiri Lake | 3,876 m (12,717 ft) | 2.8 km2 (1.1 sq mi) | La Paz |
| Alalay Lake | 3,686 m (12,093 ft) | 2.4 km2 (0.93 sq mi) | Cochabamba |
| Allqa Quta | 4,537 m (14,885 ft) | La Paz | |
| Aquiles Lake | 224 m (735 ft) | 19 km2 (7.3 sq mi) | Beni |
| Araré Lake | 160 m (520 ft) | 68 km2 (26 sq mi) | Beni |
| Aricare Lake | 180 m (590 ft) | 10.33 km2 (3.99 sq mi) | Beni |
| Awallamaya Lake | 3,825 m (12,549 ft) | 96 km2 (37 sq mi) | La Paz |
| Bahia Toco Largo Lake | 165 m (541 ft) | 6.5 km2 (2.5 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Bellavista Lake | 200 m (660 ft) | 24.8 km2 (9.6 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Bolivia Lake | 166 m (545 ft) | 11 km2 (4.2 sq mi) | Beni |
| Bravo Lake | 167 m (548 ft) | 25.7 km2 (9.9 sq mi) | Beni |
| Buenos Aires Lake (Bolivia) | 206 m (676 ft) | 7.6 km2 (2.9 sq mi) | Beni |
| Cáceres Lake | 150 m (490 ft) | 26.5 to 200 km2 (10.2 to 77.2 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Cacha Lake | 4,670 m (15,320 ft) | 0.72 km2 (0.28 sq mi) | La Paz |
| Cachimbo Lake | 196 m (643 ft) | 26.56 km2 (10.25 sq mi) | Beni |
| Carreras Lake | 135 m (443 ft) | 13 km2 (5.0 sq mi) | Beni |
| Ch'alla Quta | ≈ 4,700 m (15,400 ft) | La Paz | |
| Chaplín Lake | 190 m (620 ft) | 13 km2 (5.0 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Chilata Lake | 5,030 m (16,500 ft) | 0.05 km2 (0.019 sq mi) | La Paz |
| Chillwa Quta | ≈ 4,300 m (14,100 ft) | La Paz | |
| Ch'iyar Quta (La Paz) | 4,700 m (15,400 ft) | La Paz | |
| Ch'uxña Quta (Charasani) | 4,454 m (14,613 ft) | La Paz | |
| Ch'uxña Quta (Curva) | 5,543 m (18,186 ft) | La Paz | |
| Ch'uxña Quta (Murillo) | 4,960 m (16,270 ft) | La Paz | |
| Coipasa Lake | 3,657 m (11,998 ft) | 806 km2 (311 sq mi) | Oruro |
| Cololo Lake | 4,538 m (14,888 ft) | 5.2 km2 (2.0 sq mi) | La Paz |
| Colorado Lake | 4,278 m (14,035 ft) | 15.93 km2 (6.15 sq mi) | Beni |
| Concepción Lake | 248 m (814 ft) | 158 km2 (61 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Consuelo Lake | 2.6 km2 (1.0 sq mi) | Santa Cruz | |
| Corani Lake | 18 km2 (6.9 sq mi) | Cochabamba | |
| Coranto Lake | 4,382 m (14,377 ft) | 7.6 km2 (2.9 sq mi) | Potosí |
| Coruto Lake | 4,505 m (14,780 ft) | 15.8 km2 (6.1 sq mi) | Potosí |
| El Encanto Lake | 170 m (560 ft) | 4.5 km2 (1.7 sq mi) | Beni |
| El Océano Lake | 100 km2 (39 sq mi) | Beni | |
| El Triunfo Lake | 19.3 km2 (7.5 sq mi) | Beni | |
| España Lake | 34 km2 (13 sq mi) | Santa Cruz | |
| Francia Lake | 5.6 km2 (2.2 sq mi) | Beni | |
| Guachuna Lake | 150 m (490 ft) | 102.8 km2 (39.7 sq mi) | Beni |
| Guayaques Lake | 1.43 km2 (0.55 sq mi) | Potosí | |
| Huachi Lake | 173 m (568 ft) | 67 km2 (26 sq mi) | Beni |
| Huaytunas Lake | 146 m (479 ft) | 329.5 km2 (127.2 sq mi) | Beni |
| Isirere Lake | 258 m (846 ft) | 19.3 km2 (7.5 sq mi) | Beni |
| Jach'a Quta (Aroma) | La Paz | ||
| Jach'a Quta (Murillo) | 3,760 m (12,340 ft) | La Paz | |
| Jach'a Quta (Sud Yungas) | La Paz | ||
| Janq'u Qala Lake | 4,489 m (14,728 ft) | La Paz | |
| Janq'u Quta (Batallas) | 4,940 m (16,210 ft) | La Paz | |
| Janq'u Quta (El Alto) | 4,664 m (15,302 ft) | 1.8 km2 (0.69 sq mi) | La Paz |
| Janq'u Quta (Larecaja) | La Paz | ||
| Jara Lake | 191 m (627 ft) | 16.5 km2 (6.4 sq mi) | Beni |
| Jayu Quta (Carangas) | 7.83 km2 (3.02 sq mi) | Oruro | |
| Juri Quta (Batallas) | 4,596 m (15,079 ft) | La Paz | |
| Juri Quta (Pukarani) | 4,932 m (16,181 ft) | La Paz | |
| Kalina Lake | 4,525 m (14,846 ft) | 20.6 km2 (8.0 sq mi) | Potosí |
| Kara Lake | 4,522 m (14,836 ft) | 13 km2 (5.0 sq mi) | Potosí |
| K'ayrani Quta | La Paz | ||
| K'iski Quta | La Paz | ||
| La Angostura Lake | 2,700 m (8,900 ft) | 10.5 km2 (4.1 sq mi) | Cochabamba |
| La Gaiba Lake | 160 m (520 ft) | 98 km2 (38 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| La Laguna Lake | 2,926 m (9,600 ft) | 7.8 km2 (3.0 sq mi) | Chuquisaca |
| La Porfía Lake | 58.5 km2 (22.6 sq mi) | Beni | |
| La Sarca Lake | 136 m (446 ft) | 26 km2 (10 sq mi) | Beni |
| Laguna Azul (Bolivia) | 6.1 km2 (2.4 sq mi) | Beni | |
| Laguna Celeste | 4,529 m (14,859 ft) | 2.3 km2 (0.89 sq mi) | Potosí |
| Laguna Glaciar | 5,038 m (16,529 ft) | 0.2 km2 (0.077 sq mi) | La Paz |
| Laguna Grande (Bolivia) | 3,638 m (11,936 ft) | 6.7 km2 (2.6 sq mi) | Tarija |
| Laguna Hedionda (Sud Lípez) | 4,532 m (14,869 ft) | 3.2 km2 (1.2 sq mi) | Potosí |
| Laguna Larga (Bolivia) | 148 m (486 ft) | 100 km2 (39 sq mi) | Beni |
| Laguna Verde (Beni) | 175 m (574 ft) | 4.53 km2 (1.75 sq mi) | Beni |
| Laguna Verde (Comarapa) | 2,419 m (7,936 ft) | 0.002 km2 (0.00077 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Laguna Victoria | 201 m (659 ft) | 25 km2 (9.7 sq mi) | Beni |
| Laram Quta (El Alto) | 4,556 m (14,948 ft) | La Paz | |
| Laram Quta (Inquisivi) | 4,862 m (15,951 ft) | La Paz | |
| Laram Quta (La Paz) | La Paz | ||
| Laram Quta (Los Andes) | 3,850 m (12,630 ft) | La Paz | |
| Laram Quta (Sud Yungas) | La Paz | ||
| Larati Lake | 3,585 m (11,762 ft) | 1.36 km2 (0.53 sq mi) | Cochabamba |
| Las Habras Lake | 136 m (446 ft) | 73 km2 (28 sq mi) | Beni |
| Lawrawani Lake | 4,475 m (14,682 ft) | La Paz | |
| Luru Mayu Lake | 4,666 m (15,308 ft) | 12 km2 (4.6 sq mi) | Potosí |
| Mancornadas Lake | 163 m (535 ft) | 74.16 km2 (28.63 sq mi) | Beni |
| Mandioré Lake | 90 m (300 ft) | 152 km2 (59 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Maracaibo Lake (Bolivia) | 177 m (581 ft) | 15.8 km2 (6.1 sq mi) | Beni |
| Marfil Lake | 246 m (807 ft) | 97.5 km2 (37.6 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Matuwal Lake | 6.83 km2 (2.64 sq mi) | Beni | |
| Mentiroso Lake | 140 m (460 ft) | 6.9 km2 (2.7 sq mi) | Pando |
| Milluni Lake | 4,565 m (14,977 ft) | 2.37 km2 (0.92 sq mi) | La Paz |
| Mirim Lake (Bolivia) | 15.8 km2 (6.1 sq mi) | Santa Cruz | |
| Murillo Lake | 140 m (460 ft) | 7.6 km2 (2.9 sq mi) | Pando |
| Navidad Lake | 160 m (520 ft) | 22.5 km2 (8.7 sq mi) | Beni |
| Nuevo Mundo Lake | 180 m (590 ft) | 57.7 km2 (22.3 sq mi) | Beni |
| Omoro Lake | 193 m (633 ft) | 6 km2 (2.3 sq mi) | Beni |
| Pajaral Lake | 200 m (660 ft) | 9.3 km2 (3.6 sq mi) | Beni |
| Parina Quta (Bolivia-Peru) | 4,216 m (13,832 ft) | La Paz | |
| Parina Quta (Oruro) | 3,753 m (12,313 ft) | Oruro | |
| Pastos Grandes Lake | 4,330 m (14,210 ft) | 120 km2 (46 sq mi) | Potosí |
| Phaq'u Quta | 4,667 m (15,312 ft) | La Paz | |
| Pistola Lake | 33.52 km2 (12.94 sq mi) | Santa Cruz | |
| Portia Lake | 200 m (660 ft) | 28 km2 (11 sq mi) | Beni |
| Q'ara Quta (La Paz) | 4,400 m (14,400 ft) | La Paz | |
| Rodeo Lake | 3,485 m (11,434 ft) | 0.2 km2 (0.077 sq mi) | Cochabamba |
| Rogagua Lake | 155 km2 (60 sq mi) | Beni | |
| Sajama Lake | 0.3 km2 (0.12 sq mi) | Oruro | |
| San Antonio Lake (Bolivia) | 205 m (673 ft) | 26 km2 (10 sq mi) | Beni |
| San Francisco Lake | 138 m (453 ft) | 12.7 km2 (4.9 sq mi) | Beni |
| San Jorge Lake | 160 m (520 ft) | 68.6 km2 (26.5 sq mi) | Beni |
| San José Lake | 202 m (663 ft) | 14.7 km2 (5.7 sq mi) | Beni |
| San Lorenzo Lake | 178 m (584 ft) | 26.2 km2 (10.1 sq mi) | Beni |
| San Pedro Lake | 207 m (679 ft) | 21.9 km2 (8.5 sq mi) | Beni |
| San Roque Lake (Bolivia) | 190 m (620 ft) | 4.5 km2 (1.7 sq mi) | Beni |
| Sirk'i Quta | 4,814 m (15,794 ft) | La Paz | |
| Suárez Lake | 6 km2 (2.3 sq mi) | Beni | |
| Suches Lake | 4,605 m (15,108 ft) | 14.2 km2 (5.5 sq mi) | La Paz |
| Sura Quta (Wayna Potosí) | 4,491 m (14,734 ft) | La Paz | |
| Taborga Lake | 200 m (660 ft) | 25.5 km2 (9.8 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Tacuaral Lake | 170 m (560 ft) | 16.7 km2 (6.4 sq mi) | Beni |
| T'ala Qucha | Potosí | ||
| Tanguina Lake | 176 m (577 ft) | 14.8 km2 (5.7 sq mi) | Beni |
| Tapada Lake | 206 m (676 ft) | 19.01 km2 (7.34 sq mi) | Beni |
| Taypi Chaka Quta | 4,412 m (14,475 ft) | La Paz | |
| Tejas Lake | 5.41 km2 (2.09 sq mi) | Santa Cruz | |
| Todos Santos Lake | 193 m (633 ft) | 4.12 km2 (1.59 sq mi) | Beni |
| Tumichuqua Lake | 3.4 km2 (1.3 sq mi) | Beni | |
| Uberaba Lake | 190 m (620 ft) | 400 km2 (150 sq mi) | Santa Cruz |
| Urqu Qucha (Bolivia) | Potosí | ||
| Uru Uru Lake | 3,686 m (12,093 ft) | 214 km2 (83 sq mi) | Oruro |
| Ventarrón Lake | 185 m (607 ft) | 2.5 km2 (0.97 sq mi) | Pando |
| Volcán Lake | 0.059 km2 (0.023 sq mi) | Santa Cruz | |
| Wallatani Lake | 4,939 m (16,204 ft) | La Paz | |
| Waña Quta (Cochabamba) | 2,752 m (9,029 ft) | Cochabamba | |
| Waña Quta (La Paz) | 4,761 m (15,620 ft) | La Paz | |
| Warawara Lake (Cochabamba) | 4,105 m (13,468 ft) | Cochabamba | |
| Warawara Lake (Oruro) | Oruro | ||
| Warus Quta (Larecaja) | La Paz | ||
| Warus Quta (Loayza) | La Paz | ||
| Watir Quta | La Paz | ||
| Yusala Lake | 170 m (560 ft) | 13.67 km2 (5.28 sq mi) | Beni |
| Zapaleri Lake | 4,608 m (15,118 ft) | 2 km2 (0.77 sq mi) | Potosí |


The geography of Bolivia includes the Eastern Andes Mountain Range which bisects Bolivia roughly from north to south. To the east of that mountain chain are lowland plains of the Amazon Basin, and to the west is the Altiplano which is a highland plateau where Lake Titicaca is located. Bolivia's geography has features similar to those of Peru which abuts Bolivia's northwest border; like Bolivia, Peru is bisected from north to south by the Eastern Andes Mountains, and these two countries share Lake Titicaca which is the highest navigable lake on Earth. Unlike Peru, however, Bolivia is one of the two landlocked countries in South America, the other being Paraguay which is located along Bolivia's southeast border.

Salar de Uyuni is the world's largest salt flat, or playa, at over 10,000 square kilometres (3,900 sq mi) in area. It is in the Daniel Campos Province in Potosí in southwest Bolivia, near the crest of the Andes at an elevation of 3,656 m (11,995 ft) above sea level.

Natural salt pans or salt flats are flat expanses of ground covered with salt and other minerals, usually shining white under the sun. They are found in deserts and are natural formations.

A dry lake bed, also known as a playa, is a basin or depression that formerly contained a standing surface water body, which disappeared when evaporation processes exceeded recharge. If the floor of a dry lake is covered by deposits of alkaline compounds, it is known as an alkali flat. If covered with salt, it is known as a salt flat.

In geology and physical geography, a plateau, also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides have deep hills. Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, and erosion by water and glaciers. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones.

The Altiplano, Collao or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the area where the Andes are the widest. It is the most extensive area of high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southern parts lie in Chile.

Lake Poopó was a large saline lake in a shallow depression in the Altiplano Mountains in Oruro Department, Bolivia, at an altitude of approximately 3,700 m (12,100 ft). Because the lake was long and wide, it made up the eastern half of the department, known as a mining region in southwest Bolivia. The permanent part of the lake body covered approximately 1,000 square kilometres (390 sq mi) and it was the second-largest lake in the country. The lake received most of its water from the Desaguadero River, which flows from Lake Titicaca at the north end of the Altiplano. Since the lake lacked any major outlet and had a mean depth of less than 3 m (10 ft), the surface area differed greatly seasonally.

Uyuni is a city in the southwest of Bolivia.

Daniel Campos is a province in the north-western parts of the Bolivian Potosí Department. It is named after the poet Daniel Campos who originated from this area. The capital of the province is Llica.

Salar de Atacama is the largest salt flat in Chile. It is located 55 km (34 mi) south of San Pedro de Atacama, is surrounded by mountains, and has no drainage outlets. In the east it is enclosed by the main chain of the Andes, while to the west lies a secondary mountain range of the Andes called Cordillera de Domeyko. Large volcanoes dominate the landscape, including the Licancabur, Acamarachi, Aguas Calientes and the Láscar. The last is one of the most active volcanoes in Chile. All of them are located along the eastern side of the Salar de Atacama, forming a generally north-south trending line of volcanoes that separate it from smaller endorheic basins.

The Norte Grande is one of the five natural regions into which CORFO divided continental Chile in 1950. It borders Peru to the north, the Pacific Ocean to the west, the Altiplano, Bolivia and Argentina to the east, and the Copiapó River to the south, beyond which lies the Norte Chico natural region.

The Central Andean dry puna (NT1001) is an ecoregion in the Montane grasslands and shrublands biome, located in the Andean high plateau, in South America. It is a part of the Puna grassland.

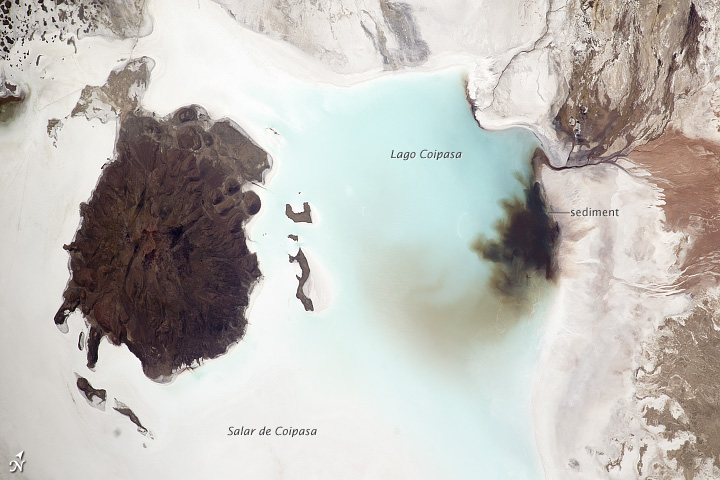
Lago Coipasa or Salar de Coipasa is a lake in Sabaya Province, Oruro Department, Bolivia. At an elevation of 3657 m, its surface area is 806 km². It is on the western part of Altiplano, 20 km north of Salar de Uyuni and south of the main road linking Oruro and Huara (Chile).

Laguna Hedionda is a saline lake in the Nor Lípez Province, Potosí Department in Bolivia. It is notable for various migratory species of pink and white flamingos.

Bolivia is a country with great tourism potential, with many attractions, due to its diverse culture, geographic regions rich history and food. In particular, the salt flats at Uyuni are a major attraction.

The geology of Bolivia comprises a variety of different lithologies as well as tectonic and sedimentary environments. On a synoptic scale, geological units coincide with topographical units. The country is divided into a mountainous western area affected by the subduction processes in the Pacific and an eastern lowlands of stable platforms and shields. The Bolivian Andes is divided into three main ranges; these are from west to east: the Cordillera Occidental that makes up the border to Chile and host several active volcanoes and geothermal areas, Cordillera Central once extensively mined for silver and tin and the relatively low Cordillera Oriental that rather than being a range by its own is the eastern continuation of the Central Cordillera as a fold and thrust belt. Between the Occidental and Central Cordillera the approximately 3,750-meter-high Altiplano high plateau extends. This basin hosts several freshwater lakes, including Lake Titicaca as well as salt-covered dry lakes that bring testimony of past climate changes and lake cycles. The eastern lowlands and sub-Andean zone in Santa Cruz, Chuquisaca, and Tarija Departments was once an old Paleozoic sedimentary basin that hosts valuable hydrocarbon reserves. Further east close to the border with Brazil lies the Guaporé Shield, made up of stable Precambrian crystalline rock.

Tunupa is a dormant volcano in the Potosí Department of southwestern Bolivia.

Lake Minchin is a name of an ancient lake in the Altiplano of South America. It existed where today the Salar de Uyuni, Salar de Coipasa and Lake Poopó lie. It was formerly considered the highest lake in the Altiplano but research indicated that the highest shoreline belongs to the later Lake Tauca instead.

Lake Tauca is a former lake in the Altiplano of Bolivia. It is also known as Lake Pocoyu for its constituent lakes: Lake Poopó, Salar de Coipasa and Salar de Uyuni. The lake covered large parts of the southern Altiplano between the Eastern Cordillera and the Western Cordillera, covering an estimated 48,000 to 80,000 square kilometres of the basins of present-day Lake Poopó and the Salars of Uyuni, Coipasa and adjacent basins. Water levels varied, possibly reaching 3,800 metres (12,500 ft) in altitude. The lake was saline. The lake received water from Lake Titicaca, but whether this contributed most of Tauca's water or only a small amount is controversial; the quantity was sufficient to influence the local climate and depress the underlying terrain with its weight. Diatoms, plants and animals developed in the lake, sometimes forming reef knolls.
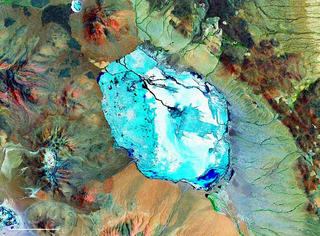
Pastos Grandes is the name of a caldera and its crater lake in Bolivia. The caldera is part of the Altiplano-Puna volcanic complex, a large ignimbrite province that is part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes. Pastos Grandes has erupted a number of ignimbrites through its history, some of which exceeded a volume of 1,000 cubic kilometres (240 cu mi). After the ignimbrite phase, the lava domes of the Cerro Chascon-Runtu Jarita complex were erupted close to the caldera and along faults.