The list of mountains of East Antarctica includes the highest mountains in East Antarctica.
The list of mountains of East Antarctica includes the highest mountains in East Antarctica.
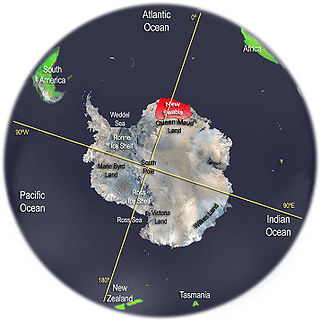
New Swabia was a disputed Antarctic claim by Nazi Germany within the Norwegian territorial claim of Queen Maud Land and is now a cartographic name sometimes given to an area of Antarctica between 20°E and 10°W in Queen Maud Land. New Swabia was explored by Germany in early 1939 and named after that expedition's ship, Schwabenland, itself named after the German region of Swabia.

The Axel Heiberg Glacier in Antarctica is a valley glacier, 30 nmi (35 mi) long, descending from the high elevations of the Antarctic Plateau into the Ross Ice Shelf between the Herbert Range and Mount Don Pedro Christophersen in the Queen Maud Mountains.

Troll is a Norwegian research station located at Jutulsessen, 235 kilometres (146 mi) from the coast in the eastern part of Princess Martha Coast in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It is Norway's only all-year research station in Antarctica, and is supplemented by the summer-only station Tor. Troll is operated by the Norwegian Polar Institute and also features facilities for the Norwegian Meteorological Institute and the Norwegian Institute for Air Research.

Troll Airfield is an airstrip located 6.8 kilometres (4.2 mi) from the research station Troll in Princess Martha Coast in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. Owned and operated by the Norwegian Polar Institute, it consists of a 3,300-by-100-metre runway on glacial blue ice on the Antarctic ice sheet. The airport is located at 1,232 metres (4,042 ft) above mean sea level and is 235 kilometres (146 mi) from the coast.

Tor research station is a Norwegian Antarctic research station in Queen Maud Land.
The Jinnah Antarctic Station is an Antarctic research station operated by the Pakistan Antarctic Programme. Located in East Antarctica, it lies in the vicinity of the Sør Rondane Mountains in Queen Maud Land, and is named after Muhammad Ali Jinnah.

Jøkulkyrkja Mountain, also known as Massiv Yakova Gakkelya, is a broad, ice-topped mountain with several radial rock spurs, standing east of Lunde Glacier in the Mühlig-Hofmann Mountains of Queen Maud Land, East Antarctica. At 3,148 metres (10,328 ft) elevation, it is the highest elevation in Queen Maud Land, and also the highest elevation within the claims of Norway. The mountain is located on the Princess Astrid Coast of the Norwegian Antarctic Territory. Håhellerskarvet, 2,910 metres (9,550 ft), is located to the southwest; the two peaks are separated by the 25-mile-long Lunde Glacier, which flows to the northwest.

Queen Maud Land is a roughly 2.7-million-square-kilometre (1.0-million-square-mile) region of Antarctica claimed by Norway as a dependent territory. It borders the claimed British Antarctic Territory 20° west and the Australian Antarctic Territory 45° east. In addition, a small unclaimed area from 1939 was annexed in June 2015. Positioned in East Antarctica, it makes out about one-fifth of the continent, and is named after the Norwegian queen Maud of Wales (1869–1938).

Norway has three dependent territories, all uninhabited and located in the Southern Hemisphere. Bouvet Island (Bouvetøya) is a sub-Antarctic island in the South Atlantic Ocean. Queen Maud Land is the sector of Antarctica between the 20th meridian west and the 45th meridian east. Peter I Island is a volcanic island located 450 kilometres (280 mi) off the coast of Ellsworth Land of continental Antarctica. Despite being unincorporated areas, neither Svalbard nor Jan Mayen is formally considered a dependency. While the Svalbard Treaty regulates some aspects of that Arctic territory, it acknowledges that the islands are part of Norway. Similarly, Jan Mayen is recognized as an integral part of Norway.

The Orvin Mountains constitute a major group of mountain ranges, extending for about 100 km (62 mi) between the Wohlthat Mountains and the Mühlig-Hofmann Mountains in Queen Maud Land. With its summit at 3,055 metres (10,023 ft), the massive Sandeggtind Peak forms the highest point in the Conrad Mountains, a subrange of the Orvin Mountains.
The Gagarin Mountains are a linear group of mountains, trending in a north–south direction for 10 miles (16 km) between the Kurze Mountains and the Conrad Mountains of the Orvin Mountains in Queen Maud Land, East Antarctica.
Jutulstraumen Glacier is a large glacier in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica, about 120 nautical miles (220 km) long, draining northward to the Fimbul Ice Shelf between the Kirwan Escarpment, Borg Massif and Ahlmann Ridge on the west and the Sverdrup Mountains on the east. It was mapped by Norwegian cartographers from surveys and air photos by the Norwegian–British–Swedish Antarctic Expedition (1949–52) and air photos by the Norwegian expedition (1958–59) and named Jutulstraumen. More specifically jutulen are troll-like figures from Norwegian folk tales. The ice stream reaches speeds of around 4 metres per day near the coast where it is heavily crevassed.

Jutulsessen is a nunatak in the Gjelsvik Mountains in Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It is located in Princess Martha Coast, 235 kilometers (146 mi) from the King Haakon VII Sea. Jutulsessen is the site of the Norwegian research station Troll and the affiliated Troll Satellite Station, which has two radomes on top of the mountain. Troll Airfield is located in the vicinity.

The Gjelsvik Mountains are a group of mountains about 25 nautical miles (50 km) long, between the Sverdrup Mountains and the Mühlig-Hofmann Mountains in Queen Maud Land, East Antarctica. With its summit at 2,705 metres (8,875 ft), the massive Risemedet Mountain forms the highest point in these mountains, also marking their eastern end.

Altarduken Glacier is a small glacier just east of The Altar at the head of Grautskala Cirque, in the Humboldt Mountains of Queen Maud Land, Antarctica. It was discovered and mapped from air photos by the Third German Antarctic Expedition, 1938–39, but was remapped by Norway from air photos and surveys by the Sixth Norwegian Antarctic Expedition, 1956–60, and named Altarduken in association with The Altar.

Research stations in Queen Maud Land are connected by the Dronning Maud Land Air Network Project (DROMLAN), which is a cooperative agreement for transportation between eleven nations with research stations in East Antarctica. Long-range aircraft fly between Cape Town, South Africa and either the Troll Airfield, located at the Troll research station, or the runway at the Novolazarevskaya Station. From these two main airfields, smaller aircraft may fly further to other Antarctic destinations.

Sivorgfjella is the central and largest mountain in the Heimefront Range in Dronning Maud Land. It is separated from the other parts of Heimefrontfjella by Kiberdalen to the south and KK-Dalen to the north. The mountain massif and nunataks cover an area of 1800 km² and the highest point is Paalnibba.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "List of mountains of East Antarctica". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "List of mountains of East Antarctica". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.