
Guerrero is a state in Southwest Mexico that is divided into 85 municipalities. According to the 2020 Mexican census, Guerrero is the 13th most populous state with 3,540,685 inhabitants and the 14th largest by land area spanning 63,803.42 square kilometres (24,634.64 sq mi).

The Oto-Manguean or Otomanguean languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that are now spoken are indigenous to Mexico, but the Manguean branch of the family, which is now extinct, was spoken as far south as Nicaragua and Costa Rica. Oto-Manguean is widely viewed as a proven language family.

The National Museum of Anthropology is a national museum of Mexico. It is the largest and most visited museum in Mexico. Located in the area between Paseo de la Reforma and Mahatma Gandhi Street within Chapultepec Park in Mexico City, the museum contains significant archaeological and anthropological artifacts from Mexico's pre-Columbian heritage, such as the Stone of the Sun and the Aztec Xochipilli statue.
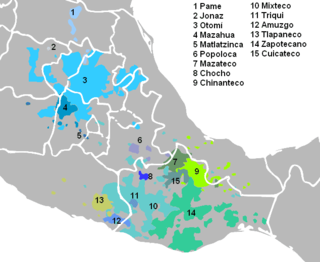
Tlapanec, or Meꞌphaa, is an indigenous Mexican language spoken by more than 98,000 Tlapanec people in the state of Guerrero. Like other Oto-Manguean languages, it is tonal and has complex inflectional morphology. The ethnic group themselves refer to their ethnic identity and language as Me̱ꞌpha̱a̱.
Pseudoeurycea amuzga, which has been given the common name of Sierra de Malinaltepec salamander, is a species of salamander in the family Plethodontidae. It is endemic to Mexico and known only from Sierra de Malinaltepec, a part of Sierra Madre del Sur in the state of Guerrero.
Malinaltepec is a municipality in the Mexican state of Guerrero. The municipality covers an area of 492 km².
Atlatlauca was a Spanish corrigimento during the colonial period of New Spain that existed from 1532 until 1743, in the later year it was merged into Antequera. It included what is today the municipality of San Juan Bautista Atatlahuca

Chilpancingo Airfield ; officially Aeródromo Nicolás Bravo(Nicolás Bravo Aerodrome) is a small airfield located in Chilpancingo, Guerrero, México. It handles domestic air traffic and supports flight training and general aviation activities. The airfield is named in honor of the Mexican President Nicolás Bravo. It does not provide scheduled passenger public services. The nearest airport that serves commercial flights is Acapulco International Airport.

Polistes carnifex, commonly known as the executioner wasp or executioner paper wasp, is a neotropical vespid wasp in the cosmopolitan genus Polistes.

The 2019 Pacific hurricane season was an above average season which produced nineteen named storms, most of which were rather weak and short-lived. Only seven hurricanes formed, the fewest since 2010. The season officially began on May 15 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1 in the Central Pacific; they both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Pacific basin. This season was one of the latest-starting Pacific hurricane seasons on record, with the first tropical cyclone, Hurricane Alvin, forming on June 25. The final system, Tropical Depression Twenty-One-E, dissipated on November 18.
Events of 2019 in Mexico. The article also lists the most important political leaders during the year at both federal and state levels and includes a brief year-end summary of major social and economic issues.
Santa Cruz del Rincón is a municipality in the Mexican state of Guerrero. It is located about 100 kilometres (62 mi) southeast of the state capital of Chilpancingo. Its creation from the municipality of Malinaltepec was approved in 2021 and went into force on 21 May 2022.

The fifth federal electoral district of Guerrero is one of the 300 electoral districts into which Mexico is divided for elections to the federal Chamber of Deputies and one of eight such districts in the state of Guerrero.









