
Metropolitan Manila, commonly shortened to Metro Manila and formally the National Capital Region, is the capital region and largest metropolitan area of the Philippines. Located on the eastern shore of Manila Bay, the region lies between the Central Luzon and Calabarzon regions. Encompassing an area of 636.00 km2 (245.56 sq mi) and with a population of 13,484,462 as of 2020, it consists of sixteen highly urbanized cities: Manila—the capital city—Caloocan, Las Piñas, Makati, Malabon, Mandaluyong, Marikina, Muntinlupa, Navotas, Parañaque, Pasay, Pasig, Quezon City, San Juan, Taguig, and Valenzuela, along with one independent municipality, Pateros. As the second most populous and the most densely populated region in the Philippines, it ranks as the 9th most populous metropolitan area in Asia and the 6th most populous urban area in the world.

Pasay, officially the City of Pasay, is a highly urbanized city in the National Capital Region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 440,656 people.
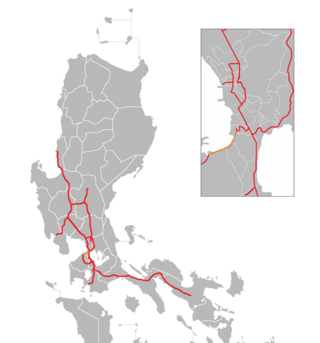
The Manila–Cavite Expressway, signed as E3 of the Philippine expressway network and R-1 of Metro Manila's arterial road network, is a 14-kilometer-long (8.7 mi) controlled-access highway linking Manila to the southern province of Cavite in the Philippines. At its north end, it feeds into and from Roxas Boulevard in Parañaque, Metro Manila, also part of R-1. At the south end, it splits into two termini along the north coast in Kawit, Cavite. The first feeds into the intersection of Covelandia Road, Tirona Highway and Antero Soriano Highway. The second southern terminus is an exit-only to Tirona Highway in Barangay Marulas.

Bay City, also known as the Manila Bay Freeport Zone and Manila Bay Area, is the name for the reclamation area on Manila Bay located west of Roxas Boulevard and the Manila–Cavite Expressway in Metro Manila, Philippines. The area is split between the cities of Manila and Pasay on the north side and Parañaque on the south.

The transportation system in Metro Manila covers the road network, rail network, ferries, ports and airports located within the metropolitan Manila area. Road transportation in Metro Manila is diverse, composed of many types of private and public transport vehicles. These include taxis, buses, jeepneys, tricycles and pedicabs. In some areas, especially in Divisoria and large public markets, two-stroke motors are fitted in the pedicabs and are used for goods transport. Regardless of modernity, horse-drawn kalesas are still used in the streets of Binondo and Intramuros. Ridesharing services such as Grab also operate within Metro Manila.

The Baclaran Mosque, formally called the Rajah Sulaiman Grand Mosque was a mosque in Barangay Baclaran at the border of Pasay and Parañaque in Metro Manila, Philippines.

Danilo Atienza Air Base is a military base used by the Philippine Air Force, located on the northern end of the Cavite Peninsula in Manila Bay, Luzon Island, Philippines. It is adjacent to Cavite City, in Cavite Province.
DMCI Homes, Inc. is the real estate arm of DMCI Holdings through its wholly owned subsidiary DMCI Project Developers, Inc. (PDI). It was incorporated and registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) on April 27, 1995. It ranked #146 in the Business World Top 1000 Corporations for 2014 and Top 1000 Corporations in the Philippines: Capturing the Big Picture of the Country’s corporate scene cited by BusinessWorld.

The Las Piñas–Parañaque Critical Habitat and Ecotourism Area (LPPCHEA), also known as the Las Piñas–Parañaque Wetland Park, is a protected area at the coasts of the cities of Las Piñas and Parañaque in Metro Manila, Philippines. The entire wetland is a declared Ramsar site under the Ramsar Convention of UNESCO.

Jose W. Diokno Boulevard, officially J. W. Diokno Boulevard, is a 4.38-kilometer (2.72 mi) long major collector road that runs north–south along the eastern perimeter of the SM Mall of Asia complex and parallel to Macapagal Boulevard in Bay City, Metro Manila, Philippines. It provides access from the Cultural Center of the Philippines Complex and Roxas Boulevard north to the shopping and lifestyle hub by Manila Bay in Pasay. Motorists use the highway as the less congested alternative route from Manila to the Bay City vis-à-vis its parallel partner road on Macapagal Boulevard. It also connects to Entertainment City further south in Parañaque, and unlike Macapagal Boulevard, it is situated along the coastline overlooking Manila Bay.

Sangley Point Airport, also referred to as Cavite Airport, is a domestic airport at Sangley Point, Cavite City in the Philippines primarily serving general aviation and turbo-propped airliners in the general vicinity of South Luzon and the Greater Manila Area.
The Makati Intra-city Subway (MkTr) was a planned underground rapid transit line to be located in Makati, Metro Manila, that will link establishments across the city's business district. The construction of it was planned through a public-private partnership program between the Makati City Government and a private consortium headed by Philippine Infradev Holdings. Proponents of the subway are expected to begin construction by December 2018, and Makati Mayor Abigail Binay projects completion by 2025. The subway will cost $1.8 billion and is expected to accommodate 500,000 passengers daily. It will also have seven stations, with connections to the existing MRT Line 3 and Pasig River Ferry Service.

Light Rail Manila Corporation (LRMC) is a rail service company based in Pasay, Metro Manila, Philippines. It is a consortium of companies engaged in the operation and maintenance of the Manila Light Rail Transit System Line 1 since September 2015. The consortium is composed of Metro Pacific Investments Corporation and Sumitomo Corporation's Metro Pacific Light Rail Corp. (MPLRC); AC Infrastructure Holdings Corp. ; and Macquarie Infrastructure Holdings (Philippines) Pte. Ltd.

Don Galo, also historically known as Dongalo, is a barangay in Parañaque, Metro Manila, Philippines. It is located along the north bank of the Parañaque River by its mouth in Manila Bay. It is located directly west of the barangay of Santo Niño, separated from it by the Estero de Tripa de Gallina stream, and between Tambo to the north and the Parañaque poblacion of La Huerta to the south. The barangay also includes the southernmost section of Bay City, including portions of the Asia World subdistrict such as Entertainment City and Marina Bay.

Tambo is a coastal barangay located in Parañaque, Metro Manila, Philippines. It is situated south of Baclaran, adjoining the Ninoy Aquino International Airport complex to the east.
Horizon Manila is an upcoming mixed-use planned community to be built on a 419-hectare reclaimed land in Manila Bay. It has been described as the biggest reclamation project in Manila, Philippines. Horizon Manila will be composed of three islands: Island 1, Island 2 and Island 3. The project was approved by the Philippine Reclamation Authority in 2019 and construction will begin in the second half of 2023.

The reclamation of land from the surrounding waters of Metro Manila is used to expand the region's limited area of usable and natural land. There are about 25 projects that aim to reclaim more than 10,000 hectares (100 km2) of land in Manila Bay from the city of Navotas to the province of Cavite. Reclamation projects have been met with opposition and criticism, especially from environmental groups.
The Navotas Boulevard Business Park is an under-construction commercial and business center in Navotas. It will rise on 650-hectare (6.5 km2) reclaimed land, and has been under-construction since 2019. The development is envisioned to create a mixed-use community with residential, institutional, commercial and industrial areas suitable for port facilities, marine and tourism. Its master plan was designed by Surbana Jurong.
Pasay Harbor City is a reclaimed area on Manila Bay. It is under the jurisdiction of Pasay, Philippines.














