The Francis Scott Key Bridge, more commonly known as the Key Bridge, is a six-lane reinforced concrete arch bridge conveying U.S. Route 29 (US 29) traffic across the Potomac River between the Rosslyn neighborhood of Arlington County, Virginia, and the Georgetown neighborhood of Washington, D.C. Completed in 1923, it is Washington's oldest surviving road bridge across the Potomac River.

High Steel Bridge is a truss arch bridge that spans the south fork of the Skokomish River on Forest Service road #2202 near the city of Shelton, Washington in Mason County, Washington. The High Steel Bridge was the second of two large steel arches to be erected by the Simpson Logging Company on Forest Service land in 1929. These bridges carried a single railroad track across formidable chasms opening up expansive tracts of previously inaccessible timber on the Olympic Peninsula.

The Power House Covered Bridge, also known as the School Street Covered Bridge, is a covered bridge from 1872 that crosses the Gihon River off State Route 100C in Johnson, Vermont, US. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974. The bridge's name is from a now obsolete hydroelectric generating station just upstream from it. The bridge is of Queen post truss design by an unknown builder.

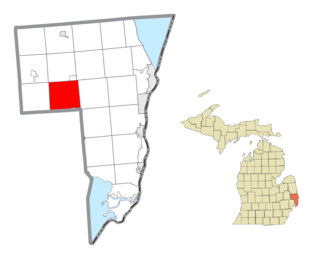
The East River Road–North Hickory Canal Bridge is a bridge located on East River Road over the North Hickory Canal, connecting Grosse Ile, Michigan with Hickory Island to the south. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000.
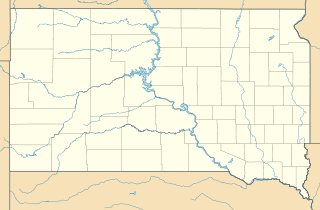
The Stamford Bridge, also known as Bridge No. 48-102-010, is a historic bridge in rural Mellette County, South Dakota, southeast of Stamford. Built in 1930, it is a three-span Bedstead Pony Truss bridge, carrying a local road over the White River, off County Road Ch 1. Each span measures 80 feet (24 m) in length, and the rest on two concrete piers and two concrete abutments with wing walls. The deck consists of steel I-beams, with wooden stringers topped by steel plates. The bridge is the longest Bedstead truss bridge in the state, and one of a modest number of surviving bridges built using this type of truss.

The Clinton Falls Bridge, also known as the Old Mill Bridge and formally as Bridge L-5573, is a historic steel Pratt through truss bridge that spans the Straight River in Clinton Falls Township, Minnesota. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1997 as Bridge No. L-5573 for having local significance in the theme of engineering. It was nominated for being an example of early steel truss bridge design in Minnesota.

The Jefferson Street Viaduct is an historic structure located in Ottumwa, Iowa, United States. The riveted Warren deck truss bridge was completed in 1936. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1998 as a part of the Highway Bridges of Iowa MPS.

The M-28–Tahquamenon River Bridge is a bridge located on M-28 over the Tahquamenon River in Chippewa Township, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in 1999.

The Blossomland Bridge is a bascule bridge in St. Joseph, Michigan, that carries M-63 across the St. Joseph River. Delayed by World War II, construction took place from 1947 though 1948. At the time, it was the longest bridge built by the Michigan State Highway Department. The bridge is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The Second Street–Gun River Bridge was a bridge in Martin Township, Michigan, USA. It was demolished in 2012. The bridge was significant as a rare example of a bridge with a plaque stating that it had been built as a result of Michigan's Covert Act. It was also one of the few remaining examples of a camelback highway bridge in Michigan.

The M-88–Intermediate River Bridge is a bridge located on M-88 over the Intermediate River in Bellaire, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1999. It is a noteworthy product of Depression-era relief work.

The Crystal Springs Street–Dowagiac River Bridge is a road bridge that carries Crystal Springs Street over the Dowagiac River near Sumnerville, Michigan. It was installed in that location in 2017. Between 1938 and 2016, the bridge was located approximately 50 miles away, and carried M-86 over the Prairie River near Nottawa, Michigan, and was known then as the M-86–Prairie River Bridge. The bridge was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000, and is the last remaining camelback pony truss bridge used on the state trunkline system in Michigan.

The US-12–Coldwater River Bridge was a road bridge carrying Old US-12 over the Coldwater River in Coldwater, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1999.

The Murray D. Van Wagoner Memorial Bridge is a bridge carrying M-156 over Silver Creek in Morenci, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000.
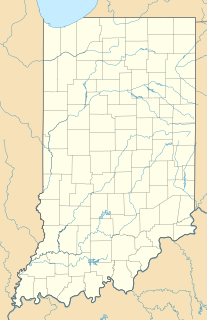
The Indian Trail Road–Belle River Bridge, also known as the Radike Mills Bridge, is a historic bridge that was originally constructed on Indian Trail Road, spanning the Belle River in China Township, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000. The bridge has been moved, and now is located at Purdue University's Steel Bridge Research, Inspection, Training and Engineering Center on South Sharon Chapel Road in West Lafayette, Indiana.

The Jeddo Road–South Branch Mill Creek Drain Bridge is a bridge carrying Jeddo Road over the south branch of the Mill Creek Drain in Brockway Township, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000.

The Derby Street-Grand Trunk Western Railroad Bridge is a bridge carrying Derby Street over the Grand Trunk Western Railroad in Birmingham, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000.

The Morseville Bridge is a bridge which formerly carryied Burt Road over the Flint River in Taymouth Township, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1990. It is the oldest surviving highway bridge in Saginaw County.
The Perrine Road Bridge is a bridge carrying North Saginaw Road over Sturgeon Creek in Larkin Township, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1999. The bridge was moved in 2001 from its location at the time of nomination to the present location, carrying Perrine Road over Sturgeon Creek.

The M-50–Sandstone Creek Bridge, also known as th Tompkins Bridge, is a road bridge carrying M-50 over Sandstone Creek in Tompkins Township, Michigan. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000.