
Midwifery is the health science and health profession that deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period, in addition to the sexual and reproductive health of women throughout their lives. In many countries, midwifery is a medical profession. A professional in midwifery is known as a midwife.
Obstetrics is the field of study concentrated on pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. As a medical specialty, obstetrics is combined with gynecology under the discipline known as obstetrics and gynecology (OB/GYN), which is a surgical field.
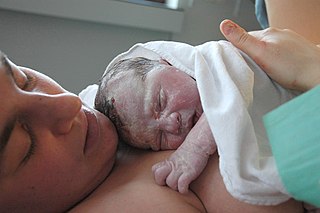
Childbirth, also known as labour, parturition and delivery, is the completion of pregnancy where one or more babies exits the internal environment of the mother via vaginal delivery or caesarean section. In 2019, there were about 140.11 million births globally. In the developed countries, most deliveries occur in hospitals, while in the developing countries most are home births.
A birthing center is a healthcare facility, staffed by nurse midwives, midwives and/or obstetricians, for mothers in labor, who may be assisted by doulas and coaches. The midwives monitor the labor, and well-being of the mother and the baby during birth. Doulas can assist the midwives and make the birth easier. Should additional medical assistance be required, the mother can be transferred to a hospital. This transfer is more likely if an epidural is needed, there is meconium staining, it is a prolonged labor, or the newborn needs intensive care. Some hospitals have birth centers as an alternative to the usual high tech maternity wards.
Natural childbirth is childbirth without routine medical interventions, particularly anesthesia. Natural childbirth arose in opposition to the techno-medical model of childbirth that has recently gained popularity in industrialized societies. Natural childbirth attempts to minimize medical intervention, particularly the use of anesthetic medications and surgical interventions such as episiotomies, forceps and ventouse deliveries and caesarean sections. Natural childbirth may occur during a physician or midwife attended hospital birth, a midwife attended homebirth, or an unassisted birth. The term "natural childbirth" was coined by obstetrician Grantly Dick-Read upon publication of his book Natural Childbirth in the 1930s, which was followed by the 1942 Childbirth Without Fear.

Ina May Gaskin is an American midwife who has been described as "the mother of authentic midwifery." She helped found the self-sustaining community, The Farm, with her husband Stephen Gaskin in 1971 where she markedly launched her career in midwifery. She is known for the Gaskin Maneuver, has written several books on midwifery and childbirth, and continues to educate society through lectures and conferences and spread her message of natural, old-age inspired, fearless childbirth.

Unassisted childbirth (UC) refers to the process of intentionally giving birth without the assistance of a medical birth attendant. It may also be known as freebirth, DIY (do-it-yourself) birth, unhindered birth, and unassisted home birth. Unassisted childbirth is by definition a planned process, and is thus distinct from unassisted birth due to reasons of emergency, lack of access to a skilled birth attendant, or other. It is also different from homebirth, although most UCs also happen within the home.

In the United States, a Certified Nurse-Midwife (CNM) is a nurse midwife who exceeds the International Confederation of Midwives essential competencies for a midwife and is also an advanced practice registered nurse, having completed registered nursing and midwifery education leading to practice as a nurse midwife and credentialing as a Certified Nurse-Midwife. CNMs provide care of women across their lifespan, including pregnancy and the postpartum period, and well woman care and birth control. Certified Nurse-Midwives are exceptionally recognized by the International Confederation of Midwives as a type of midwife in the U.S.
The Bradley method of natural childbirth is a method of natural childbirth developed in 1947 by Robert A. Bradley, M.D. (1917–1998) and popularized by his book Husband-Coached Childbirth, first published in 1965. The Bradley method emphasizes that birth is a natural process: mothers are encouraged to trust their body and focus on diet and exercise throughout pregnancy; and it teaches couples to manage labor through deep breathing and the support of a partner or labor coach.
Jane Sharp was an English midwife. Her work The Midwives Book: or the Whole Art of Midwifery Discovered, published in 1671, was the first on the subject to be produced by an Englishwoman.
A birth attendant, also known as skilled birth attendant, is a health professional who provides basic and emergency care to women and their newborns during pregnancy, childbirth and the postpartum period. A birth attendant, who may be a midwife, physician, obstetrician, or nurse, is trained to be present at ("attend") childbirth, whether the delivery takes place in a health care institution or at home, to recognize and respond appropriately to medical complications, and to implement interventions to help prevent them in the first place, including through prenatal care. Different birth attendants are able to provide different levels of care.

Catharina Geertruida Schrader (1656–1746), also known as the Frisian Midwife, was a successful Dutch midwife in the Early Modern Era, known for her detailed notebooks and memoirs relating the numerous births she participated in.

Midwifery is a women's profession that assists women from pregnancy to newborn care. In some traditional Maya communities, a goddess of midwifery is invoked, and midwives are generally believed to be assigned their profession through signs and visions. In pre-Spanish Yucatan, the aged midwife goddess was called Ixchel.

Childbirth and obstetrics in Classical Antiquity were studied by the physicians of ancient Greece and Rome. Their ideas and practices during this time endured in Western medicine for centuries and many themes are seen in modern women's health. Classical Gynecology and obstetrics were originally studied and taught mainly by midwives in the ancient world, but eventually scholarly physicians of both sexes became involved as well. Obstetrics is traditionally defined as the surgical specialty dealing with the care of a woman and her offspring during pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium (recovery). Gynecology involves the medical practices dealing with the health of women's reproductive organs and their breasts.
Childbirth in rural Appalachia has long been a subject of concern amongst the population because infant mortality rates are higher in Appalachia than in other parts of the United States. Additionally, poor health in utero, at birth, and in childhood can contribute to poor health throughout life. The region's low income, geographic isolation, and low levels of educational attainment reduce both access to and utilization of modern medical care. Traditional medical practices, including lay midwifery, persisted longer in Appalachia than in other U.S. regions.
Midwives in the United States assist childbearing women during pregnancy, labor and birth, and the postpartum period. Some midwives also provide primary care for women including well-woman exams, health promotion, and disease prevention, family planning options, and care for common gynecological concerns. Before the turn of the 20th century, traditional midwives were informally trained and helped deliver almost all births. Today, midwives are professionals who must undergo formal training. Midwives in the United States formed the Midwifery Education, Regulation, and Association task force to establish a framework for midwifery.

A direct-entry midwife is a midwife who has become credentialed without first becoming a nurse. There are direct-entry midwifery programs that prepare students to become Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs) or Certified Professional Midwives (CPMs). Certified Professional Midwives are known for being "more natural and less intervention oriented." In other words, these midwives typically work outside of the hospital setting in homes and birth centers and do not employ methods for childbirth that physicians in hospitals commonly use such as caesarean section, forceps and other types of equipment and drugs.

Elizabeth Nihell was an Englishwoman from London, who was a famous midwife, obstetrics writer, and polemicist. She was most famous for her outspoken stance against male midwives and for her publications.
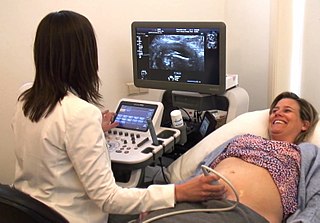
A midwife is a health professional who cares for mothers and newborns around childbirth, a specialization known as midwifery.

A nurse midwife is both a nurse and a midwife, having completed nursing and midwifery education leading to practice as a nurse midwife and sometimes credentialed in the specialty. Nurse midwives provide care of women across the lifespan, including during pregnancy and the postpartum period, and well woman care and birth control.












