The Let-7 microRNA precursor was identified from a study of developmental timing in C. elegans, and was later shown to be part of a much larger class of non-coding RNAs termed microRNAs. miR-98 microRNA precursor from human is a let-7 family member. Let-7 miRNAs have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species (MIPF0000002). miRNAs are initially transcribed in long transcripts called primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs), which are processed in the nucleus by Drosha and Pasha to hairpin structures of about 70 nucleotide. These precursors (pre-miRNAs) are exported to the cytoplasm by exportin5, where they are subsequently processed by the enzyme Dicer to a ~22 nucleotide mature miRNA. The involvement of Dicer in miRNA processing demonstrates a relationship with the phenomenon of RNA interference.

The miR-103 microRNA precursor, is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. miR-103 and miR-107 have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in human.
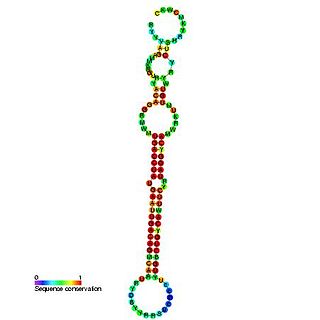
The miR-192 microRNA precursor, is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. miR-192 and miR-215 have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in mouse and human.

The miR-10 microRNA precursor is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. It is part of an RNA gene family which contains miR-10, miR-51, miR-57, miR-99 and miR-100. miR-10, miR-99 and miR-100 have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species. mir-51 and mir-57 have currently only been identified in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans.

In molecular biology, miR-130 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA that regulates gene expression. This microRNA has been identified in mouse, and in human. miR-130 appears to be vertebrate-specific miRNA and has now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a range of vertebrate species. Mature microRNAs are processed from the precursor stem-loop by the Dicer enzyme. In this case, the mature sequence is excised from the 3' arm of the hairpin. It has been found that miR-130 is upregulated in a type of cancer called hepatocellular carcinoma. It has been shown that miR-130a is expressed in the hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell compartment but not in mature blood cells.

The miR-135 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA that is involved in regulating gene expression. It has been shown to be expressed in human, mouse and rat. miR-135 has now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of vertebrate species. Precursor microRNAs are ~70 nucleotides in length and are processed by the Dicer enzyme to produce the shorter 21-24 nucleotide mature sequence. In this case the mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin.
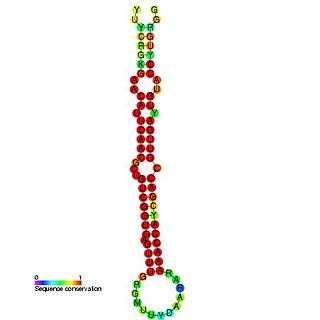
In molecular biology miR-181 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA molecule. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the RNase-III type enzyme Dicer to give a ~22 nucleotide mature product. In this case the mature sequence comes from the 5' arm of the precursor. They target and modulate protein expression by inhibiting translation and / or inducing degradation of target messenger RNAs. This new class of genes has recently been shown to play a central role in malignant transformation. miRNA are downregulated in many tumors and thus appear to function as tumor suppressor genes. The mature products miR-181a, miR-181b, miR-181c or miR-181d are thought to have regulatory roles at posttranscriptional level, through complementarity to target mRNAs. miR-181 which has been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide number of vertebrate species as rat, zebrafish, and in the pufferfish.
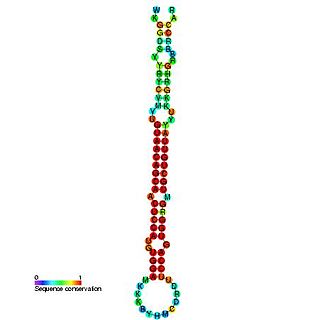
In molecular biology, miR-194 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA gene that regulated gene expression. Its expression has been verified in mouse and in human. mir-194 appears to be a vertebrate-specific miRNA and has now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a range of vertebrate species. The mature microRNA is processed from the longer hairpin precursor by the Dicer enzyme. In this case, the mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin.

miR-196 is a non-coding RNA called a microRNA that has been shown to be expressed in humans and mice. miR-196 appears to be a vertebrate specific microRNA and has now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of vertebrate species. In many species the miRNA appears to be expressed from intergenic regions in HOX gene clusters. The hairpin precursors are predicted based on base pairing and cross-species conservation—their extents are not known. In this case the mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin.

The miR-199 microRNA precursor is a short non-coding RNA gene involved in gene regulation. miR-199 genes have now been predicted or experimentally confirmed in mouse, human and a further 21 other species. microRNAs are transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. The mature products are thought to have regulatory roles through complementarity to mRNA.

There are 89 known sequences today in the microRNA 19 (miR-19) family but it will change quickly. They are found in a large number of vertebrate species. The miR-19 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA molecule that regulates gene expression. Within the human and mouse genome there are three copies of this microRNA that are processed from multiple predicted precursor hairpins:

miR-218 microRNA precursor is a small non-coding RNA that regulates gene expression by antisense binding.
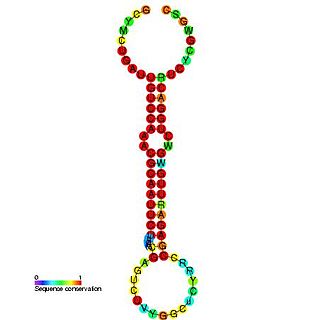
In molecular biology, the microRNA miR-219 was predicted in vertebrates by conservation between human, mouse and pufferfish and cloned in pufferfish. It was later predicted and confirmed experimentally in Drosophila. Homologs of miR-219 have since been predicted or experimentally confirmed in a wide range of species, including the platyhelminth Schmidtea mediterranea, several arthropod species and a wide range of vertebrates. The hairpin precursors are predicted based on base pairing and cross-species conservation; their extents are not known. In this case, the mature sequence is excised from the 5' arm of the hairpin.

The miR-29 microRNA precursor, or pre-miRNA, is a small RNA molecule in the shape of a stem-loop or hairpin. Each arm of the hairpin can be processed into one member of a closely related family of short non-coding RNAs that are involved in regulating gene expression. The processed, or "mature" products of the precursor molecule are known as microRNA (miRNA), and have been predicted or confirmed in a wide range of species.

microRNA 21 also known as hsa-mir-21 or miRNA21 is a mammalian microRNA that is encoded by the MIR21 gene.

In molecular biology mir-22 microRNA is a short RNA molecule. MicroRNAs are an abundant class of molecules, approximately 22 nucleotides in length, which can post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression by binding to the 3' UTR of mRNAs expressed in a cell.

miR-138 is a family of microRNA precursors found in animals, including humans. MicroRNAs are typically transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. The excised region or, mature product, of the miR-138 precursor is the microRNA mir-138.

miR-27 is a family of microRNA precursors found in animals, including humans. MicroRNAs are typically transcribed as ~70 nucleotide precursors and subsequently processed by the Dicer enzyme to give a ~22 nucleotide product. The excised region or, mature product, of the miR-27 precursor is the microRNA mir-27.

miR-191 is a family of microRNA precursors found in mammals, including humans. The ~22 nucleotide mature miRNA sequence is excised from the precursor hairpin by the enzyme Dicer. This sequence then associates with RISC which effects RNA interference.


















