Related Research Articles
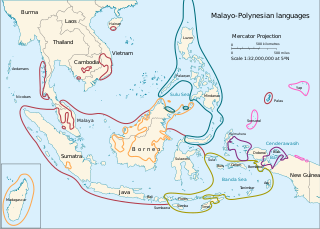
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula, with Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier.

Maranao is an Austronesian language spoken by the Maranao people in the provinces of Lanao del Sur and Lanao del Norte and the cities of Marawi and Iligan City in the Philippines, as well as in Sabah, Malaysia. It is a subgroup of the Danao languages of the Moros in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao.

The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw and a few languages of Palawan—and form a subfamily of Austronesian languages. Although the Philippines is near the center of Austronesian expansion from Formosa, there is little linguistic diversity among the approximately 150 Philippine languages, suggesting that earlier diversity has been erased by the spread of the ancestor of the modern Philippine languages.
Ambala is a Sambalic language spoken in the Philippines. It has more than 2,000 speakers and is spoken within Aeta communities in the Zambal municipalities of Subic, San Marcelino, and Castillejos; in the city of Olongapo; and in Dinalupihan, Bataan.
Mariveleño is a Sambalic language. It has around 500 speakers and is spoken within an Aeta community in Mariveles in the Philippines.

Robert A. Blust was an American linguist who worked in several areas, including historical linguistics, lexicography and ethnology. He was Professor of Linguistics at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa. Blust specialized in the Austronesian languages and made major contributions to the field of Austronesian linguistics.

Lun Bawang or Lundayeh is the language spoken by the Lun Bawangs. It belongs to the Malayo-Polynesian family.
The Northern Mindoro languages are one of two small clusters of languages spoken by the Mangyan people of Mindoro Island in the Philippines.
The Gorontalo–Mongondow languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia.
The Greater North Borneo languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The subgroup covers languages that are spoken throughout much of Borneo, as well as parts of Sumatra and Java, and Mainland Southeast Asia. The Greater North Borneo hypothesis was first proposed by Robert Blust (2010) and further elaborated by Alexander Smith. The evidence presented for this proposal are solely lexical.
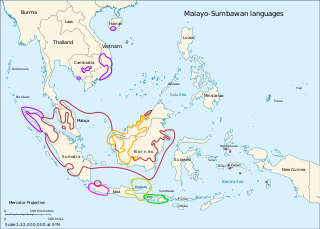
The Malayo-Sumbawan languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian languages that unites the Malayic and Chamic languages with the languages of Java and the western Lesser Sunda Islands, except for Javanese. If valid, it would be the largest demonstrated family of Malayo-Polynesian outside Oceanic. The Malayo-Sumbawan subgroup is however not universally accepted, and is rejected e.g. by Blust (2010) and Smith (2017), who supported the Greater North Borneo and Western Indonesian hypotheses. In a 2019 paper published in Oceanic Linguistics, Adelaar accepted both of these groupings, in addition to Smith's (2018) redefinition of Barito languages as forming a linkage.
The Sabahan languages are a group of Austronesian languages centered on the Bornean province of Sabah.
The Palawanic languages are a subgroup in the Greater Central Philippine-family spoken on the island of Palawan and nearby islets.
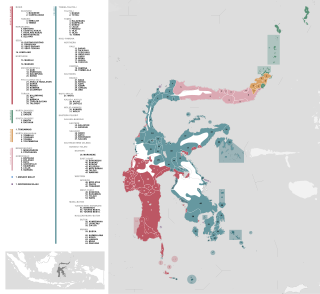
On the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, 114 native languages are spoken, all of which belong to the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. With a total number of 17,200,000 inhabitants, Sulawesi displays a high linguistic diversity when compared with the most densely populated Indonesian island Java, which hosts 4–8 languages spoken by 145,100,000 inhabitants.
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *R to *g. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field.
Molbog is an Austronesian language spoken in the Philippines and Sabah, Malaysia. The majority of speakers are concentrated at the southernmost tip of the Philippine province of Palawan, specifically the municipalities of Bataraza and Balabac. Both municipalities are considered as bastions for environmental conservation in the province. The majority of Molbog speakers are Muslims.
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification.
Ponosakan is an Austronesian language spoken in the vicinity of the town of Belang, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. This language is almost extinct, with only four fluent speakers left as of November 2014.
Kasiguranin (Casiguranin) is a Tagalogic language that is indigenous to the Casiguran town of Aurora in the northern Philippines. It is descended from an early Tagalog dialect that had borrowed heavily from Northeastern Luzon Agta languages, and Ilocano, Visayan languages, Bikol languages, Kapampangan, Gaddang, Itawis and Ibanag, which were spoken by settlers from other parts of the Philippines.
Abai is a Murutic language of Borneo spoken in by the Abai people in the villages of Sembuak and Tubu. Ethnologue mistakenly classifies it as a dialect of Putoh.
References
- ↑ Lobel, Jason William (2013). "Southwest Sabah Revisited". Oceanic Linguistics. 52 (1): 36–68. doi:10.1353/ol.2013.0013. JSTOR 43286760. S2CID 142990330.
- ↑ Blust, Robert (2010). "The Greater North Borneo Hypothesis". Oceanic Linguistics. 49 (1): 44–118. doi:10.1353/ol.0.0060. JSTOR 40783586. S2CID 145459318.
- ↑ Thiessen, Henry Arnold (1981). Phonological reconstruction of Proto Palawan. Anthropological Papers, no. 10. Manila: National Museum of the Philippines.
- ↑ Smith, Alexander (2017). The Languages of Borneo: A Comprehensive Classification (PDF) (PhD thesis). University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa.
- ↑ Lobel, Jason William (2013). "Southwest Sabah Revisited". Oceanic Linguistics. 52 (1): 36–68. doi:10.1353/ol.2013.0013. JSTOR 43286760. S2CID 142990330.