Related Research Articles

Ranong is one of Thailand's southern provinces (changwat), on the west coast along the Andaman Sea. It has the fewest inhabitants of all Thai provinces. Provinces neighboring Ranong are (clockwise) Chumphon, Surat Thani, and Phang Nga. To the west, it borders Kawthaung, Tanintharyi, Myanmar.

Phang Nga is one of the southern provinces (Changwat) of Thailand, on the shore of the Andaman Sea to the west and Phang Nga Bay to the south. Neighbouring provinces, from north and moving clockwise, are Ranong, Surat Thani, and Krabi. Towards the south of Phang Nga is the Phuket province, connected by the Sarasin Bridge.

Phuket ; Thai: ภูเก็ต,, Malay: Bukit or Tongkah is one of the southern provinces (changwat) of Thailand. It consists of the island of Phuket, the country's largest island, and another 32 smaller islands off its coast. Phuket lies off the west coast of mainland Thailand in the Andaman Sea. Phuket Island is connected by the Sarasin Bridge to Phang Nga province to the north. The next nearest province is Krabi, to the east across Phang Nga Bay.

Krabi is the capital of and main town in Krabi Province, on the west coast of southern Thailand, where the Krabi River flows into Phang Nga Bay. The town lies 650 km (400 mi) south of Bangkok, and as of 2020, has a population of 32,644. As in much of southern Thailand, the local economy centres largely on tourism.

Khao Lak is a small village in Phang Nga province, located South of the main mountain. Tour operators like to use the popular name as location for a series of other villages, now tourist-oriented, mainly in the Takua Pa District of Phang Nga Province, Thailand.

Southern Thai, also known as Dambro, Pak Tai, or "Southern language", is a Southwestern Tai ethnolinguistic identity and language spoken in southern Thailand, as well as by small communities in the northernmost states of Malaysia. It is spoken by roughly five million people and as a second language by the 1.5 million speakers of Pattani and other ethnic groups such as the local Peranakan communities, Negritos and other tribal groups. Most speakers are also fluent in or understand the Central Thai dialects.

The Moken are an Austronesian people of the Mergui Archipelago, a group of approximately 800 islands claimed by both Myanmar and Thailand, and the Surin Islands. Most of the 2,000 to 3,000 Moken live a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyle heavily based on the sea, though this lifestyle is increasingly under threat.

The Surin Islands is a continental archipelago of five islands in the Andaman Sea, 55 kilometres (34 mi) from the Thai mainland. Administratively, the islands are part of Tambon Ko Phra Thong, Khura Buri district, in Phang Nga province, Thailand.

Thalang ; (Malay: Telong or Tanjung Salang is a district in the north of Phuket province, Thailand.

Kawthaung is a border town located in the southernmost part of Myanmar, in the Tanintharyi Region. During British rule in Burma between 1824 and 1948, it was known as Victoria Point. As of 2021, it has a population of 57,949. Facing Ranong in Thailand, Kawthaung is one of 7 official border trade posts with Thailand.

Highway 401 is a national highway in Southern Thailand. It starts from the west coast of the Thai-Malay Peninsula at an intersection with Phetkasem Road near Amphoe Takua Pa, Phang Nga Province.

Takua Thung is a district (amphoe) in the Phang Nga province in the south of Thailand.

Ko Yao is a district (amphoe) in Phang Nga province in Thailand's south.
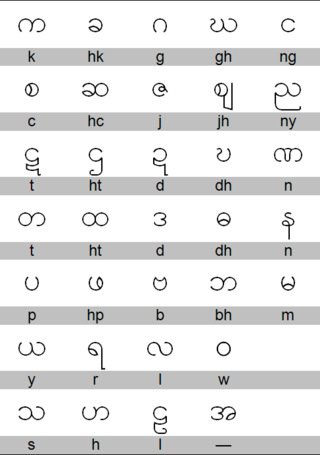
There are approximately a hundred languages spoken in Myanmar. Burmese, spoken by two-thirds of the population, is the official language.
Ko Phra Thong is an island in Khura Buri District, Phang Nga Province, southern Thailand on the Andaman Sea. It has an area of 88 square kilometres (34 sq mi) and is separated from the mainland by a seven-metre-deep (23 ft) canal. The nearest town is Khura Buri, on the mainland about 10 km (6.2 mi) east.
Moken is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by inhabitants in southern Myanmar and Southern Thailand, who refer to themselves as Moken (people) and Mawken.

Burmese Malays, primarily live in Tanintharyi Region in the southern part of Myanmar. There are some dispersed Malay from the northernmost states of Malaysia and from southern Thailand. They are believed to be of Kedahan Malay descent. Some of the Moken people in the Mergui Archipelago speak a dialect of Malay.
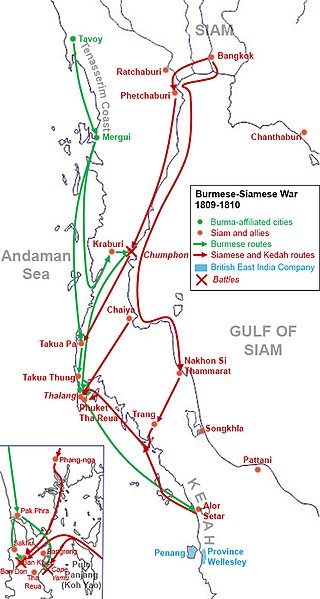
The Burmese–Siamese War (1809–1812) or the Burmese Invasion of Thalang was an armed conflict fought between Burma under Konbaung dynasty and Siam under the Chakri dynasty, during the period of June 1809 and January 1812. The war centered on the control of the Phuket Island, also known as Thalang or Junk Ceylon, and the tin rich Andaman Coast. The war also involved the Kedah Sultanate. This occasion was the last Burmese offensive expedition into Siamese territories in Thai history, with British acquisition of the Tenasserim Coast in 1826, following the First Anglo-Burmese War, removing several hundred miles of the existing land border between Siam and Burma. The war also left Phuket devastated and depopulated for many decades until its reemergence as a tin mining center in the late 19th century.
The Moklenic or Moken–Moklen languages consist of a pair of two closely related but distinct languages, namely Moken and Moklen. Larish (1999) establishes the two languages as forming two distinct subgroups of a larger Moken–Moklen branch. Larish (2005) suggests Moklenic as an alternative name for Moken–Moklen, the latter term which was originally used by Larish (1999).
References
- ↑ Moklen at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)