
Madura Island is an Indonesian island off the northeastern coast of Java. The island comprises an area of approximately 4,436.77 square kilometres (1,713.05 sq mi). Administratively, Madura is part of the province of East Java. It is separated from Java by the narrow Madura Strait. The administered area had a density of 755.6 people per km2 in mid-2023, while the main island had a somewhat higher figure of 840 per km2.
The Balinese script, natively known as Aksara Bali and Hanacaraka, is an abugida used in the island of Bali, Indonesia, commonly for writing the Austronesian Balinese language, Old Javanese, and the liturgical language Sanskrit. With some modifications, the script is also used to write the Sasak language, used in the neighboring island of Lombok. The script is a descendant of the Brahmi script, and so has many similarities with the modern scripts of South and Southeast Asia. The Balinese script, along with the Javanese script, is considered the most elaborate and ornate among Brahmic scripts of Southeast Asia.
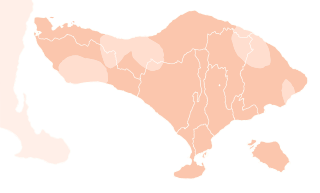
Balinese is an Austronesian language spoken on the Indonesian island of Bali, as well as Northern Nusa Penida, Western Lombok, Southern Sumatra, and Sulawesi. Most Balinese speakers also use Indonesian. The 2000 national census recorded 3.3 million people speakers of Balinese, however the Bali Cultural Agency estimated in 2011 that the number of people still using the Balinese language in their daily lives is under 1 million. The language has been classified as "not endangered" by Glottolog.

Javanese is a Malayo-Polynesian language of the Austronesian language family spoken primarily by the Javanese people from the central and eastern parts of the island of Java, Indonesia. There are also pockets of Javanese speakers on the northern coast of western Java. It is the native language of more than 68 million people.
Old Javanese or Kawi is the oldest attested phase of the Javanese language. It was spoken in the eastern part of what is now Central Java and the whole of East Java, Indonesia. As a literary language, Kawi was used across Java and on the islands of Madura, Bali, and Lombok. It had a sizable vocabulary of Sanskrit loanwords but had not yet developed the formal krama language register, to be used with one's social superiors that is characteristic of modern Javanese.

Madurese is a language of the Madurese people, native to the Madura Island and Eastern Java, Indonesia; it is also spoken by migrants to other parts of Indonesia, namely the eastern salient of Java, the Masalembu Islands and even some on Kalimantan. It was traditionally written in the Javanese script, but the Latin script and the Pegon script is now more commonly used. The number of speakers, though shrinking, is estimated to be 10-13 million, making it one of the most widely spoken languages in the country. Bawean Madurese, which is a dialect of Madurese, is also spoken by Baweanese descendants in Malaysia and Singapore.

Jawi is a writing system used for writing several languages of Southeast Asia, such as Acehnese, Magindanawn, Malay, Mëranaw, Minangkabau, Tausūg, and Ternate. Jawi is based on the Arabic script, consisting of all 31 original Arabic letters, six letters constructed to fit phonemes native to Malay, and one additional phoneme used in foreign loanwords, but not found in Classical Arabic, which are ca, nga, pa, ga, va, and nya.
Javanese script is one of Indonesia's traditional scripts developed on the island of Java. The script is primarily used to write the Javanese language, but in the course of its development has also been used to write several other regional languages such as Sundanese and Madurese, the regional lingua franca Malay, as well as the historical languages Kawi and Sanskrit. It heavily influenced the Balinese script from which the system for Sasak developed. Javanese script was actively used by the Javanese people for writing day-to-day and literary texts from at least the mid-16th century CE until the mid-20th century CE, before it was gradually supplanted by the Latin alphabet. Today, the script is taught in the Yogyakarta Special Region as well as the provinces of Central Java and East Java as part of the local curriculum, but with very limited function in everyday use.

Madurese, Madurans, Madurites or Madurace are one of the Javan ethnic groups native to the Indonesian island of Madura in Java Sea, off the northeastern coast of Java. They speak their own native Madurese, sharing a common history, traditions, and cultural identity. Nationwide, the Madurese are the third-largest ethnic group in Indonesia, and one of the well-known Indonesian national dishes, Satay, is attributed to the Madurese as part of their culinary heritage.

The Kangean Islands or simply Kangean is a collective name for a group of islands lying to the east of Madura. Kangean and its surrounding islands lie to the north of Bali in the northern Bali Sea, to the northwest of the Lesser Sunda Islands, and administratively they form three districts within Sumenep Regency, East Java Province. The group comprises a total of 91 islands including 27 inhabited islands. Kangean is located approximately 120 km (75 mi) in the north of Bali, the northwest of Lombok, and 120 km east of Madura. The biggest and most populous district is Arjasa, which includes the town of that name located in the west of the island. The Kangean Islands have a large potential for natural resources, such as natural gas, teak, coconut, and salt production.

The Sasak language is spoken by the Sasak ethnic group, which make up the majority of the population of Lombok, an island in the West Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. It is closely related to the Balinese and Sumbawa languages spoken on adjacent islands, and is part of the Austronesian language family. Sasak has no official status; the national language, Indonesian, is the official and literary language in areas where Sasak is spoken.

The Bawean, or Baweans, or also Baweanese, also called Bawean Madurese are an ethnic group native to the island of Bawean, located in the Java Sea off the coast of Java, Indonesia. They are considered a distinct ethnic group within the larger Javanese cultural sphere. The Bawean people have their own unique language, also called Bawean, which belongs to the Austronesian language family.

Sumenep Regency is a regency of the East Java province, Indonesia. It has an area of 2,093.47 km2 and a population of 1,042,312 inhabitants according to the 2010 census ; the 2020 census resulted in a total of 1,124,436. The official estimate as at mid 2023 was 1,142,210.

Indonesia is home to over 700 living languages spoken across its extensive archipelago. This significant linguistic variety constitutes approximately 10% of the world’s total languages, positioning Indonesia as the second most linguistically diverse nation globally, following Papua New Guinea. The majority of these languages belong to the Austronesian language family, prevalent in the western and central regions of Indonesia, including languages such as Acehnese, Sundanese, and Buginese. In contrast, the eastern regions, particularly Papua and the Maluku Islands, are home to over 270 Papuan languages, which are distinct from the Austronesian family and represent a unique linguistic heritage. The language most widely spoken as a native language is Javanese, primarily by the Javanese people in the central and eastern parts of Java Island, as well as across many other islands due to migration.
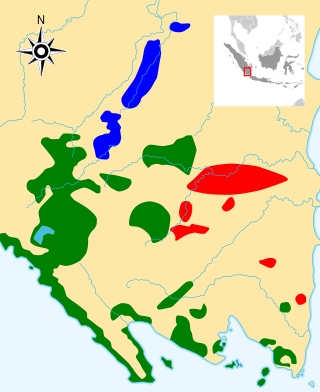
Lampung or Lampungic is an Austronesian language or dialect cluster with around 1.5 million native speakers, who primarily belong to the Lampung ethnic group of southern Sumatra, Indonesia. It is divided into two or three varieties: Lampung Api, Lampung Nyo, and Komering. The latter is sometimes included in Lampung Api, sometimes treated as an entirely separate language. Komering people see themselves as ethnically separate from, but related to, Lampung people.

Pegon is a modified Arabic script used to write the Javanese, Sundanese, and Madurese languages, as an alternative to the Latin script or the Javanese script and the Old Sundanese script. It was used in a variety of applications, from religion, to diplomacy, to poetry. But today particularly, it is used for religious (Islamic) writing and poetry, particularly in writing commentaries of the Qur'an. Pegon includes letters that are not present in Modern Standard Arabic. Pegon has been studied far less than its Jawi counterpart which is used for Malay, Acehnese and Minangkabau.

Golekan is a type of traditional boat from Madura, Indonesia. They once plied as far as Singapore, where they are referred to as Madurese traders. In the present this type of boat is only known locally, especially near Bangkalan in Western Madura and around the Kangean islands.
Buda script, Aksara Buda, or Gunung script is an archaic script. Based on its shape, the Buda Script still has a close relationship with the Kawi script. This script was previously used on the island of Java and Bali. This type of script is called the Buda script because it is considered to have originated from the pre-Islamic era which is called the Buddhist Age. The word Buda is based on the Buddha word. Manuscripts containing writing using the Buda script are commonly found in mountainous areas. Because of that, this type of script is also called the "Mountain script".
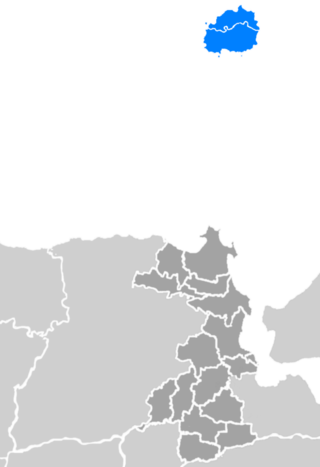
Bawean dialect, also known as Bawean language, is a dialect of Madurese language spoken predominantly by Bawean people in Bawean island. This dialect have 4 major sub-dialects each spoken predominantly in village of Daun and Suwari in the villages of Sangkapura, and the village of Kepuhteluk in the district of Tambak. As well as additional sub-dialects of Bawean Creole.

Indonesian Arabic is a variety of Arabic spoken in Indonesia. It is primarily spoken by people of Arab descents and by students (santri) who study Arabic at Islamic educational institutions or pesantren. This language generally incorporates loanwords from regional Indonesian languages in its usage, reflecting the areas where it is spoken.















