Related Research Articles
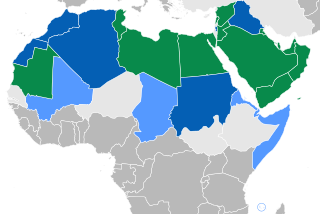
Arabic is a Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The ISO assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as al-ʿarabiyyatu l-fuṣḥā or simply al-fuṣḥā (اَلْفُصْحَىٰ).

French is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the (Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to the French colonial empire, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French.

German is a West Germanic language in the Indo-European language family, mainly spoken in Western and Central Europe. It is the most spoken native language within the European Union. It is the most widely spoken and official language in Germany, Austria, Switzerland, Liechtenstein, and the Italian autonomous province of South Tyrol. It is also an official language of Luxembourg, Belgium and the Italian autonomous region of Friuli-Venezia Giulia, as well as a recognized national language in Namibia. There are also notable German-speaking communities in France (Alsace), the Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, Denmark, Romania and Hungary (Sopron). Overseas, sizeable communities of German-speakers are found in Brazil, South Africa (Kroondal), Namibia, among others, some communities have decidedly Austrian German or Swiss German characters.

Portuguese is a Western Romance language of the Indo-European language family originating from the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is the official language of Angola, Brazil, Cape Verde, Guinea-Bissau, Mozambique, Portugal and São Tomé and Príncipe, and has co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea and Macau. Portuguese-speaking people or nations are known as Lusophone. As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Celtic phonology.

The United States does not have an official language at the federal level, but the most commonly used language is English, which is the de facto national language. In addition, 32 U.S. states out of 50 and all five U.S. territories have declared English as an official language. The majority of the U.S. population (77.5%) speaks only English at home as of 2023. The remainder of the population speaks many other languages at home, most notably Spanish, according to the American Community Survey (ACS) of the U.S. Census Bureau; others include indigenous languages originally spoken by Native Americans, Alaska Natives, Native Hawaiians, and native populations in the U.S. unincorporated territories. Other languages were brought in by people from Europe, Africa, Asia, other parts of the Americas, and Oceania, including multiple dialects, creole languages, pidgin languages, and sign languages originating in what is now the United States. Interlingua, an international auxiliary language, was also created in the U.S.

Asia is home to hundreds of languages comprising several families and some unrelated isolates. The most spoken language families on the continent include Austroasiatic, Austronesian, Japonic, Dravidian, Indo-European, Afroasiatic, Turkic, Sino-Tibetan, Kra–Dai and Koreanic. Many languages of Asia, such as Chinese, Sanskrit, Arabic, Tamil or Telugu, have a long history as a written language.

Languages spoken in the Republic of India belong to several language families, the major ones being the Indo-Aryan languages spoken by 78.05% of Indians and the Dravidian languages spoken by 19.64% of Indians; both families together are sometimes known as Indic languages. Languages spoken by the remaining 2.31% of the population belong to the Austroasiatic, Sino–Tibetan, Tai–Kadai, and a few other minor language families and isolates. According to the People's Linguistic Survey of India, India has the second highest number of languages (780), after Papua New Guinea (840). Ethnologue lists a lower number of 456.
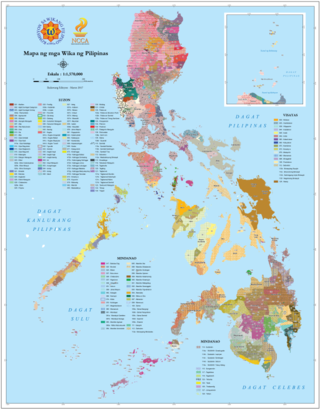
There are some 130 to 195 languages spoken in the Philippines, depending on the method of classification. Almost all are Malayo-Polynesian languages native to the archipelago. A number of Spanish-influenced creole varieties generally called Chavacano along with some local varieties of Chinese are also spoken in certain communities. The 1987 constitution designates Filipino, a standardized version of Tagalog, as the national language and an official language along with English. Filipino is regulated by Commission on the Filipino Language and serves as a lingua franca used by Filipinos of various ethnolinguistic backgrounds.

The Bisayan languages or Visayan languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken in the Philippines. They are most closely related to Tagalog and the Bikol languages, all of which are part of the Central Philippine languages. Most Bisayan languages are spoken in the whole Visayas section of the country, but they are also spoken in the southern part of the Bicol Region, islands south of Luzon, such as those that make up Romblon, most of the areas of Mindanao and the province of Sulu located southwest of Mindanao. Some residents of Metro Manila also speak one of the Bisayan languages.

There are over 525 native languages spoken in Nigeria. The official language and most widely spoken lingua franca is English, which was the language of Colonial Nigeria. Nigerian Pidgin – an English-based creole – is spoken by over 60 million people.

Buol Regency is a regency of Central Sulawesi Province of Indonesia. It was created on 4 October 1999, having previously been the eastern half of a larger Buol Tolitoli Regency. It covers an area of 4,043.57 km2, and had a population of 132,330 at the 2010 Census; and 145,254 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 150,524. The administrative centre is the town of Buol, in Biau District.

Bone Bolango is a regency of Gorontalo Province, Indonesia, on the island of Sulawesi. It was established in 2003 under Law Number 6/2003 from the former eastern districts of Gorontalo Regency. It has an area of 1,915.44 km2 and had a population of 141,915 at the 2010 Census and 162,778 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 172,301. The administrative centre of the regency is the town of Suwawa.
The Gorontalo–Mongondow languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia.
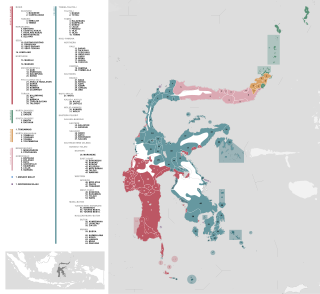
On the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, 114 native languages are spoken, all of which belong to the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. With a total number of 17,200,000 inhabitants, Sulawesi displays a high linguistic diversity when compared with the most densely populated Indonesian island Java, which hosts 4–8 languages spoken by 145,100,000 inhabitants.
Atinggola is a small town and district in Gorontalo Regency in Gorontalo, northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. It is located on the Celebes Sea. In 1981 the district had a population of around 15,000 Bolango people. The people speak a local dialect of the Bolango language, called the Atinggola language.
Suwawa is a Philippine language spoken in North Sulawesi (Celebes), Indonesia. It is also known as Bonda, Bone, Bunda, Bune, Suvava, and Toewawa. The language mostly spoken in Suwawa District, Regency of Bone Bolango.

The Mongondow or Bolaang Mongondow people are an ethnic group native to the north-eastern part of the Indonesian island of Sulawesi. The Mongondows are predominantly Muslim. They have traditionally been concentrated in the provinces of North Sulawesi and Gorontalo. This ethnic group used to be united by a single entity, the Kingdom of Bolaang Mongondow, which became the western regencies of North Sulawesi after the Indonesian independence.

The Bikol languages or Bicolano languages are a group of Central Philippine languages spoken mostly in the Bicol Peninsula in the southeastern part of Luzon, the neighboring island-province of Catanduanes, and the island of Burias in Masbate.

Gorontalo is a province of Indonesia on the island of Sulawesi. Located on the Minahasa Peninsula, Gorontalo was formerly part of the province of North Sulawesi until its inauguration as a separate province on 5 December 2000. The province is bordered by the provinces of North Sulawesi to the east and Central Sulawesi to the west, as well sharing a maritime border with the Philippines in the Sulawesi Sea to the north, and a coastline on the Gulf of Tomini to the south. The provincial capital, as well as the main gateway to the province and its most populated city, is Gorontalo. The size is comparable to Vanuatu.
References
- ↑ Bolango at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)
