Related Research Articles

Zambales, officially the Province of Zambales, is a province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is Iba, which is located in the middle of the province. Olongapo is the largest city of the province wherein it is geographically located but politically independent.

Olongapo, officially the City of Olongapo, is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Central Luzon region of the Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 260,317 people.

Aeta, Agta and Dumagat, are collective terms for several indigenous peoples who live in various parts of Luzon island in the Philippines. They are included in the wider Negrito grouping of the Philippines and the rest of Southeast Asia, with whom they share superficial common physical characteristics such as: dark skin tones; short statures; frizzy to curly hair; and a higher frequency of naturally lighter hair colour (blondism) relative to the general population. They are thought to be among the earliest inhabitants of the Philippines—preceding the Austronesian migrations. Regardless, the modern Aeta populations have significant Austronesian admixture, and speak Austronesian languages.

San Marcelino, officially the Municipality of San Marcelino, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Zambales, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 37,719 people.
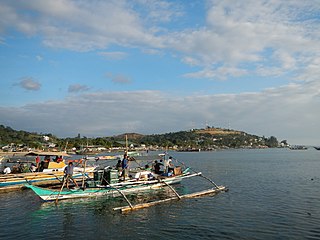
Subic, officially the Municipality of Subic, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Zambales, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 111,912 people.
The legislative districts of Zambales are the representations of the province of Zambales and the highly urbanized city of Olongapo in the various national legislatures of the Philippines. The province and the city are currently represented in the lower house of the Congress of the Philippines through their first and second congressional districts.
The Sambalic languages are a part of the Central Luzon language family spoken by the Sambals, an ethnolinguistic group on the western coastal areas of Central Luzon and the Zambales mountain ranges.
The Indi language or Mag-indi is a Sambalic language with around 5,000 speakers. It is spoken within Philippine Aeta communities in San Marcelino, Zambales, and in the Pampango municipalities of Floridablanca and Porac. There are also speakers in Lumibao and Maague-ague.
Mariveleño is a Sambalic language. It has around 500 speakers and is spoken within an Aeta community in Mariveles in the Philippines.
The Northern Mindoro languages are one of two small clusters of languages spoken by the Mangyan people of Mindoro Island in the Philippines.
Remontado, also known in literature as Sinauna, Kabalat, Remontado Dumagat, and more commonly by the autonym Hatang-Kayi, is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in Tanay, Rizal, General Nakar, Quezon, Rodriguez, Rizal and Antipolo, in the Philippines. It is one of the Philippine Negrito languages. It is a moribund language.
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *R to *g. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, eastern and western parts of Sabah, Malaysia and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field.
Arta is a highly endangered Negrito language of the northern Philippines.

Dupaningan Agta, or Eastern Cagayan Agta, is a language spoken by a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer Negrito people of Cagayan and Isabela provinces in northern Luzon, Philippines. Its Yaga dialect is only partially intelligible.
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification.
Inagta Rinconada is a Bikol language spoken by a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer Agta (Negrito) people of the Philippines. It is spoken to the east of Iriga City up to the shores of Lake Buhi. The language is largely intelligible with Mount Iraya Agta on the other side of the lake.
Umiray Dumaget is an Aeta language spoken in southern Luzon Island, Philippines.
The Southern Cordilleran languages are a group of closely related languages within the Northern Luzon subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in an area stretching from the southern shore of Lingayen Gulf to the highlands of Quirino province. The most widely spoken Southern Cordilleran language is Pangasinan, one of the eight major languages of the Philippines.
The Central Cordilleran languages are a group of closely related languages within the Northern Luzon subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in the interior highlands of Northern Luzon in the Cordillera Central mountain range.

Zambales's 1st congressional district is one of the two congressional districts of the Philippines in the province of Zambales. It has been represented in the House of Representatives since 1987. The district consists of the city of Olongapo and adjacent municipalities in the southernmost part of Zambales, namely Castillejos, San Marcelino and Subic. It is currently represented in the 19th Congress by Jefferson F. Khongun of the Nacionalista Party (NP).
References
- 1 2 Ambala at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Ramos 2004
- ↑ Reid, Lawrence A. (1994). "Possible Non-Austronesian Lexical Elements in Philippine Negrito Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 33 (1): 37–72. doi:10.2307/3623000. hdl: 10125/32986 . JSTOR 3623000.
- ↑ Himes, Ronald S. (2012). "The Central Luzon Group of Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 51 (2): 490–537. doi:10.1353/ol.2012.0013. JSTOR 23321866. S2CID 143589926.