Related Research Articles
The Central Philippine languages are the most geographically widespread demonstrated group of languages in the Philippines, being spoken in southern Luzon, Visayas, Mindanao, and Sulu. They are also the most populous, including Tagalog, Bikol, and the major Visayan languages Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Waray, Kinaray-a, and Tausug, with some forty languages all together.

Aeta, Agta and Dumagat, are collective terms for several indigenous peoples who live in various parts of Luzon island in the Philippines. They are included in the wider Negrito grouping of the Philippines and the rest of Southeast Asia, with whom they share superficial common physical characteristics such as: dark skin tones; short statures; frizzy to curly hair; and a higher frequency of naturally lighter hair colour (blondism) relative to the general population. They are thought to be among the earliest inhabitants of the Philippines—preceding the Austronesian migrations. Regardless, the modern Aeta populations have significant Austronesian admixture, and speak Austronesian languages.

The Commission on the Filipino Language (CFL), also referred to as the Komisyon sa Wikang Filipino (KWF), is the official regulating body of the Filipino language and the official government institution tasked with developing, preserving, and promoting the various local Philippine languages. The commission was established in accordance with the 1987 Constitution of the Philippines.
The Bolinao language or Binubolinao is a Central Luzon language spoken primarily in the municipalities of Bolinao and Anda, Pangasinan in the Philippines. It has approximately 50,000 speakers, making it the second most widely spoken Sambalic language. Most Bolinao speakers can speak Pangasinan and/or Ilocano. Ethnologue reports 510 monolinguals for this language.
The Sambalic languages are a part of the Central Luzon language family spoken by the Sambals, an ethnolinguistic group on the western coastal areas of Central Luzon and the Zambales mountain ranges.
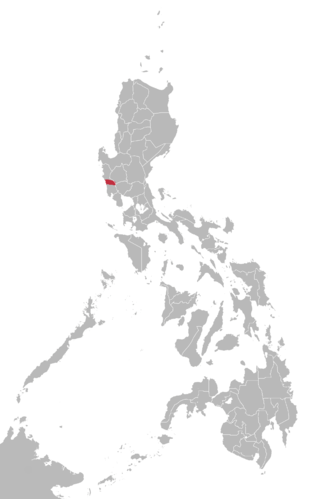
Botolan is a Sambalic language spoken by 32,867 Sambal, primarily in the Zambal municipalities of Botolan and Cabangan in the Philippines. Language status is 5 (developing).
Ambala is a Sambalic language spoken in the Philippines. It has more than 2,000 speakers and is spoken within Aeta communities in the Zambal municipalities of Subic, San Marcelino, and Castillejos; in the city of Olongapo; and in Dinalupihan, Bataan.
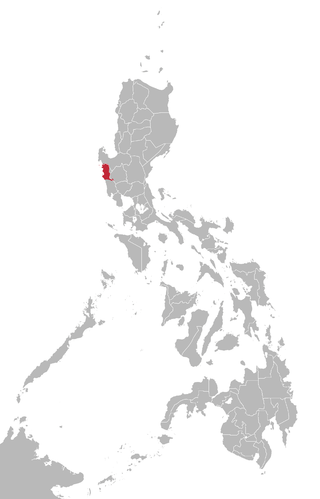
Sambal or Sambali is a Sambalic language spoken primarily in the Zambal municipalities of Santa Cruz, Candelaria, Masinloc, Palauig, and Iba, in the Pangasinense municipality of Infanta, and areas of Pampanga in the boundary with Zambales in the Philippines; speakers can also be found in Panitian, Quezon, Palawan and Barangay Mandaragat or Buncag of Puerto Princesa. The speakers of the language are decreasing due to the fact that many of the speakers are shifting to Tagalog and Ilocano.
The Antsi (Anchi) language or Mag-antsi is a Sambalic language with around 4,200 speakers. It is spoken within Philippine Aeta communities in the Zambal municipalities of Botolan, San Marcelino, and Castillejos; in the Tarlaqueño municipalities of Capas and Bamban; in Mabalacat, Pampanga; and in Angeles City. The use of the language is declining as its speakers are shifting to Kapampangan or Ilocano. The language is mutually intelligible with Mag-Indi Ayta (77%) and Ambala Ayta (65%).
Abellen, Abenlen, Aburlin, or Ayta Abellen, is a Sambalic language. It has about 3,500 speakers and is spoken in a few Aeta communities in Tarlac province, Philippines. Ayta Abellen itself is part of the Sambalic language family in the Philippines and is closely related to not only the five other Ayta dialects but also the Botolan dialect of Sambal. Ethnologue reports 45 monolinguists.
Mariveleño is a Sambalic language. It has around 500 speakers and is spoken within an Aeta community in Mariveles in the Philippines.
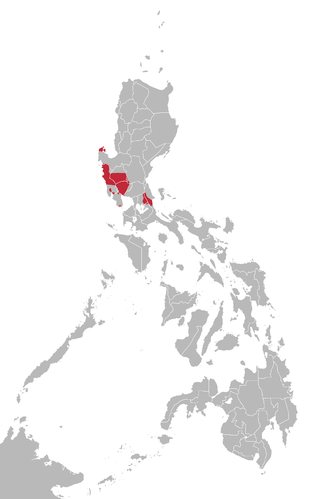
The Central Luzon languages are a group of languages belonging to the Philippine languages. These are predominantly spoken in the western portions of Central Luzon in the Philippines. One of them, Kapampangan, is the major language of the Pampanga-Mount Pinatubo area. However, despite having three to four million speakers, it is threatened by the diaspora of its speakers after the June 1991 eruption of that volcano. Globalization also threatened the language, with the younger generation more on using and speaking Tagalog and English, but promotion and everyday usage boosted the vitality of Kapampangan. Another Central Luzon language, Sambal or Sambali, experiences same situation, the speakers of the language are decreasing due to the globalization that many of the speakers of younger generation are shifting to Tagalog & Ilocano. The only Central Luzon language spoken outside Central Luzon is Hatang Kayi or Sinauna, located in northeast Calabarzon.
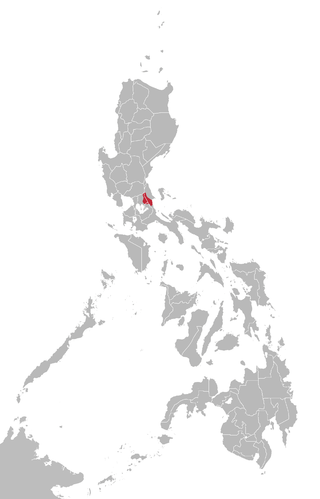
Remontado, also known in literature as Sinauna, Kabalat, Remontado Dumagat, and more commonly by the autonym Hatang-Kayi, is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in Tanay, Rizal, General Nakar, Quezon, Rodriguez, Rizal and Antipolo, in the Philippines. It is one of the Philippine Negrito languages. It is a moribund language.
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *R to *g. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, eastern and western parts of Sabah, Malaysia and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field.
Arta is a highly endangered Negrito language of the northern Philippines.

Itneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
Manide is a Philippine language spoken throughout the province of Camarines Norte in Bicol region and near the eastern edge of Quezon in Southern Tagalog of southern Luzon in the Philippines. Manide is spoken by nearly 4,000 Negrito people, most of whom reside in the towns of Labo, Jose Panganiban, and Paracale.
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification.

Southern Alta, is a distinctive Aeta language of the mountains of northern Philippines. Southern Alta is one of many endangered languages that risks being lost if it is not passed on by current speakers. Most speakers of Southern Alta also speak Tagalog.
Umiray Dumaget is an Aeta language spoken in southern Luzon Island, Philippines.
References
- ↑ Indi language at Ethnologue (17th ed., 2013)

- 1 2 Indi at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Stone, Roger (2008). "The Sambalic Languages of Central Luzon" (PDF). Studies in Philippine Languages and Cultures. 19: 158–183. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-05-17. Retrieved 2016-03-30.
- ↑ Himes, Ronald S. (2012). "The Central Luzon Group of Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 51 (2): 490–537. doi:10.1353/ol.2012.0013. JSTOR 23321866. S2CID 143589926.
- ↑ Stone, Roger (2017). Introduction to Ayta Mag-Indi Orthography.