
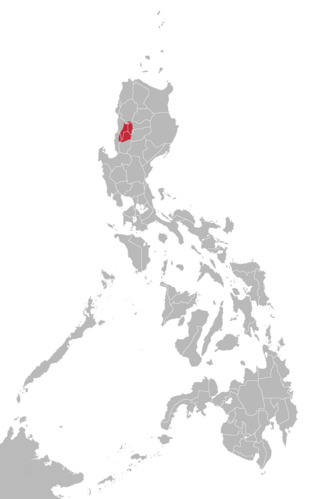
Nueva Vizcaya, officially the Province of Nueva Vizcaya, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Cagayan Valley region in Luzon. Its capital and largest town is Bayombong. It is bordered by Benguet to the west, Ifugao to the north, Isabela to the northeast, Quirino to the east, Aurora to the southeast, Nueva Ecija to the south, and Pangasinan to the southwest. Quirino province was created from Nueva Vizcaya in 1966.
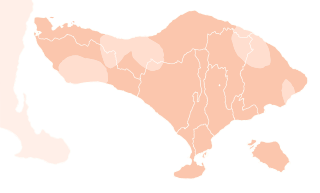
Balinese is an Austronesian language spoken on the Indonesian island of Bali, as well as Northern Nusa Penida, Western Lombok, Southern Sumatra, and Sulawesi. Most Balinese speakers also use Indonesian. The 2000 national census recorded 3.3 million people speakers of Balinese, however the Bali Cultural Agency estimated in 2011 that the number of people still using the Balinese language in their daily lives is under 1 million. The language has been classified as "not endangered" by Glottolog.
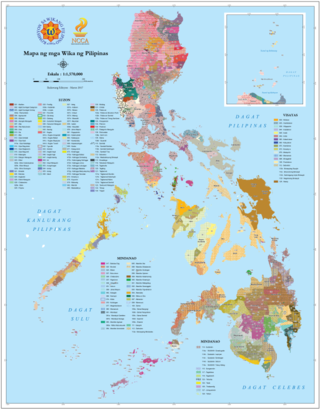
There are some 130 to 195 languages spoken in the Philippines, depending on the method of classification. Almost all are Malayo-Polynesian languages native to the archipelago. A number of Spanish-influenced creole varieties generally called Chavacano along with some local varieties of Chinese are also spoken in certain communities. The 1987 constitution designates Filipino, a standardized version of Tagalog, as the national language and an official language along with English. Filipino is regulated by Commission on the Filipino Language and serves as a lingua franca used by Filipinos of various ethnolinguistic backgrounds.

Bambang, officially the Municipality of Bambang, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Nueva Vizcaya, Philippines. According to the 2020 censusus, it has a population of 55,789 people.

Dupax del Norte, officially the Municipality of Dupax del Norte, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Nueva Vizcaya, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,295 people. Dupax del Norte, situated on the south-eastern part of Nueva Vizcaya, has a total land area of 396 square kilometers. It is bounded by the town of Kasibu in the north, Alfonso Castañeda in the east, Dupax del Sur in the south, and Bambang in the west. It has wide tracts of virgin forests, rich, fertile plains and valleys with mineral deposits and has a climate suitable for agriculture.

Surigaonon is an Austronesian language spoken by Surigaonon people. As a regional Philippine language, it is spoken in the province of Surigao del Norte, Dinagat Islands, Surigao del Sur, and some portions of Agusan del Norte, especially the towns near Lake Mainit, Agusan del Sur and Davao Oriental.
Kankanaey is a South-Central Cordilleran language under the Austronesian family spoken on the island of Luzon in the Philippines primarily by the Kankanaey people. Alternate names for the language include Central Kankanaey, Kankanai, and Kankanay. It is widely used by Cordillerans, alongside Ilocano, specifically people from Mountain Province and people from the northern part of the Benguet Province. Kankanaey has a slight mutual intelligibility with the Ilocano language.
Kamayo, also called Kadi, Kinadi, or Mandaya, is a minor Austronesian language of the central eastern coast of Mindanao in the Philippines.

Aritao, officially the Municipality of Aritao, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Nueva Vizcaya, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 42,197 people.

Dupax del Sur, officially the Municipality of Dupax del Sur, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Nueva Vizcaya, Philippines. At the 2020 census, it had a population of 21,224 people.
Dupax, officially the Municipality of Dupax, was a municipality in the province of Nueva Vizcaya, Philippines. Founded during the Spanish era, it was divided into Dupax del Norte and Dupax del Sur in 1971.
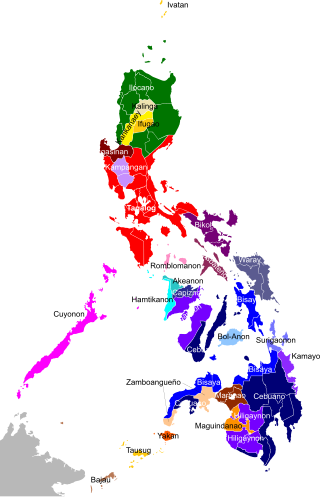
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous people groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither Indigenous nor Moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.

Ifugao or Batad is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in the northern valleys of Ifugao, Philippines. It is a member of the Northern Luzon subfamily and is closely related to the Bontoc and Kankanaey languages. It is a dialect continuum, and its four main varieties—such as Tuwali—are sometimes considered separate languages.
The Gaddang language is spoken by up to 30,000 speakers in the Philippines, particularly along the Magat and upper Cagayan rivers in the Region II provinces of Nueva Vizcaya and Isabela and by overseas migrants to countries in Asia, Australia, Canada, Europe, in the Middle East, United Kingdom and the United States. Most Gaddang speakers also speak Ilocano, the lingua franca of Northern Luzon, as well as Tagalog and English. Gaddang is associated with the "Christianized Gaddang" people, and is closely related to the highland tongues of Ga'dang with 6,000 speakers, Yogad, Cagayan Agta with less than 1,000 and Atta with 2,000, and more distantly to Ibanag, Itawis, Isneg and Malaweg.

The Sama–Bajaw languages are a well-established group of languages spoken by the Sama-Bajau peoples of the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia.
Agusan is a Manobo language of northeastern Mindanao in the Philippines.
Tirahi is a nearly extinct if not already extinct Indo-Aryan language spoken in a few villages in the southeast of Jalalabad in the Nangarhar Province of eastern Afghanistan. It is spoken by older adults, who are likewise fluent in Pashto.

Kalanguya, also called Kallahan, is a dialect cluster spoken by the Kalanguya people of northern Luzon, Philippines.

Saint Vincent Ferrer Parish Church, commonly known as Dupax Church or Dupax del Sur Church, is an 18th-century Baroque Roman Catholic church located at Brgy. Dopaj, Dupax del Sur, Nueva Vizcaya, Philippines. The parish church, under the advocation of Saint Vincent Ferrer, is under the jurisdiction of the Diocese of Bayombong. The church complex has been declared a National Cultural Treasure by the National Museum of the Philippines in July 2001.
The Central Cordilleran languages are a group of closely related languages within the Northern Luzon subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in the interior highlands of Northern Luzon in the Cordillera Central mountain range.














