Related Research Articles

Mountain Province is a landlocked province of the Philippines in the Cordillera Administrative Region in Luzon. Its capital is Bontoc while Bauko is the largest municipality. Mountain Province was formerly referred to as Mountain in some foreign references. The name is usually shortened by locals to Mt. Province.

The Cordillera Central or Cordillera Range is a massive mountain range 320 kilometres (200 mi) long north–south and 118 kilometres (73 mi) east-west situated in the north-central part of the island of Luzon, in the Philippines. The mountain range encompasses all provinces of the Cordillera Administrative Region, as well as portions of eastern Ilocos Norte, eastern Ilocos Sur, eastern La Union, northeastern Pangasinan, western Nueva Vizcaya, and western Cagayan.

The indigenous peoples of the Cordillera in northern Luzon, Philippines, often referred to by the exonym Igorot people, or more recently, as the Cordilleran peoples, are an ethnic group composed of nine main ethnolinguistic groups whose domains are in the Cordillera Mountain Range, altogether numbering about 1.8 million people in the early 21st century.

The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw and the Molbog language—and form a subfamily of Austronesian languages. Although the Philippines is near the center of Austronesian expansion from Taiwan, there is relatively little linguistic diversity among the approximately 150 Philippine languages, suggesting that earlier diversity has been erased by the spread of the ancestor of the modern Philippine languages.
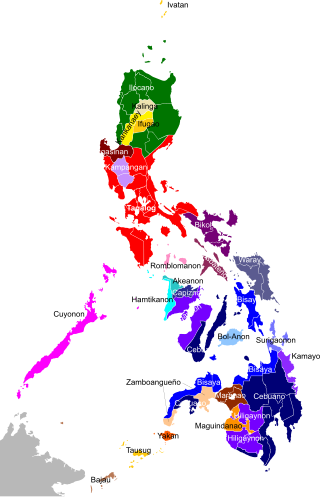
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous people groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither Indigenous nor Moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.
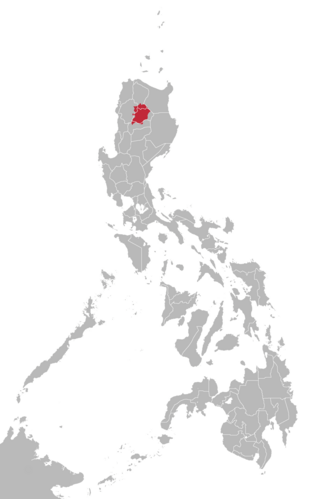
Kalinga is a dialect continuum of Kalinga Province in the Philippines, spoken by the Kalinga people, alongside Ilocano. The Banao Itneg variety is not one of the neighboring Itneg languages.

Bontoc (Bontok) is the native language of the indigenous Bontoc people of the Mountain Province, in the northern part of the Philippines.

The Kalinga people are an indigenous ethnic group whose ancestral domain is in the Cordillera Mountain Range of the northern Philippines. They are mainly found in Kalinga province which has an area of 3,282.58 sq. km. Some of them, however, already migrated to Mountain Province, Apayao, Cagayan, and Abra. The Kalinga numbered 163,167 as of 2010.

The Itneg are an Austronesian indigenous peoples from the upland province of Abra and Nueva Era, Ilocos Norte in northwestern Luzon, Philippines.

Itneg is a South-Central Cordilleran dialect continuum found in the island of Luzon, Philippines. This language and Ilocano are spoken by the Itneg people in Abra.
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification.

Isinai is a Northern Luzon language primarily spoken in Nueva Vizcaya province in the northern Philippines. By linguistic classification, it is more divergent from other Central Cordilleran languages, such as Kalinga, Itneg or Ifugao and Kankanaey.

Southern Alta, is a distinctive Aeta language of the mountains of northern Philippines. Southern Alta is one of many endangered languages that risks being lost if it is not passed on by current speakers. Most speakers of Southern Alta also speak Tagalog.
Alta is a pair of Meso-Cordilleran languages spoken in northern Luzon. As both are primary splits from Proto-South-Central Cordilleran, they are paraphyletic and do not form a subgroup with each other.
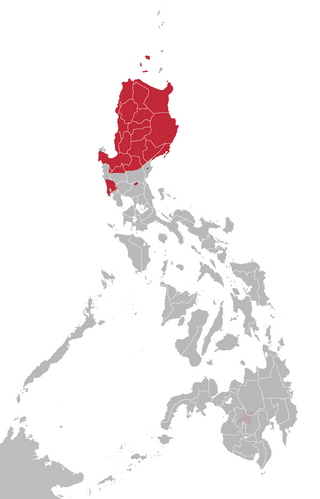
The Northern Luzon languages are one of the few established large groups within Philippine languages. These are mostly located in and around the Cordillera Central of northern Luzon in the Philippines. Among its major languages are Ilocano, Pangasinan and Ibanag.
The Southern Cordilleran languages are a group of closely related languages within the Northern Luzon subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in an area stretching from the southern shore of Lingayen Gulf to the highlands of Quirino province. The most widely spoken Southern Cordilleran language is Pangasinan, one of the eight major languages of the Philippines.
The Central Cordilleran languages are a group of closely related languages within the Northern Luzon subgroup of the Austronesian language family. They are spoken in the interior highlands of Northern Luzon in the Cordillera Central mountain range.

Batok, batek, patik, batik, or buri, among other names, are general terms for indigenous tattoos of the Philippines. Tattooing on both sexes was practiced by almost all ethnic groups of the Philippine Islands during the pre-colonial era. Like other Austronesian groups, these tattoos were made traditionally with hafted tools tapped with a length of wood. Each ethnic group had specific terms and designs for tattoos, which are also often the same designs used in other art forms and decorations such as pottery and weaving. Tattoos range from being restricted only to certain parts of the body to covering the entire body. Tattoos were symbols of tribal identity and kinship, as well as bravery, beauty, and social or wealth status.
Central Bontok is a language of the Bontoc group from the Philippines. The 2007 census claimed there were 19,600 speakers.
Southwestern Bontoc is a variety of the Bontoc language of the Philippines. This language is a moribund language, with only 2,470 speakers left in 2007.
References
- ↑ Himes, Ronald S. 2005. The Meso-Cordilleran Group of Philippine Languages. In Hsiu-chuan Liao and Carl R. Galvez Rubino (eds.), Current Issues in Philippine Linguistics and Anthropology: Parangal kay Lawrence A. Reid, 81-92. Manila, Philippines: Linguistic Society of the Philippines and SIL Philippines.