Related Research Articles

The Bicol Region, designated as Region V, is an administrative region of the Philippines. It comprises six provinces, four on the Bicol Peninsula : Albay, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, and Sorsogon, and two off the shore: Catanduanes and Masbate.

Camarines Sur, officially the Province of Camarines Sur, is a province in the Philippines located in the Bicol Region on Luzon. Its capital is Pili and the province borders Camarines Norte and Quezon to the northwest, and Albay to the south. To the east lies the island province of Catanduanes across the Maqueda Channel.

Buhi, officially the Municipality of Buhi, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 81,306 people.

Iriga, officially the City of Iriga, is a component city in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 114,457 people.
The Iraya language is a language spoken by Mangyans on the island of Mindoro in the Philippines. Zorc (1974) places the Iraya language within the North Mangyan group of Malayo-Polynesian languages, though Lobel (2013) notes that it shows "considerable differences" to Tadyawan and Alangan, the other languages in this group. There are 6,000 to 8,000 Iraya speakers, and that number is growing. The language status of Iraya is developing, meaning that this language is being put to use in a strong and healthy manner by its speakers, and it also has its own writing system.

Rinconada Bikol or simply Rinconada, spoken in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines, is one of several languages that compose the Inland Bikol group of the Bikol macrolanguage. It belongs to the Austronesian language family that also includes most Philippine languages, the Formosan languages of Taiwanese aborigines, Malay, the Polynesian languages and Malagasy.

Coastal Bikol is one of the three groups or family languages of Bikol languages. It includes Mt. Isarog Agta, Mt. Iraya Agta, Central Bikol, and Southern Catanduanes Bikol, sometimes classified as a dialect of Central Bikol.
Remontado, also known in literature as Sinauna, Kabalat, Remontado Dumagat, and more commonly by the autonym Hatang-Kayi, is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in Tanay, Rizal, General Nakar, Quezon, Rodriguez, Rizal and Antipolo, in the Philippines. It is one of the Philippine Negrito languages. It is a moribund language.
The Mamanwa language is a Central Philippine language spoken by the Mamanwa people. It is spoken in the provinces of Agusan del Norte and Surigao del Norte in the Lake Mainit area of Mindanao, Philippines. It had about 5,000 speakers in 1990.
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification.
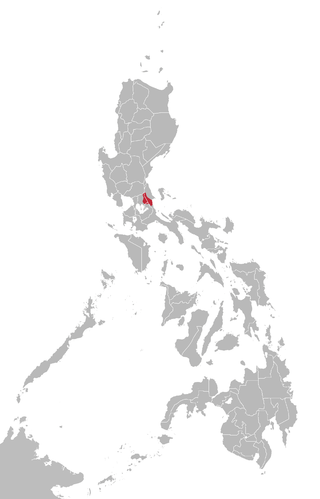
Inagta Rinconada is a Bikol language spoken by a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer Agta (Negrito) people of the Philippines. It is spoken to the east of Iriga City up to the shores of Lake Buhi. The language is largely intelligible with Mount Iraya Agta on the other side of the lake.
Inagta Partido or alternatively Katubung is a nearly extinct Bikol language spoken by a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer Agta (Negrito) people of the Philippines. It is found on Mount Isarog east of Naga City particularly in the town of Ocampo where the most recent survey of the language was conducted.
Casiguran Dumagat Agta, also known as Casiguran Agta, is a Northeastern Luzon language spoken in the northern Philippines. It is spoken by around 610 speakers, most of whom live in the San Ildefonso Peninsula, across the bay from Casiguran, Aurora.
Dicamay Agta is an extinct Aeta language of the northern Philippines. The Dicamay Agta lived on the Dicamay River, on the western side of the Sierra Madre near Jones, Isabela. The Dicamay Agta were killed by Ilocano homesteaders sometime between 1957 and 1974.
Kasiguranin (Casiguranin) is a Tagalogic language that is indigenous to the Casiguran town of Aurora in the northern Philippines. It is descended from an early Tagalog dialect that had borrowed heavily from Northeastern Luzon Agta languages, and, to a lesser extent, from Ilocano, Bikol languages, Kapampangan, Gaddang, Itawis, Ibanag, and Paranan, which were spoken by settlers from other parts of the Philippines.
Inagta Alabat is a Philippine Negrito language spoken in central Alabat Island, Philippines. Its speakers began arriving on the island in the 1970s but originated from Villa Espina in Lopez, with earlier settlements in Gumaca and perhaps other towns. Predating the Agta on Alabat Island were communities of individuals self-identifying as "dumagat" but who now only speak Tagalog as a native language. Less than a dozen individuals can still speak the Inagta Alabat language whether on Alabat Island, where it is being lost in favor of Tagalog, or in Lopez, where it is being replaced by the language of the Manide who have migrated to the area in large numbers and intermarried with the Agta, and also replaced by Tagalog. Those Agta who can still speak the Inagta language in Lopez speak the same language as the Agta who have migrated to Alabat over the past 50 years. Other Agta in Lopez either speak only Manide, or a mixture of Manide and Inagta Alabat-Lopez.
Katabangan is an extinct Aeta language that was spoken in the Bondoc Peninsula of Quezon Province, southern Luzon in the Philippines. It is misspelled Katabaga in Ethnologue.
The Northeastern Luzon languages is a primary subgroup of the Northern Luzon languages, proposed by Robinson & Lobel (2013) based on historical phonology, functors, and lexicon.
Nagtipunan Agta is a Northeastern Luzon language. It is one of the Aeta languages. The language was discovered by Jason Lobel and Laura Robinson in Nagtipunan, Quirino. Nagtipunan Agta is most closely related to Casiguran Dumagat Agta.

The Bikol languages or Bicolano languages are a group of Central Philippine languages spoken mostly in the Bicol Peninsula in the southeastern part of Luzon, the neighboring island-province of Catanduanes, and the island of Burias in Masbate.
References
- Lobel, Jason William (2013). Philippine and North Bornean Languages: Issues in Description, Subgrouping, and Reconstruction (PDF) (PhD dissertation). University of Hawaii at Manoa.