Related Research Articles

Mindoro is the seventh largest and eighth-most populous island in the Philippines. With a total land area of 10,571 km2, it has a population of 1,408,454, as of the 2020 census. It is located off the southwestern coast of Luzon and northeast of Palawan. Mindoro is divided into two provinces: Occidental Mindoro and Oriental Mindoro. Calapan is the only city in the island while San Jose is the largest settlement on the island with a total population of 143,430 inhabitants as of 2015. The southern coast of Mindoro forms the northeastern extremum of the Sulu Sea. Mount Halcon is the highest point on the island, standing at 8,484 feet (2,586 m) above sea level located in Oriental Mindoro. Mount Baco is the island's second highest mountain with an elevation of 8,163 feet (2,488 m), located in the province of Occidental Mindoro.

Oriental Mindoro, officially the Province of Oriental Mindoro, is a province in the Philippines located on the island of Mindoro under Mimaropa region in Luzon, about 140 kilometres (87 mi) southwest of Manila. The province is bordered by the Verde Island Passage and the rest of Batangas to the north, by Marinduque, Maestre de Campo Island, Tablas Strait and the rest of Romblon to the east, by Semirara and the rest of Caluya Islands, Antique to the south, and by Occidental Mindoro to the west. Its provincial capital Calapan, the only city in the island, is the most-populous in the province, and Mimaropa's regional center.

Occidental Mindoro, officially the Province of Occidental Mindoro, is a province in the Philippines located in the Mimaropa region. The province occupies the western half of the island of Mindoro. Its capital is Mamburao, but the most populous municipality is San Jose. Sablayan is its largest municipality in terms of area, occupying almost half of the entire province. As of 2020, Occidental Mindoro has 525,354 inhabitants.

Southern Tagalog, designated as Region IV, was an administrative region in the Philippines that comprised the current regions of Calabarzon and Mimaropa, the province of Aurora in Central Luzon, and most of the National Capital Region. It was the largest region in the Philippines in terms of both land area and population. After its partition on May 17, 2002, Southern Tagalog continues to exist as a cultural-geographical region.
The Central Philippine languages are the most geographically widespread demonstrated group of languages in the Philippines, being spoken in southern Luzon, Visayas, Mindanao, and Sulu. They are also the most populous, including Tagalog, Bikol, and the major Visayan languages Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Waray, Kinaray-a, and Tausug, with some forty languages all together.
Ratagnon is a regional language spoken by the Ratagnon people, an indigenous group from Occidental Mindoro. It is a part of the Bisayan language family and is closely related to other Philippine languages. Its speakers are shifting to Tagalog. In 2000, there were only two to five speakers of the language. However, in 2010 Ethnologue had reported there were 310 new speakers.
Ratagnon is one of the eight indigenous groups of Mangyan in the southernmost tip of Occidental Mindoro and the Mindoro Islands along the Sulu Sea, in the Philippines. The Ratagnon live in the southernmost part of the municipality of Magsaysay in Occidental Mindoro. Their language is similar to the Visayan Cuyunon language, spoken by the inhabitants of Cuyo Island in Northern Palawan.

Mangyan is the generic name for the eight indigenous groups found in Mindoro each with its own tribal name, language, and customs. The total population may be around 280,001, but official statistics are difficult to determine under the conditions of remote areas, reclusive tribal groups and some having little if any outside world contact.

Socorro, officially the Municipality of Socorro, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Oriental Mindoro, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 41,585 people.

Naujan Lake is a freshwater lake in the Philippines located in the northeastern corner of the province of Oriental Mindoro on Mindoro Island. The lake is the fifth largest in the country and the main geographical feature of the Naujan Lake National Park. The entire area is a Ramsar Wetland Site since 1999.
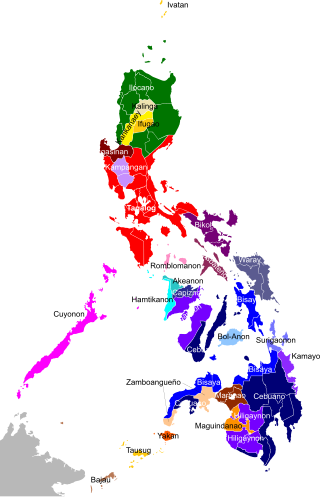
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous people groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither Indigenous nor Moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.
The Buhid language is a language spoken by Mangyans in the island of Mindoro, Philippines. It is divided into eastern and western dialects.
Hanunoo, or Hanunó'o, is a language spoken by Mangyans in the island of Mindoro, Philippines.
The Alangan language is a language spoken by Mangyans in the province of Mindoro in the Philippines.
The Iraya language is a language spoken by Mangyans on the island of Mindoro in the Philippines. Zorc (1974) places the Iraya language within the North Mangyan group of Malayo-Polynesian languages, though Lobel (2013) notes that it shows "considerable differences" to Tadyawan and Alangan, the other languages in this group. There are 6,000 to 8,000 Iraya speakers, and that number is growing. The language status of Iraya is developing, meaning that this language is being put to use in a strong and healthy manner by its speakers, and it also has its own writing system.
Mina de Oro Catholic School is a Private Parochial Catholic School in Socorro, Oriental Mindoro, Philippines. It is located on Fr. Bernard Peters Street, Zone III, Socorro, Oriental Mindoro, Philippines and was established in August 1963.
Iraya can refer to:
The Southern Mindoro languages are one of two small clusters of Austronesian languages spoken by the Mangyan people of Mindoro Island in the Philippines. They make up a branch of the Greater Central Philippine subgroup.
The Northern Mindoro languages are one of two small clusters of languages spoken by the Mangyan people of Mindoro Island in the Philippines.
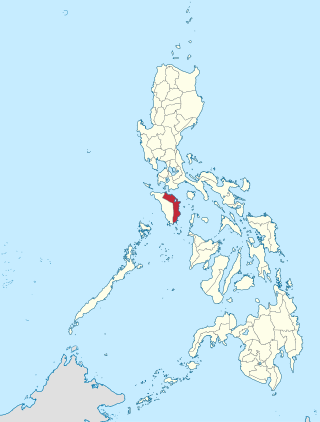
Oriental Mindoro's 1st congressional district is one of the two congressional districts of the Philippines in the province of Oriental Mindoro. It has been represented in the House of Representatives since 1987. The district encompasses the province's northern half composed of its capital city Calapan and the municipalities of Baco, Naujan, Pola, Puerto Galera, San Teodoro, Socorro and Victoria. It is currently represented in the 19th Congress by Arnan C. Panaligan of the Lakas–CMD.
References
- ↑ Tadyawan at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Tweddell, Colin E. 1970. “The Identity and Distribution of the Mangyan Tribes of Mindoro, Philippines”. Anthropological Linguistics 12 (6).
- ↑ Barbian, Karl-Josef. 1977. English-Mangyan vocabulary. Cebu City: University of San Carlos.