Related Research Articles

Palawan, officially the Province of Palawan, is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in terms of total area of 14,649.73 km2 (5,656.29 sq mi). The capital and largest city is Puerto Princesa which is geographically grouped with but administered independently from the province. Palawan is known as the Philippines' Last Frontier and as the Philippines' Best Island.

Mimaropa, officially the Southwestern Tagalog Region, is an administrative region in the Philippines. The name is an acronym combination of its constituent provinces: Mindoro, Marinduque, Romblon, and Palawan. It is the only region in the country outside the Visayas that has no land border with another region.

Southern Tagalog, designated as Region IV, was an administrative region in the Philippines that comprised the current regions of Calabarzon and Mimaropa, the province of Aurora in Central Luzon, and most of the National Capital Region. It was the largest region in the Philippines in terms of both land area and population. After its partition on May 17, 2002, Southern Tagalog continues to exist as a cultural-geographical region.

Tagbanwa is one of the scripts indigenous to the Philippines, used by the Tagbanwa and the Palawan people as their ethnic writing system.

The Batak are one of about 140 indigenous peoples of the Philippines. They are located in the northeastern portions of Palawan, a relatively large island in the southwest of the archipelago. Since ancient times, the Batak have inhabited a series of river valleys along the coastline of what is today Puerto Princesa City.
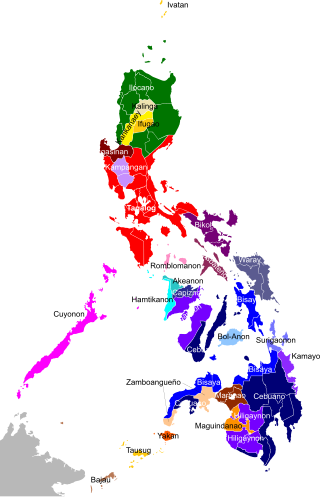
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous people groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither Indigenous nor Moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.

Palawan, the largest province in the Philippines, is home to several indigenous ethnolinguistic groups namely, the Kagayanen, Tagbanwa, Palawano, Taaw't Bato, Molbog, and Batak tribes. They live in remote villages in the mountains and coastal areas.

The babandil is a single, narrow-rimmed Philippine gong used primarily as the “timekeeper” of the Maguindanao kulintang ensemble.

The Tagbanwa people are an indigenous peoples and one of the oldest ethnic groups in the Philippines, mainly found in central and northern Palawan. Research has shown that the Tagbanwa are possible descendants of the Tabon Man, thus making them one of the original inhabitants of the Philippines. They are a brown-skinned, slim, and straight-haired ethnic group.
The Palawano languages are spoken in the province of Palawan in the Philippines, by the Palawano people.
The Kalamian languages are a small cluster of languages spoken in the Philippines: Calamian Tagbanwa and Agutaynen. Other languages called Tagbanwa, the Aborlan Tagbanwa language and Central Tagbanwa language are members of the Palawanic languages.
The Northwest Sumatra–Barrier Islands languages are a group of Malayo-Polynesian languages spoken by the Batak and related peoples in the interior of North Sumatra and by the Nias, Mentawai people, and others on the Barrier islands off the western coast of Sumatra, Indonesia.
The Palawanic languages are a subgroup in the Greater Central Philippine-family spoken on the island of Palawan and nearby islets.
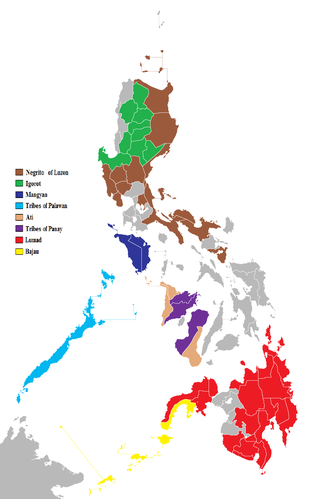
The indigenous peoples of the Philippines are ethnolinguistic groups or subgroups that maintain partial isolation or independence throughout the colonial era, and have retained much of their traditional pre-colonial culture and practices.
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *R to *g. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, eastern and western parts of Sabah, Malaysia and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field.
Molbog is an Austronesian language spoken in the Philippines and Sabah, Malaysia. The majority of speakers are concentrated at the southernmost tip of the Philippine province of Palawan, specifically the municipalities of Bataraza and Balabac. Both municipalities are considered as bastions for environmental conservation in the province. The majority of Molbog speakers are Muslims.
Calamian Tagbanwa is spoken in the Calamian Islands just north of Palawan Island, Philippines. It is not mutually intelligible with the other languages of the Tagbanwa people. Ethnologue reports that it is spoken in Busuanga, Coron, Culion, and Linapacan municipalities.
Aborlan Tagbanwa is spoken on Palawan Island in the Philippines. It is not mutually intelligible with the other languages of the Tagbanwa people.
Central Tagbanwa is spoken on Palawan Island in the Philippines. It is not mutually intelligible with the other languages of the Tagbanwa people.
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification.
References
- 1 2 Batak at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Lobel, Jason (2013). Philippine and North Bornean Languages: Issues in Description, Subgrouping, and Reconstruction (PDF) (PhD thesis). University of Hawaiʻi. p. 87.
- 1 2 Reid, Lawrence A. (1971). Philippine Minor Languages: Word Lists and Phonologies. Oceanic Linguistics Special Publications. University of Hawai'i Press. p. 4. ISBN 087022-691-6. JSTOR 20019132. LCCN 70-150659.
- ↑ Morey, Virginia (1961). "Some particles and pronouns in Batak". Philippine Journal of Science. 90: 263–270.