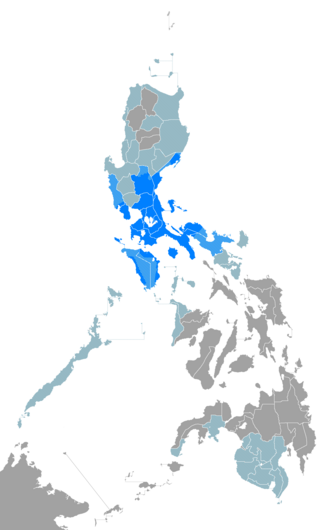
Tagalog is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority, mostly as or through Filipino. Its standardized, codified, national or nationalized, intellectualized, more linguistically inclusive, more linguistically dynamic, and expanded or broaden form, officially named Filipino, is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of the latter's two official languages, alongside English. Tagalog, like the other and as one of the regional languages of the Philippines, which majority are Austronesian, is one of the auxiliary official languages of the Philippines in the regions and also one of the auxiliary media of instruction therein.

Zambales, officially the Province of Zambales, is a province in the Philippines located in the Central Luzon region. Its capital is Iba, which is located in the middle of the province. Olongapo is the largest city of the province wherein it is geographically located but politically independent.
Baybayin or Sulat Tagalog, also called Basahan by Bicolanos, sometimes erroneously referred to as alibata, is a Philippine script widely used primarily in Luzon during the 16th and 17th centuries and prior to write Tagalog and to a lesser extent Visayan languages, Kampampangan, Ilocano, and several other Philippine languages.
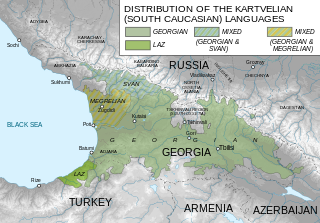
Svan is a Kartvelian language spoken in the western Georgian region of Svaneti primarily by the Svan people. With its speakers variously estimated to be between 30,000 and 80,000, the UNESCO designates Svan as a "definitely endangered language". It is of particular interest because it has retained many features that have been lost in the other Kartvelian languages.

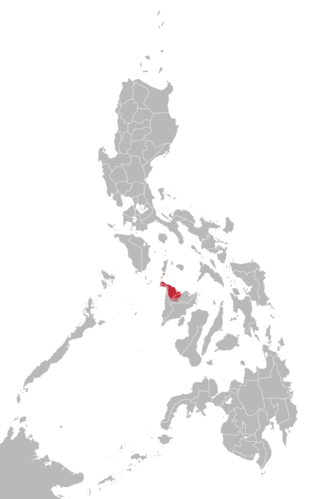
Kapampangan, Capampáñgan, or Pampangan is an Austronesian language, and one of the eight major languages of the Philippines. It is the primary and predominant language of the entire province of Pampanga and southern Tarlac, on the southern part of Luzon's central plains geographic region, where the Kapampangan ethnic group resides. Kapampangan is also spoken in northeastern Bataan, as well as in the provinces of Bulacan, Nueva Ecija, and Zambales that border Pampanga. It is further spoken as a second language by a few Aeta groups in the southern part of Central Luzon. The language is known honorifically as Amánung Sísuan.

Marshallese, also known as Ebon, is a Micronesian language spoken in the Marshall Islands. The language of the Marshallese people, it is spoken by nearly all of the country's population of 59,000, making it the principal language. There are also roughly 27,000 Marshallese citizens residing in the United States, nearly all of whom speak Marshallese, as well as residents in other countries such as Nauru and Kiribati.

Maranao is an Austronesian language spoken by the Maranao people in the provinces of Lanao del Sur and Lanao del Norte and the cities of Marawi and Iligan City in the Philippines, as well as in Sabah, Malaysia. It is a subgroup of the Danao languages of the Moros in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao.
Tagalog grammar are the rules that describe the structure of expressions in the Tagalog language, one of the languages in the Philippines.

The Sambal people are a Filipino ethnolinguistic group living primarily in the province of Zambales and the Pangasinense municipalities of Bolinao, Anda, and Infanta. The term may also refer to the general inhabitants of Zambales. They were also referred to as the Zambales during the Spanish colonial era.
Aklanon (Akeanon), also known as Bisaya/Binisaya nga Aklanon/Inaklanon or simply Aklan, is an Austronesian language of the Bisayan subgroup spoken by the Aklanon people in the province of Aklan on the island of Panay in the Philippines. Its unique feature among other Bisayan languages is the close-mid back unrounded vowel occurring as part of diphthongs and traditionally written with the letter ⟨Ee⟩ such as in the autonyms Akean and Akeanon. However, this phoneme is also present in other but geographically scattered and distant Philippine languages, namely Itbayat, Isneg, Manobo, Samal and Sagada.
The Tawbuid language is a language spoken by Tawbuid Mangyans in the province of Mindoro in the Philippines. It is divided into eastern and western dialects. The Bangon Mangyans also speak the western dialect of Tawbuid.
The Bolinao language or Binubolinao is a Central Luzon language spoken primarily in the municipalities of Bolinao and Anda, Pangasinan in the Philippines. It has approximately 50,000 speakers, making it the second most widely spoken Sambalic language. Most Bolinao speakers can speak Pangasinan and/or Ilocano. Ethnologue reports 510 monolinguals for this language.

Hajong is an Indo-Aryan language with a possible Tibeto-Burman language substratum. It is spoken by approximately 80,000 ethnic Hajongs across the northeast of the Indian subcontinent, specifically in the states of Assam, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh, and West Bengal in present-day India, and the divisions of Mymensingh and Sylhet in present-day Bangladesh. It is written in Bengali-Assamese script and Latin script. It has many Sanskrit loanwords. The Hajongs originally spoke a Tibeto-Burman language, but it later mixed with Assamese and Bengali.
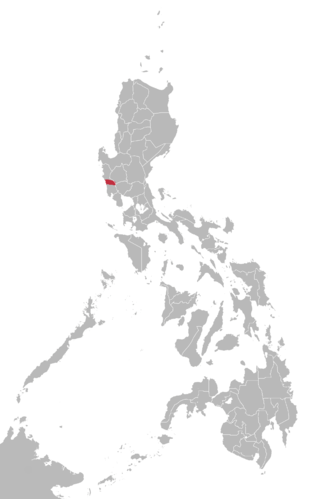
The Sambalic languages are a part of the Central Luzon language family spoken by the Sambals, an ethnolinguistic group on the western coastal areas of Central Luzon and the Zambales mountain ranges.
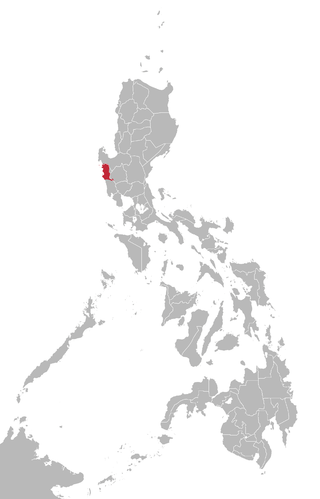
Sambal or Sambali is a Sambalic language spoken primarily in the Zambal municipalities of Santa Cruz, Candelaria, Masinloc, Palauig, and Iba, in the Pangasinense municipality of Infanta, and areas of Pampanga in the boundary with Zambales in the Philippines; speakers can also be found in Panitian, Quezon, Palawan and Barangay Mandaragat or Buncag of Puerto Princesa. The speakers of the language are decreasing due to the fact that many of the speakers are shifting to Tagalog and Ilocano.
Abellen, Abenlen, Aburlin, or Ayta Abellen, is a Sambalic language. It has about 3,500 speakers and is spoken in a few Aeta communities in Tarlac province, Philippines. Ayta Abellen itself is part of the Sambalic language family in the Philippines and is closely related to not only the five other Ayta dialects but also the Botolan dialect of Sambal. Ethnologue reports 45 monolinguists.

Rinconada Bikol or simply Rinconada, spoken in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines, is one of several languages that compose the Inland Bikol group of the Bikol macrolanguage. It belongs to the Austronesian language family that also includes most Philippine languages, the Formosan languages of Taiwanese aborigines, Malay, the Polynesian languages and Malagasy.
Pech or Pesh is a Chibchan language spoken in Honduras. It was formerly known as Paya, and continues to be referred to in this manner by several sources, though there are negative connotations associated with this term. It has also been referred to as Seco. There are 300 speakers according to Yasugi (2007). It is spoken near the north-central coast of Honduras, in the Dulce Nombre de Culmí municipality of Olancho Department.
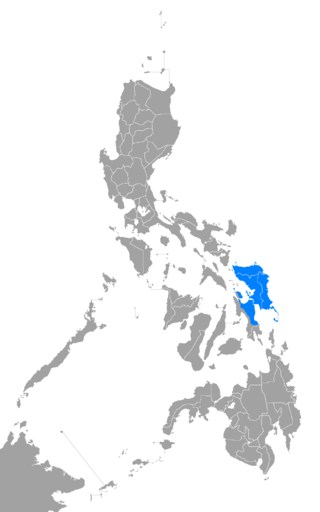
Waray is an Austronesian language and the fifth-most-spoken native regional language of the Philippines, native to Eastern Visayas. It is the native language of the Waray people and second language of the Abaknon people of Capul, Northern Samar, and some Cebuano-speaking peoples of western and southern parts of Leyte island. It is the third most spoken language among the Bisayan languages, only behind Cebuano and Hiligaynon.

Iloco is an Austronesian language predominantly spoken in the Philippines by the Ilocano people. It ranks as the third most widely spoken native language in the country and serves as a lingua franca in Northern Luzon, particularly among the Igorot people and the indigenous settlers of Cagayan Valley.