Related Research Articles
Mongondow, or Bolaang Mongondow, is one of the Philippine languages spoken in Bolaang Mongondow Regency and neighbouring regencies of North Sulawesi (Celebes) and Gorontalo Provinces, Indonesia. With more than 200,000 speakers, it is the major language of the regency. Historically, it served as the official language of the Bolaang Mongondow Kingdom.
The Murutic languages are a family of half a dozen closely related Austronesian languages, spoken in the northern inland regions of Borneo by the Murut and Tidung.

Buol Regency is a regency of Central Sulawesi Province of Indonesia. It was created on 4 October 1999, having previously been the eastern half of a larger Buol Tolitoli Regency. It covers an area of 4,043.57 km2, and had a population of 132,330 at the 2010 Census; and 145,254 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 150,524. The administrative centre is the town of Buol, in Biau District.
The Gorontalo–Mongondow languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia.
The Paitanic languages are a group of languages spoken in Sabah (Borneo) Several go by the name Lobu.
The Sabahan languages are a group of Austronesian languages centered on the Bornean province of Sabah.
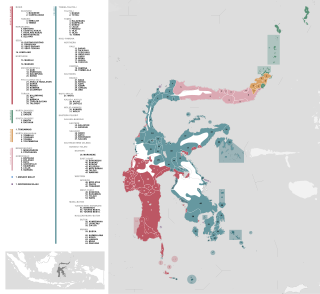
On the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, 114 native languages are spoken, all of which belong to the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. With a total number of 17,200,000 inhabitants, Sulawesi displays a high linguistic diversity when compared with the most densely populated Indonesian island Java, which hosts 4–8 languages spoken by 145,100,000 inhabitants.
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *R to *g. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, eastern and western parts of Sabah, Malaysia and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field.
The Mamanwa language is a Central Philippine language spoken by the Mamanwa people. It is spoken in the provinces of Agusan del Norte and Surigao del Norte in the Lake Mainit area of Mindanao, Philippines. It had about 5,000 speakers in 1990.

Bolaang Mongondow Regency is a regency of North Sulawesi Province, Indonesia, situated on the island of Sulawesi. The principal town lies at Kotamobagu, which since 2007 has been administratively separated from the regency, the administrative centre of which is now at the town of Lolak. The regency covers a land area of 2,933.6 km2, and had a population of 213,484 at the 2010 Census and 248,751 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 254,945.
Molbog is an Austronesian language spoken in the Philippines and Sabah, Malaysia. The majority of speakers are concentrated at the southernmost tip of the Philippine province of Palawan, specifically the municipalities of Bataraza and Balabac. Both municipalities are considered as bastions for environmental conservation in the province. The majority of Molbog speakers are Muslims.
Arta is a highly endangered Negrito language of the northern Philippines.
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification.
Inagta Partido or alternatively Katubung is a nearly extinct Bikol language spoken by a semi-nomadic hunter-gatherer Agta (Negrito) people of the Philippines. It is found on Mount Isarog east of Naga City particularly in the town of Ocampo where the most recent survey of the language was conducted.
Ponosakan is a moribund Austronesian language spoken in the vicinity of the town of Belang, North Sulawesi, Indonesia. This language is almost extinct, with only four fluent speakers left as of November 2014.
Casiguran Dumagat Agta, also known as Casiguran Agta, is a Northeastern Luzon language spoken in the northern Philippines. It is spoken by around 610 speakers, most of whom live in the San Ildefonso Peninsula, across the bay from Casiguran, Aurora.
Umiray Dumaget is an Aeta language spoken in southern Luzon Island, Philippines.
Inagta Alabat is a Philippine Negrito language spoken in central Alabat Island, Philippines. Its speakers began arriving on the island in the 1970s but originated from Villa Espina in Lopez, with earlier settlements in Gumaca and perhaps other towns. Predating the Agta on Alabat Island were communities of individuals self-identifying as "dumagat" but who now only speak Tagalog as a native language. Less than a dozen individuals can still speak the Inagta Alabat language whether on Alabat Island, where it is being lost in favor of Tagalog, or in Lopez, where it is being replaced by the language of the Manide who have migrated to the area in large numbers and intermarried with the Agta, and also replaced by Tagalog. Those Agta who can still speak the Inagta language in Lopez speak the same language as the Agta who have migrated to Alabat over the past 50 years. Other Agta in Lopez either speak only Manide, or a mixture of Manide and Inagta Alabat-Lopez.
The Northeastern Luzon languages is a primary subgroup of the Northern Luzon languages, proposed by Robinson & Lobel (2013) based on historical phonology, functors, and lexicon.
Nagtipunan Agta is a Northeastern Luzon language. It is one of the Aeta languages. The language was discovered by Jason Lobel and Laura Robinson in Nagtipunan, Quirino. Nagtipunan Agta is most closely related to Casiguran Dumagat Agta.
References
- Lobel, Jason William; Paputungan, Ade Tatak (2017). "Notes from the field: Lolak: Another moribund language of Indonesia, with supporting audio". Language Documentation & Conservation. 11: 328–366. hdl: 10125/24758 .