Related Research Articles
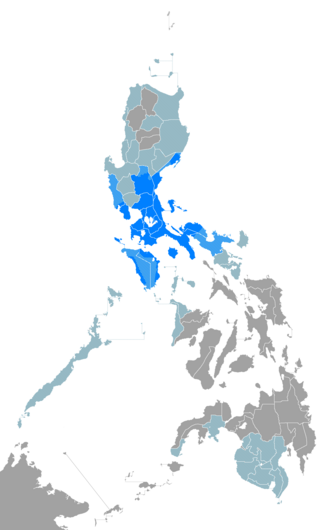
Tagalog is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority, mostly as or through Filipino. Its standardized, codified, national or nationalized, intellectualized, more linguistically inclusive, more linguistically dynamic, and expanded or broaden form, officially named Filipino, is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of the latter's two official languages, alongside English. Tagalog, like the other and as one of the regional languages of the Philippines, which majority are Austronesian, is one of the auxiliary official languages of the Philippines in the regions and also one of the auxiliary media of instruction therein.

Palawan, officially the Province of Palawan, is an archipelagic province of the Philippines that is located in the region of Mimaropa. It is the largest province in the country in terms of total area of 14,649.73 km2 (5,656.29 sq mi). The capital and largest city is Puerto Princesa which is geographically grouped with but administered independently from the province. Palawan is known as the Philippines' Last Frontier and as the Philippines' Best Island.

Cebuano is an Austronesian language spoken in the southern Philippines. It is natively, though informally, called by its generic term Bisayâ or Binisayâ and sometimes referred to in English sources as Cebuan. It is spoken by the Visayan ethnolinguistic groups native to the islands of Cebu, Bohol, Siquijor, the eastern half of Negros, the western half of Leyte, and the northern coastal areas of Northern Mindanao and the eastern part of Zamboanga del Norte due to Spanish settlements during the 18th century. In modern times, it has also spread to the Davao Region, Cotabato, Camiguin, parts of the Dinagat Islands, and the lowland regions of Caraga, often displacing native languages in those areas.

Tagbanwa is one of the scripts indigenous to the Philippines, used by the Tagbanwa and the Palawan people as their ethnic writing system.

The Bisayan languages or Visayan languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken in the Philippines. They are most closely related to Tagalog and the Bikol languages, all of which are part of the Central Philippine languages. Most Bisayan languages are spoken in the whole Visayas section of the country, but they are also spoken in the southern part of the Bicol Region, islands south of Luzon, such as those that make up Romblon, most of the areas of Mindanao and the province of Sulu located southwest of Mindanao. Some residents of Metro Manila also speak one of the Bisayan languages.

Tausūg is an Austronesian language spoken in the province of Sulu in the Philippines and in the eastern area of the state of Sabah, Malaysia as well as in the Nunukan Regency, province of North Kalimantan, Indonesia by the Tausūg people. It is widely spoken in the Sulu Archipelago, the Zamboanga Peninsula, southern Palawan, Malaysia and Indonesia.
Palawan is the largest island of the province of Palawan in the Philippines and fifth-largest by area and tenth-most populous island of the country, with a total population of 994,101 as of 2020 census. The northwest coast of the island is along the Palawan Passage in the eastern South China Sea, while the southeast coast forms part of the northern limit of the Sulu Sea. Much of the island remains traditional and is considered by some as under-developed. Abundant wildlife, jungle mountains, and some white sandy beaches attract many tourists, as well as international companies looking for development opportunities.
The Central Philippine languages are the most geographically widespread demonstrated group of languages in the Philippines, being spoken in southern Luzon, Visayas, Mindanao, and Sulu. They are also the most populous, including Tagalog, Bikol, and the major Visayan languages Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Waray, Kinaray-a, and Tausug, with some forty languages all together.
Ratagnon is a regional language spoken by the Ratagnon people, an indigenous group from Occidental Mindoro. It is a part of the Bisayan language family and is closely related to other Philippine languages. Its speakers are shifting to Tagalog. In 2000, there were only two to five speakers of the language. However, in 2010 Ethnologue had reported there were 310 new speakers.

Agutaya, officially the Municipality of Agutaya, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Palawan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 12,867 people.

Cuyo, officially the Municipality of Cuyo, is a 4th class municipality in the province of Palawan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 23,489 people.

Magsaysay, officially the Municipality of Magsaysay, is a 5th class municipality in the province of Palawan, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 12,603 people.
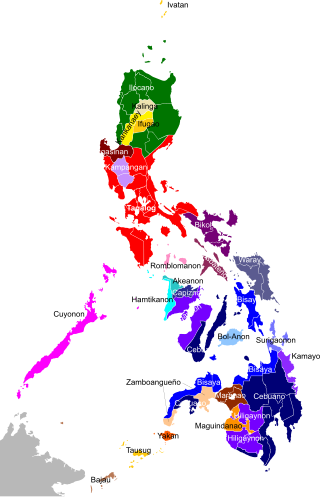
The Philippines is inhabited by more than 182 ethnolinguistic groups, many of which are classified as "Indigenous Peoples" under the country's Indigenous Peoples' Rights Act of 1997. Traditionally-Muslim peoples from the southernmost island group of Mindanao are usually categorized together as Moro peoples, whether they are classified as Indigenous peoples or not. About 142 are classified as non-Muslim Indigenous people groups, and about 19 ethnolinguistic groups are classified as neither Indigenous nor Moro. Various migrant groups have also had a significant presence throughout the country's history.
Cuyonon refers to an ethnic group populating the Cuyo Islands, along with northern and central Palawan. The Cuyonons hail originally from Cuyo and the surrounding Cuyo Islands, a group of islands and islets in the northern Sulu Sea, to the north east of Palawan. They are considered an elite class among the hierarchy of native Palaweños. They are part of the wider Visayan ethnolinguistic group, who constitute the largest Filipino ethnolinguistic group.
The Palawano languages are spoken in the province of Palawan in the Philippines, by the Palawano people.
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *R to *g. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines, eastern and western parts of Sabah, Malaysia and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field.

The Ibanag language is an Austronesian language spoken by up to 500,000 speakers, most particularly by the Ibanag people, in the Philippines, in the northeastern provinces of Isabela and Cagayan, especially in Tuguegarao, Solana, Abulug, Camalaniugan, Lal-lo, Cabagan, Tumauini, San Pablo, Sto. Tomas, Sta. Maria, and Ilagan and other neighboring towns and villages around the Cagayan River and with overseas immigrants in countries located in the Middle East, United Kingdom, and the United States. Most of the speakers can also speak Ilocano, the lingua franca of northern Luzon island. The name Ibanag comes from the prefix I which means 'people of', and bannag, meaning 'river'. It is closely related to Gaddang, Itawis, Agta, Atta, Yogad, Isneg, and Malaweg.

The Karay-a language is an Austronesian regional language in the Philippines spoken by the Karay-a people, mainly in Antique.

Hiligaynon, also often referred to as Ilonggo or Binisayâ/Bisayâ nga Hiniligaynon/Inilonggo, is an Austronesian regional language spoken in the Philippines by about 9.1 million people, predominantly in Western Visayas, Negros Island Region, and Soccsksargen, most of whom belong to the Hiligaynon people. It is the second-most widely spoken language in the Visayas and belongs to the Bisayan languages, and it is more distantly related to other Philippine languages.
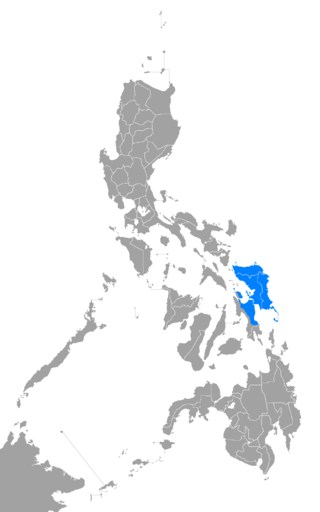
Waray is an Austronesian language and the fifth-most-spoken native regional language of the Philippines, native to Eastern Visayas. It is the native language of the Waray people and second language of the Abaknon people of Capul, Northern Samar, and some Cebuano-speaking peoples of western and southern parts of Leyte island. It is the third most spoken language among the Bisayan languages, only behind Cebuano and Hiligaynon.
References
- ↑ Cuyonon at Ethnologue (25th ed., 2022)

- ↑ Palawan Tourism Council. Accessed August 28, 2008.
- ↑ DeVries; Roe, Virginia H.; G. Richard (1967). Semivowels in the Coyono Alphabet. Manila Bureau of Printing. pp. 268–273.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)