Related Research Articles

Malay is an Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore. It is also spoken in East Timor and southern part of Thailand. Altogether, it is spoken by 290 million people across Maritime Southeast Asia.

Makassarese, sometimes called Makasar, Makassar, or Macassar, is a language of the Makassarese people, spoken in South Sulawesi province of Indonesia. It is a member of the South Sulawesi group of the Austronesian language family, and thus closely related to, among others, Buginese, also known as Bugis. The areas where Makassarese is spoken include the Gowa, Sinjai, Maros, Takalar, Jeneponto, Bantaeng, Pangkajene and Islands, Bulukumba, and Selayar Islands Regencies, and Makassar. Within the Austronesian language family, Makassarese is part of the South Sulawesi language group, although its vocabulary is considered divergent compared to its closest relatives. In 2000, Makassarese had approximately 2.1 million native speakers.

In addition to its classical and modern literary form, Malay had various regional dialects established after the rise of the Srivijaya empire in Sumatra, Indonesia. Also, Malay spread through interethnic contact and trade across the south East Asia Archipelago as far as the Philippines. That contact resulted in a lingua franca that was called Bazaar Malay or low Malay and in Malay Melayu Pasar. It is generally believed that Bazaar Malay was a pidgin, influenced by contact among Malay, Hokkien, Portuguese, and Dutch traders.
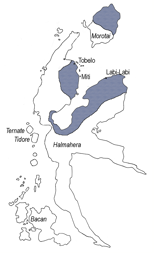
Tobelo is a North Halmahera language spoken on the eastern Indonesian island of Halmahera and on parts of several neighboring islands. The Tobelo-speaking heartland is in the six administrative districts of Tobelo, located on the western shore of Kao Bay and forming the central part of Halmahera Utara Regency. Other Tobelo speaking areas are the five districts of Wasile on the south and east coast of Kao Bay, and the northern half of Morotai Island. The district capital, also known as Tobelo, serves as a regional commercial and administrative center and is the largest settlement on Halmahera.

Jambi Malay, is a Malayic language primarily spoken by the Jambi Malay people in Jambi, Indonesia, but also spoken by migrants who have settled in Jambi. Jambi Malay is considered as a dialect of the Malay language that is mainly spoken in Jambi, but it is also used in the southern part of Riau and the northern part of South Sumatra. In Jambi, Jambi Malay has eight dialects, including the Tanjung Jabung dialect, Jambi City dialect, Muaro Jambi dialect, Batanghari dialect, Tebo dialect, Bungo dialect, Sarolangun dialect, and Merangin dialect. Jambi Malay is used as a lingua franca and for interaction among the various ethnic groups in Jambi. The differences between each dialect in Jambi Malay range from about 51 to 80 percent.

The Banjar or Banjarese is an Austronesian language predominantly spoken by the Banjarese—an indigenous ethnic group native to Banjar regions— in the southeastern Kalimantan of Indonesia. The Banjarese language is the de facto lingua franca for various indigenous community especially in South Kalimantan, as well as Central Kalimantan and East Kalimantan in general.
Sougb, or Sogh, is a Papuan language of the East Bird's Head language family spoken in the east of the Bird's Head Peninsula to the east of Meyah and to the south of Manokwari, including the area of Soug Jaya District, Teluk Wondama Regency. It consists of four dialects and is spoken by around 12,000 people in all. The language is alternatively known as Mantion, or Manikion, an originally derogatory term used by the Biak people.

Acehnese is an Austronesian language natively spoken by the Acehnese people in Aceh, Sumatra, Indonesia. This language is also spoken by Acehnese descendants in some parts of Malaysia like Yan, in Kedah. Acehnese is used as the co-official language in the province of Aceh, alongside Indonesian.

Maʼya is an Austronesian language of the Raja Ampat islands in Southwest Papua, Indonesia. It is part of the South Halmahera–West New Guinea (SHWNG) subgroup and is spoken by about 6,000 people in coastal villages on the islands Misool, Salawati, and Waigeo, on the boundary between Austronesian and Papuan languages.
The Bima language, or Bimanese, is an Austronesian language spoken on the eastern half of Sumbawa Island, Indonesia, which it shares with speakers of the Sumbawa language. Bima territory includes the Sanggar Peninsula, where the extinct Papuan language Tambora was once spoken. Bima is an exonym; the autochthonous name for the territory is Mbojo and the language is referred to as Nggahi Mbojo. There are over half a million Bima speakers. Neither the Bima nor the Sumbawa people have alphabets of their own for they use the alphabets of the Bugis and the Malay language indifferently.
Yaqay is a Papuan language spoken in Indonesia by over 10,000 people. It is also called Mapi or Sohur; dialects are Oba-Miwamon, Nambiomon-Mabur, Bapai.
Irarutu, Irahutu, or Kasira is an Austronesian language of most of the interior of the Bomberai Peninsula of north-western New Guinea in Teluk Bintuni Regency. The name Irarutu comes from the language itself, where ira conjoins with ru to create 'their voice'. When put together with tu, which on its own means 'true', the meaning of the name becomes 'Their true voice' or 'The people's true language'.
Talaud is an Austronesian language spoken on the Talaud Islands north of Sulawesi, Indonesia. There are 2 dialects, namely Lami dialect which is spoken on Miangas, Nanusa Islands, and Esang in the northern part of Karakelang Island; Tirawata dialect is used in Lirung, Kabaruan, and the southern part of Karakelang Island.

Mambai, also called Mambae or Manbae, is a language spoken by the Mambai people, the second largest ethnic group in the island country of East Timor.
Pakpak, or Batak Dairi, is an Austronesian language of Sumatra. It is spoken in Dairi Regency, Pakpak Bharat Regency, Parlilitan district of Humbang Hasundutan Regency, Manduamas district of Central Tapanuli Regency, and Subulussalam and Aceh Singkil Regency.

The Kerinci language is an Austronesian language primarily spoken by the Kerinci people in Sungai Penuh, Kerinci Regency, and parts of Merangin and Bungo Regency in western Jambi, as well as several hamlets in Mukomuko Regency in Bengkulu. This language is also spoken by the Kerinci diaspora in other regions of Indonesia, such as West Sumatra and Java; as well as outside Indonesia, such as in Negeri Sembilan and Selangor in Malaysia. The total number of Kerinci language speakers is estimated to be around 250,000 in 2000. As an Austronesian language from the Malayo-Polynesian sub-group, the Kerinci language is also closely related to the Minangkabau and Jambi Malay languages spoken in neighboring regions.
Ot Danum is a Barito language of the central Borneo, Indonesia, spoken by the Ot Danum people. Dialects include Cihie and Dohoi.
Bunama is an Austronesian language spoken in the D'Entrecasteaux Islands of Papua New Guinea.
Perak Malay is one of the Malay dialects spoken within the state of Perak, Malaysia. Although it is neither the official language nor the standard dialect in the whole state of Perak, its existence which co-exists with other major dialects in the state of Perak still plays an important role in maintaining the identity of Perak. In spite of the fact that there are five main dialects traditionally spoken in Perak, only one of which is intended by the name "Perak Malay". There are subtle phonetic, syntactic and lexical distinctions from other major Malay dialects. Perak Malay can be divided into two sub-dialects, Kuala Kangsar and Perak Tengah, named after the daerah (districts) where they are predominantly spoken.

Pontianak Malay is a Malayic language primarily spoken by the Malay people in Pontianak and the surrounding areas in West Kalimantan, Indonesia. It is also widely spoken in neighboring regencies, including Kubu Raya and Mempawah, both of which were historically part of the now-dissolved Pontianak Regency. Pontianak Malay was also the primary language of the Pontianak Sultanate, a Malay state that once governed the area now known as Pontianak. In these regions, Pontianak Malay is not limited to being spoken exclusively by the Malay community. It functions as a lingua franca alongside standard Indonesian, enabling communication among the diverse ethnic groups in the area. However, the use of Pontianak Malay faces a slight threat as many speakers are gradually shifting to Indonesian, the national language.
References
- ↑ Waropen at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- 1 2 Held, Gerrit J. (1942). Grammatica van het Waropensch (Nederlandsch Noord Nieuw-Guinea). A.C. Nix, Bandoeng.
- ↑ Flassy, Don A.L.; Animung, Lisidus; Sawaki, Rachel (1994). Fonologi bahasa Waropen. Jakarta: Pusat Pembinaan dan Pengembangan Bahasa, Departemen Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan.
- ↑ Suryawan, I Ngurah (2018-10-27). "Kampung Papua, Antara Eksploitasi dan Konservasi (1)". tatkala.co. Retrieved 2024-06-07.