Related Research Articles

The Barat Daya Islands are a group of islands in the Maluku province of Indonesia. The Indonesian phrase barat daya means 'south-west'.
Damar may refer to:
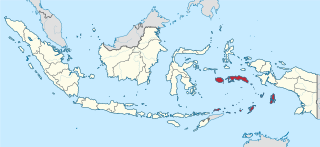
Maluku is a province of Indonesia. It comprises the central and southern regions of the Maluku Islands. The largest city and capital of Maluku province is Ambon on the small Ambon Island. It is directly adjacent to North Maluku, Southwest Papua, and West Papua in the north, Central Sulawesi, and Southeast Sulawesi in the west, Banda Sea, Australia, East Timor and East Nusa Tenggara in the south and Arafura Sea, Central Papua and South Papua in the east. The land area is 57803.81 km2, and the total population of this province at the 2010 census was 1,533,506 people, rising to 1,848,923 at the 2020 census, the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 1,908,753. Maluku is located in Eastern Indonesia.
Roma or Romang is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken by about 1,700 people in Jersusu village on Romang island in Maluku, Indonesia.

Wetar is a tropical island which belongs to the Indonesian province of Maluku and is the largest island of the Maluku Barat Daya Islands Regency of the Maluku Islands. It lies east of the Lesser Sunda Islands, which include nearby Alor and Timor, but it is politically part of the Maluku Islands. To the south, across the Wetar Strait, lies the island of Timor; at its closest it is 50 km away. To the west, across the Ombai Strait, lies the island of Alor. To the southwest is the very small island of Liran, which is also part of West Wetar District and, further southwest, the small East Timorese island of Atauro. To the north is the Banda Sea and to the east lie Romang and Damar Islands, while to the southeast lie the other principal islands of the Barat Daya Islands. Including Liran and other small offshore islands, Wetar has an area of 2,651.8 km2, and had a population of 7,916 at the 2010 Census and 8,622 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 11,109. Administratively, Wetar is divided into four of the districts (kecamatan) of the Maluku Barat Daya Regency.
The Central Malayo-Polynesian languages (CMP) are a proposed branch in the Malayo-Polynesian subgroup of the Austronesian language family. The languages are spoken in the Lesser Sunda and Maluku Islands of the Banda Sea, in an area corresponding closely to the Indonesian provinces of East Nusa Tenggara and Maluku and the nation of East Timor, but with the Bima language extending to the eastern half of Sumbawa Island in the province of West Nusa Tenggara and the Sula languages of the Sula archipelago in the southwest corner of the province of North Maluku. The principal islands in this region are Sumbawa, Sumba, Flores, Timor, Buru, and Seram. The numerically most important languages are Bima, Manggarai of western Flores, Uab Meto of West Timor, and Tetum, the national language of East Timor.

The blue-and-white kingfisher is a species of bird in the family Alcedinidae. It is endemic to North Maluku in Indonesia. It can be found on the islands of Morotai, Ngelengele, Halmahera, Damar, Ternate, Tidore, Moti, Bacan, Obi and Obilatu.

Jamides aratus is a butterfly of the lycaenids or blues family. It is found on Peninsular Malaysia, most of Indonesia and some surrounding islands.
The Central Maluku languages are a proposed subgroup of the Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian branch of the Austronesian language family which comprises around fifty languages spoken principally on the Seram, Buru, Ambon, Kei, and the Sula Islands. None of the languages have as many as fifty thousand speakers, and several are extinct.
The Babar languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian language family spoken on the Babar Islands.
The Timoric languages are a group of Austronesian languages spoken on the islands of Timor, neighboring Wetar, and Southwest Maluku to the east.
South Halmahera Regency is a regency of North Maluku Province, Indonesia. It lies partly on Halmahera Island and partly on smaller islands to the west and south of Halmahera. It covers a land area of 8,779.32 km2, and at the 2010 Census it had a population of 198,911 people, while the 2020 Census showed that this had risen to 248,395 and the official estimate in mid 2023 was 255,384 The capital lies at the town of Labuha on Bacan Island.
West Damar, or North Damar, is an Austronesian language of Damar Island, one of the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. In spite of rather low cognacy rates with its neighboring languages, it can be classified as part of the Babar languages based on qualitative evidence.
Nila is an extinct Austronesian language originally spoken on Nila Island in Maluku, Indonesia. Speakers were relocated to Seram due to volcanic activity on Nila.
Serua is an extinct Austronesian language originally spoken on Serua Island in Maluku, Indonesia. Speakers were relocated to Seram due to volcanic activity on Serua. The language continues in communities in Waipia in Seram, where the islanders were resettled, along with those also from Nila and Teun. Here, the older generation retained the island language as a strong form of identity. It was found to be extinct in 2024.
Serili is an Austronesian language spoken on Marsela Island in South Maluku, Indonesia.
Emplawas is an Austronesian language spoken in a single village on Babar Island in South Maluku, Indonesia.
Imroing is an Austronesian language spoken in a single village on Babar Island in South Maluku, Indonesia.
Telaʼa, or Tela-Masbuar (Masbuar-Tela) is an Austronesian language spoken in the two villages with those names on Babar Island in South Maluku, Indonesia.

Damer, or Damar,, also called Kenli Island, is a small volcanic island in the Barat Daya Islands group in Indonesia's Maluku province, on the southern side of the Banda Sea. It is flanked by four smaller uninhabited islands - one to the east (Layeni), one to the west and two to the south. Together they are called the Damar Islands, and constitute one administrative district within the Maluku Barat Daya Regency, lying on the undersea ridge which forms the most easterly extension of the Lesser Sunda Islands. Continuing the line of the ridge further to the northeast are several small and remote islands at increasing distances from Damer Island; these are Teon Island, Nila Island, tiny 'Nil Desperandum' islet, Serua Island and - far to the north and administered as part of Maluku Tengah Regency - Manuk Island; all of these far-flung islands are isolated stratovolcanoes and are uninhabited. The district has a combined land area of 201.80 km2 and had a population of 5,718 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 6,362, all on Damer Island itself.
References
- ↑ East Damar at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ Taber, Mark (1993). "Toward a better understanding of the Indigenous Languages of Southwestern Maluku". Oceanic Linguistics. 32 (2): 389–441. doi:10.2307/3623199. JSTOR 3623199.