Related Research Articles

Jalāl al-Dīn Muḥammad Rūmī, or simply Rumi, was a 13th-century poet, Hanafi faqih (jurist), Islamic scholar, Maturidi theologian (mutakallim), and Sufi mystic originally from Greater Khorasan in Greater Iran.

Timor is an island at the southern end of Maritime Southeast Asia, in the north of the Timor Sea. The island is divided between the sovereign states of East Timor in the eastern part and Indonesia in the western part. The Indonesian part, known as West Timor, constitutes part of the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Within West Timor lies an exclave of East Timor called Oecusse District. The island covers an area of 30,777 square kilometres. The name is a variant of timur, Malay for "east"; it is so called because it lies at the eastern end of the Lesser Sunda Islands. Mainland Australia is less than 500 km away, separated by the Timor Sea.
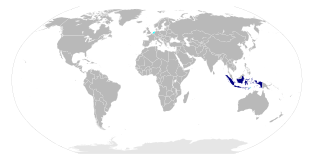
Indonesian is the official and national language of Indonesia. It is a standardized variety of Malay, an Austronesian language that has been used as a lingua franca in the multilingual Indonesian archipelago for centuries. With over 280 million inhabitants, Indonesia ranks as the fourth most populous nation globally. According to the 2020 census, over 97% of Indonesians are fluent in Indonesian, making it the largest language by number of speakers in Southeast Asia and one of the most widely spoken languages in the world. Indonesian vocabulary has been influenced by various regional languages such as Javanese, Sundanese, Minangkabau, Balinese, Banjarese, and Buginese, as well as by foreign languages such as Arabic, Dutch, Portuguese, and English. Many borrowed words have been adapted to fit the phonetic and grammatical rules of Indonesian, enriching the language and reflecting Indonesia's diverse linguistic heritage.

Malay is an Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore. It is also spoken in East Timor and southern part of Thailand. Altogether, it is spoken by 290 million people across Maritime Southeast Asia.
HI or Hi may refer to:
A caronKARR-ən. or háček, is a diacritic mark placed over certain letters in the orthography of some languages, to indicate a change of the related letter's pronunciation. Typographers tend to use the term caron, while linguists prefer the Czech word háček.

Chernivtsi Oblast, also referred to as Chernivechchyna (Чернівеччина), is an oblast (province) in western Ukraine, consisting of the northern parts of the historical regions of Bukovina and Bessarabia. It has an international border with Romania and Moldova. The region spans 8,100 square kilometres (3,100 sq mi). The oblast is the smallest in Ukraine both by area and population. It has a population of 890,457, and its administrative center is the city of Chernivtsi.

Orhei, also formerly known as Orgeev, is a city, municipality and the administrative centre of Orhei District in the Republic of Moldova, with a population of 21,065. Orhei is approximately 40 kilometres north of the capital, Chișinău.

The Naqshbandi order is a Sufi order of Sunni Islam named after Baha al-Din Naqshband. They trace their silsila to Prophet Muhammad through the first caliph Abu Bakr by the way of Ja'far al-Sadiq. The Naqshbandi Sufi order is most distinguished from other Sunni schools by the high level of importance they assign to the sharia, highlighted by major Naqshbandi scholars such as Ahmad Sirhindi and Shah Waliullah Dehlawi.

The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet.
A spelling alphabet is a set of words used to represent the letters of an alphabet in oral communication, especially over a two-way radio or telephone. The words chosen to represent the letters sound sufficiently different from each other to clearly differentiate them. This avoids any confusion that could easily otherwise result from the names of letters that sound similar, except for some small difference easily missed or easily degraded by the imperfect sound quality of the apparatus. For example, in the Latin alphabet, the letters B, P, and D sound similar and could easily be confused, but the words "bravo", "papa" and "delta" sound completely different, making confusion unlikely.

Din Tai Fung is a Taiwanese restaurant chain specializing in Chinese cuisine, particularly famous for its xiaolongbao. Based in Taipei, Taiwan, Din Tai Fung also has branches in Australia, Mainland China, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Japan, Macau, Malaysia, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and the United States.

Malay Indonesians are ethnic Malays living throughout Indonesia. They are one of the indigenous peoples of the country. Indonesian, the national language of Indonesia, is a standardized form of Riau Malay. There were numerous kingdoms associated with the Indonesian Malays along with other ethnicities in what is now Indonesia, mainly on the islands of Borneo and Sumatra. These included Srivijaya, the Melayu Kingdom, Dharmasraya, the Sultanate of Deli, the Sultanate of Siak Sri Indrapura, the Riau-Lingga Sultanate, the Sultanate of Bulungan, Pontianak Sultanate, and the Sultanate of Sambas. The 2010 census states that there are 8 million Malays in Indonesia; this number comes from the classification of Malays in East Sumatra and the coast of Kalimantan which is recognized by the Indonesian government. This classification is different from the Malaysia and Singapore census which includes all ethnic Muslims from the Indonesian archipelago as Malays.

Kutai is a historical region in what is now the Indonesian province of East Kalimantan on the island of Borneo. The region shares its name with the native ethnic group of the region, with a total population around 300,000, who have their own language known as the Kutainese language which accompanies their own rich history. Today, the name is preserved in the names of three regencies in East Kalimantan province which are the Kutai Kartanegara Regency, the West Kutai Regency and East Kutai Regency with the major river flowing in the heart of the region known as the Mahakam River. The Kutai Martadipura Kingdom (399–1635) was the earliest Hindu kingdom in the East Indies. It was later succeeded by the Muslim sultanate of Kutai Kartanegara (1300–1844).

The Yam languages, also known as the Morehead River languages, are a family of Papuan languages. They include many of the languages south and west of the Fly River in Papua New Guinea and Indonesian Western New Guinea.

Kopi Tubruk is an Indonesian-style coffee where hot water is poured over fine coffee grounds directly in the glass, without any filtration, usually with added sugar.

Pegon is a modified Arabic script used to write the Javanese, Sundanese, and Madurese languages, as an alternative to the Latin script or the Javanese script and the Old Sundanese script. It was used in a variety of applications, from religion, to diplomacy, to poetry. But today particularly, it is used for religious (Islamic) writing and poetry, particularly in writing commentaries of the Qur'an. Pegon includes letters that are not present in Modern Standard Arabic. Pegon has been studied far less than its Jawi counterpart which is used for Malay, Acehnese and Minangkabau.
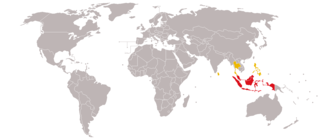
The Malay world or Malay realm is a concept or an expression that has been used by different authors and groups over time to denote several different notions, derived from varied interpretations of 'Malay' either as an ethnic group, as a racial category, as a linguistic group or as a cultural group. The use of the term Malay in much of the conceptualisation is largely based on the prevalent Malay cultural influence, manifested in particular through the spread of the Malay language in Southeast Asia as observed by different colonial powers during the Age of Discovery and spread of Islam. The term remains highly controversial in Indonesia and outside the Malay-speaking areas, because it is considered politically charged and irredentist rather than purely cultural.

Abd al-Rauf ibn Ali al-Fansuri al-Sinkili was a renowned Islamic scholar, spiritual leader of the Shattariyya tariqa and mufti of the Aceh Sultanate. He was a confidant of Sultana Safiat al-Din and first to spread the Shattari Sufi order in Indonesia and Southeast Asia. Many of his students became disseminators of Islam. He is commonly known as Sheikh Abd al-Rauf al-Sinkili and posthumously as Teungku Syiah Kuala.
Abū ‘Abd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Shihāb ad-Dīn Jalāl ad-Dīn al-Maḥallī ; aka Jalaluddin was an Egyptian renowned mufassir and a leading specialist in the principles of the law in Shafi'i jurisprudence. He authored numerous and lengthy works on various branches of Islamic Studies, among which the most important two are Tafsir al-Jalalayn and Kanz al-Raghibin, an explanation of Al-Nawawi's Minhaj al-Talibin, a classical manual on Islamic Law according to Shafi'i fiqh.
References
- ↑ Maremgi at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ↑ United States of America. Defense Mapping Agency. (1982). Gazetteer of Indonesia: Names Approved by the United States Board on Geographic Names.
- ↑ "Dineor Swadesh List".
- ↑ Voorhoeve, C.L. (1975). Languages of Irian Jaya: Checklist. Preliminary classification, language maps, wordlists. Pacific Linguistics, B(31), 108. https://doi.org/10.15144/PL-B31
- ↑ Max Planck Society, https://mpi-lingweb.shh.mpg.de/numeral/Dineor-Maremgi.htm, retrieved 28/04/2020